mirror of
https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah.git
synced 2026-03-02 05:11:57 +01:00
readme and documentation updates
This commit is contained in:
parent
f212ffa22d
commit
496a0e2ca4
3 changed files with 80 additions and 45 deletions
78
README.md
78
README.md
|
|
@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
> Document Layout Analysis, Binarization and OCR with Deep Learning and Heuristics
|
> Document Layout Analysis, Binarization and OCR with Deep Learning and Heuristics
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/eynollah)
|
||||||
[](https://pypi.org/project/eynollah/)
|
[](https://pypi.org/project/eynollah/)
|
||||||
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/test-eynollah.yml)
|
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/test-eynollah.yml)
|
||||||
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/build-docker.yml)
|
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/build-docker.yml)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -11,24 +12,22 @@
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Features
|
## Features
|
||||||
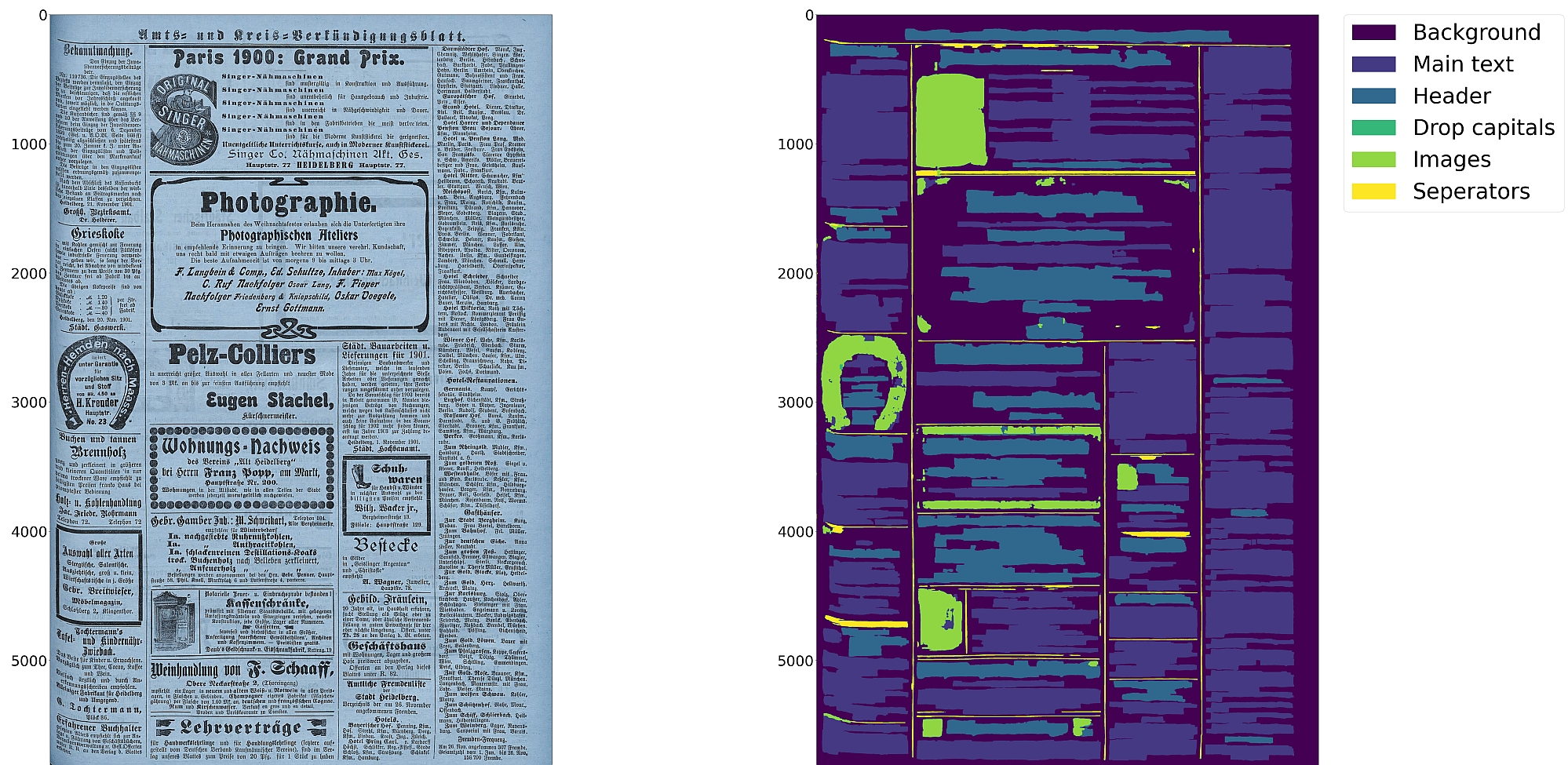
* Support for 10 distinct segmentation classes:
|
* Document layout analysis using pixelwise segmentation models with support for 10 distinct segmentation classes:
|
||||||
* background, [page border](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyRand.html), [text region](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lytextregion.html#textregionen__textregion_), [text line](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/pagexml/pagecontent_xsd_Complex_Type_pc_TextLineType.html), [header](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyUeberschrift.html), [image](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyBildbereiche.html), [separator](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lySeparatoren.html), [marginalia](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyMarginalie.html), [initial](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyInitiale.html), [table](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyTabellen.html)
|
* background, [page border](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyRand.html), [text region](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lytextregion.html#textregionen__textregion_), [text line](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/pagexml/pagecontent_xsd_Complex_Type_pc_TextLineType.html), [header](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyUeberschrift.html), [image](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyBildbereiche.html), [separator](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lySeparatoren.html), [marginalia](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyMarginalie.html), [initial](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyInitiale.html), [table](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyTabellen.html)
|
||||||
* Support for various image optimization operations:
|
|
||||||
* cropping (border detection), binarization, deskewing, dewarping, scaling, enhancing, resizing
|
|
||||||
* Textline segmentation to bounding boxes or polygons (contours) including for curved lines and vertical text
|
* Textline segmentation to bounding boxes or polygons (contours) including for curved lines and vertical text
|
||||||
* Text recognition (OCR) using either CNN-RNN or Transformer models
|
* Document image binarization with pixelwise segmentation or hybrid CNN-Transformer models
|
||||||
* Detection of reading order (left-to-right or right-to-left) using either heuristics or trainable models
|
* Text recognition (OCR) with CNN-RNN or TrOCR models
|
||||||
|
* Detection of reading order (left-to-right or right-to-left) using heuristics or trainable models
|
||||||
* Output in [PAGE-XML](https://github.com/PRImA-Research-Lab/PAGE-XML)
|
* Output in [PAGE-XML](https://github.com/PRImA-Research-Lab/PAGE-XML)
|
||||||
* [OCR-D](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah#use-as-ocr-d-processor) interface
|
* [OCR-D](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah#use-as-ocr-d-processor) interface
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
:warning: Development is focused on achieving the best quality of results for a wide variety of historical
|
:warning: Development is focused on achieving the best quality of results for a wide variety of historical
|
||||||
documents and therefore processing can be very slow. We aim to improve this, but contributions are welcome.
|
documents using a combination of multiple deep learning models and heuristics; therefore processing can be slow.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Installation
|
## Installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Python `3.8-3.11` with Tensorflow `<2.13` on Linux are currently supported.
|
Python `3.8-3.11` with Tensorflow `<2.13` on Linux are currently supported.
|
||||||
|
For (limited) GPU support the CUDA toolkit needs to be installed.
|
||||||
For (limited) GPU support the CUDA toolkit needