mirror of
https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah.git
synced 2026-02-21 00:41:56 +01:00
Merge branch 'main' into ro-fixes and resolve conflicts…
major conflicts resolved manually:
- branches for non-`light` segmentation already removed in main
- Keras/TF setup and no TF1 sessions, esp. in new ModelZoo
- changes to binarizer and its CLI (`mode`, `overwrite`, `run_single()`)
- writer: `build...` w/ kwargs instead of positional
- training for segmentation/binarization/enhancement tasks:
* drop unused `generate_data_from_folder()`
* simplify `preprocess_imgs()`: turn `preprocess_img()`, `get_patches()`
and `get_patches_num_scale_new()` into generators, only writing
result files in the caller (top-level loop) instead of passing
output directories and file counter
- training for new OCR task:
* `train`: put keys into additional `config_params` where they belong,
resp. (conditioned under existing keys), and w/ better documentation
* `train`: add new keys as kwargs to `run()` to make usable
* `utils`: instead of custom data loader `data_gen_ocr()`, re-use
existing `preprocess_imgs()` (for cfg capture and top-level loop),
but extended w/ new kwargs and calling new `preprocess_img_ocr()`;
the latter as single-image generator (also much simplified)
* `train`: use tf.data loader pipeline from that generator w/ standard
mechanisms for batching, shuffling, prefetching etc.
* `utils` and `train`: instead of `vectorize_label`, use `Dataset.padded_batch`
* add TensorBoard callback and re-use our checkpoint callback
* also use standard Keras top-level loop for training
still problematic (substantially unresolved):
- `Patches` now only w/ fixed implicit size
(ignoring training config params)
- `PatchEncoder` now only w/ fixed implicit num patches and projection dim
(ignoring training config params)
This commit is contained in:
commit
27f43c175f
77 changed files with 5597 additions and 4952 deletions
43
docs/docker.md
Normal file
43
docs/docker.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
|||
## Inference with Docker
|
||||
|
||||
docker pull ghcr.io/qurator-spk/eynollah:latest
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. ocrd resource manager
|
||||
(just once, to get the models and install them into a named volume for later re-use)
|
||||
|
||||
vol_models=ocrd-resources:/usr/local/share/ocrd-resources
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $vol_models ocrd/eynollah ocrd resmgr download ocrd-eynollah-segment default
|
||||
|
||||
Now, each time you want to use Eynollah, pass the same resources volume again.
|
||||
Also, bind-mount some data directory, e.g. current working directory $PWD (/data is default working directory in the container).
|
||||
|
||||
Either use standalone CLI (2) or OCR-D CLI (3):
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. standalone CLI
|
||||
(follow self-help, cf. readme)
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah eynollah binarization --help
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah eynollah layout --help
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah eynollah ocr --help
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. OCR-D CLI
|
||||
(follow self-help, cf. readme and https://ocr-d.de/en/spec/cli)
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah ocrd-eynollah-segment -h
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah ocrd-sbb-binarize -h
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, just "log in" to the container once and use the commands there:
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data -it ocrd/eynollah bash
|
||||
|
||||
## Training with Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Build the Docker training image
|
||||
|
||||
cd train
|
||||
docker build -t model-training .
|
||||
|
||||
Run the Docker training image
|
||||
|
||||
cd train
|
||||
docker run --gpus all -v $PWD:/entry_point_dir model-training
|
||||
18
docs/examples.md
Normal file
18
docs/examples.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
|||
# Examples
|
||||
|
||||
Example outputs of various Eynollah models
|
||||
|
||||
# Binarisation
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/952378/63592437-e433e400-c5b1-11e9-9c2d-889c6e93d748.jpg" width="45%"><img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/952378/63592435-e433e400-c5b1-11e9-88e4-3e441b61fa67.jpg" width="45%">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/952378/63592440-e4cc7a80-c5b1-11e9-8964-2cd1b22c87be.jpg" width="45%"><img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/952378/63592438-e4cc7a80-c5b1-11e9-86dc-a9e9f8555422.jpg" width="45%">
|
||||
|
||||
# Reading Order Detection
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/42df2582-4579-415e-92f1-54858a02c830" alt="Input Image" width="45%">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/77fc819e-6302-4fc9-967c-ee11d10d863e" alt="Output Image" width="45%">
|
||||
|
||||
# OCR
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/71054636-51c6-4117-b3cf-361c5cda3528" alt="Input Image" width="45%"><img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/cfb3ce38-007a-4037-b547-21324a7d56dd" alt="Output Image" width="45%">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/343b2ed8-d818-4d4a-b301-f304cbbebfcd" alt="Input Image" width="45%"><img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/accb5ba7-e37f-477e-84aa-92eafa0d136e" alt="Output Image" width="45%">
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,8 @@ Two Arabic/Persian terms form the name of the model suite: عين الله, whic
|
|||
|
||||
See the flowchart below for the different stages and how they interact:
|
||||
|
||||
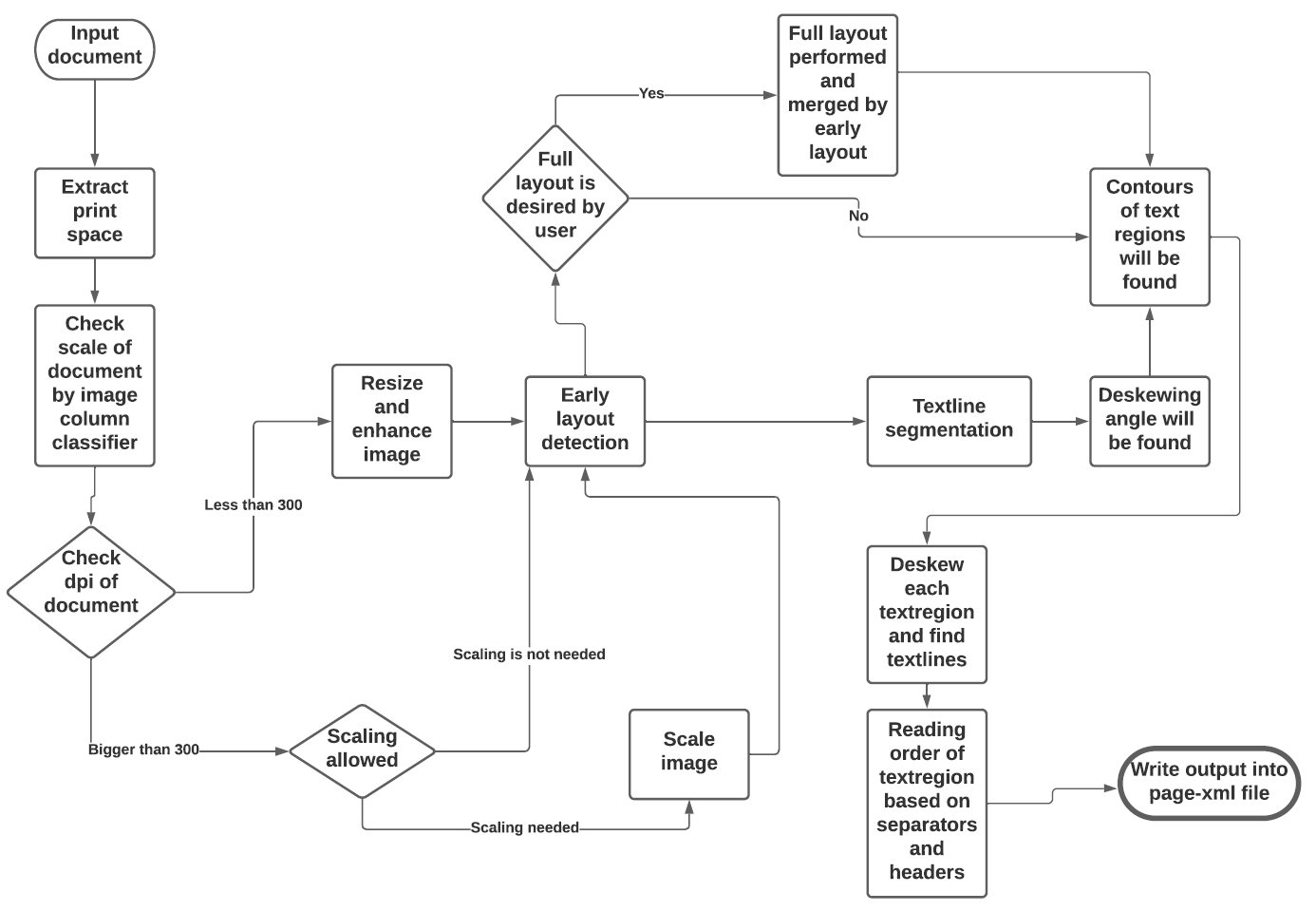
|
||||
<img width="810" height="691" alt="eynollah_flowchart" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/42dd55bc-7b85-4b46-9afe-15ff712607f0" />
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
|
|
@ -151,15 +152,75 @@ This model is used for the task of illustration detection only.
|
|||
|
||||
Model card: [Reading Order Detection]()
|
||||
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
The model extracts the reading order of text regions from the layout by classifying pairwise relationships between them. A sorting algorithm then determines the overall reading sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
### OCR
|
||||
|
||||
We have trained three OCR models: two CNN-RNN–based models and one transformer-based TrOCR model. The CNN-RNN models are generally faster and provide better results in most cases, though their performance decreases with heavily degraded images. The TrOCR model, on the other hand, is computationally expensive and slower during inference, but it can possibly produce better results on strongly degraded images.
|
||||
|
||||
#### CNN-RNN model: model_eynollah_ocr_cnnrnn_20250805
|
||||
|
||||
This model is trained on data where most of the samples are in Fraktur german script.
|
||||
|
||||
| Dataset | Input | CER | WER |
|
||||
|-----------------------|:-------|:-----------|:----------|
|
||||
| OCR-D-GT-Archiveform | BIN | 0.02147 | 0.05685 |
|
||||
| OCR-D-GT-Archiveform | RGB | 0.01636 | 0.06285 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### CNN-RNN model: model_eynollah_ocr_cnnrnn_20250904 (Default)
|
||||
|
||||
Compared to the model_eynollah_ocr_cnnrnn_20250805 model, this model is trained on a larger proportion of Antiqua data and achieves superior performance.
|
||||
|
||||
| Dataset | Input | CER | WER |
|
||||
|-----------------------|:------------|:-----------|:----------|
|
||||
| OCR-D-GT-Archiveform | BIN | 0.01635 | 0.05410 |
|
||||
| OCR-D-GT-Archiveform | RGB | 0.01471 | 0.05813 |
|
||||
| BLN600 | RGB | 0.04409 | 0.08879 |
|
||||
| BLN600 | Enhanced | 0.03599 | 0.06244 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Transformer OCR model: model_eynollah_ocr_trocr_20250919
|
||||
|
||||
This transformer OCR model is trained on the same data as model_eynollah_ocr_trocr_20250919.
|
||||
|
||||
| Dataset | Input | CER | WER |
|
||||
|-----------------------|:------------|:-----------|:----------|
|
||||
| OCR-D-GT-Archiveform | BIN | 0.01841 | 0.05589 |
|
||||
| OCR-D-GT-Archiveform | RGB | 0.01552 | 0.06177 |
|
||||
| BLN600 | RGB | 0.06347 | 0.13853 |
|
||||
|
||||
##### Qualitative evaluation of the models
|
||||
|
||||
| <img width="1600" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/120fec0c-c370-46a6-b132-b0af800607cf"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/d84e6819-0a2a-4b3a-bb7d-ceac941babc4"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/bdd27cdb-bbec-4223-9a86-de7a27c6d018"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/1a507c75-75de-4da3-9545-af3746b9a207"> |
|
||||
|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| Image | cnnrnn_20250805 | cnnrnn_20250904 | trocr_20250919 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| <img width="2000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/9bc13d48-2a92-45fc-88db-c07ffadba067"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/2b294aeb-1362-4d6e-b70f-8aeffd94c5e7"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/9911317e-632e-4e6a-8839-1fb7e783da11"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/2c5626d9-0d23-49d3-80f5-a95f629c9c76"> |
|
||||
|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| Image | cnnrnn_20250805 | cnnrnn_20250904 | trocr_20250919 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| <img width="2000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/d54d8510-5c6a-4ab0-9ba7-f6ec4ad452c6"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/a418b25b-00dc-493a-b3a3-b325b9b0cb85"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/df6e2b9e-a821-4b4c-8868-0c765700c341"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/b90277f5-40f4-4c99-80a2-da400f7d3640"> |
|
||||
|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| Image | cnnrnn_20250805 | cnnrnn_20250904 | trocr_20250919 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| <img width="2000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/7ec49211-099f-4c21-9e60-47bfdf21f1b6"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/00ef9785-8885-41b3-bf6e-21eab743df71"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/13eb9f62-4d5a-46dc-befc-b02eb4f31fc1"> | <img width="1000" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/a5c078d1-6d15-4d12-9040-526d7063d459"> |
|
||||
|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| Image | cnnrnn_20250805 | cnnrnn_20250904 | trocr_20250919 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Heuristic methods
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, some heuristic methods are employed to further improve the model predictions:
|
||||
|
||||
* After border detection, the largest contour is determined by a bounding box, and the image cropped to these coordinates.
|
||||
* For text region detection, the image is scaled up to make it easier for the model to detect background space between text regions.
|
||||
* Unlike the non-light version, where the image is scaled up to help the model better detect the background spaces between text regions, the light version uses down-scaled images. In this case, introducing an artificial class along the boundaries of text regions and text lines has helped to isolate and separate the text regions more effectively.
|
||||
* A minimum area is defined for text regions in relation to the overall image dimensions, so that very small regions that are noise can be filtered out.
|
||||
* Deskewing is applied on the text region level (due to regions having different degrees of skew) in order to improve the textline segmentation result.
|
||||
* After deskewing, a calculation of the pixel distribution on the X-axis allows the separation of textlines (foreground) and background pixels.
|
||||
* Finally, using the derived coordinates, bounding boxes are determined for each textline.
|
||||
* In the non-light version, deskewing is applied at the text-region level (since regions may have different degrees of skew) to improve text-line segmentation results. In contrast, the light version performs deskewing only at the page level to enhance margin detection and heuristic reading-order estimation.
|
||||
* After deskewing, a calculation of the pixel distribution on the X-axis allows the separation of textlines (foreground) and background pixels (only in non-light version).
|
||||
* Finally, using the derived coordinates, bounding boxes are determined for each textline (only in non-light version).
|
||||
* As mentioned above, the reading order can be determined using a model; however, this approach is computationally expensive, time-consuming, and less accurate due to the limited amount of ground-truth data available for training. Therefore, our tool uses a heuristic reading-order detection method as the default. The heuristic approach relies on headers and separators to determine the reading order of text regions.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
26
docs/ocrd.md
Normal file
26
docs/ocrd.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|||
## Use as OCR-D processor
|
||||
|
||||
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as [OCR-D](https://ocr-d.de) [processor](https://ocr-d.de/en/spec/cli),
|
||||
formally described in [`ocrd-tool.json`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/src/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json).
|
||||
|
||||
When using Eynollah in OCR-D, the source image file group with (preferably) RGB images should be used as input like this:
|
||||
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||
|
||||
If the input file group is PAGE-XML (from a previous OCR-D workflow step), Eynollah behaves as follows:
|
||||
- existing regions are kept and ignored (i.e. in effect they might overlap segments from Eynollah results)
|
||||
- existing annotation (and respective `AlternativeImage`s) are partially _ignored_:
|
||||
- previous page frame detection (`cropped` images)
|
||||
- previous derotation (`deskewed` images)
|
||||
- previous thresholding (`binarized` images)
|
||||
- if the page-level image nevertheless deviates from the original (`@imageFilename`)
|
||||
(because some other preprocessing step was in effect like `denoised`), then
|
||||
the output PAGE-XML will be based on that as new top-level (`@imageFilename`)
|
||||
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-XYZ -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||
|
||||
In general, it makes more sense to add other workflow steps **after** Eynollah.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also an OCR-D processor for binarization:
|
||||
|
||||
ocrd-sbb-binarize -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P models default-2021-03-09
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,41 @@
|
|||
# Prerequisistes
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. Install Eynollah with training dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Clone the repository and install eynollah along with the dependencies necessary for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah
|
||||
cd eynollah
|
||||
pip install '.[training]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. Pretrained encoder
|
||||
|
||||
Download our pretrained weights and add them to a `train/pretrained_model` folder:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
cd train
|
||||
wget -O pretrained_model.tar.gz https://zenodo.org/records/17243320/files/pretrained_model_v0_5_1.tar.gz?download=1
|
||||
tar xf pretrained_model.tar.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. Example data
|
||||
|
||||
### Binarization
|
||||
A small sample of training data for binarization experiment can be found on [Zenodo](https://zenodo.org/records/17243320/files/training_data_sample_binarization_v0_5_1.tar.gz?download=1),
|
||||
which contains `images` and `labels` folders.
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. Helpful tools
|
||||
|
||||
* [`pagexml2img`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/page2img)
|
||||
> Tool to extract 2-D or 3-D RGB images from PAGE-XML data. In the former case, the output will be 1 2-D image array which each class has filled with a pixel value. In the case of a 3-D RGB image,
|
||||
each class will be defined with a RGB value and beside images, a text file of classes will also be produced.
|
||||
* [`cocoSegmentationToPng`](https://github.com/nightrome/cocostuffapi/blob/17acf33aef3c6cc2d6aca46dcf084266c2778cf0/PythonAPI/pycocotools/cocostuffhelper.py#L130)
|
||||
> Convert COCO GT or results for a single image to a segmentation map and write it to disk.
|
||||
* [`ocrd-segment-extract-pages`](https://github.com/OCR-D/ocrd_segment/blob/master/ocrd_segment/extract_pages.py)
|
||||
> Extract region classes and their colours in mask (pseg) images. Allows the color map as free dict parameter, and comes with a default that mimics PageViewer's coloring for quick debugging; it also warns when regions do overlap.
|
||||
|
||||
# Training documentation
|
||||
|
||||
This document aims to assist users in preparing training datasets, training models, and
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue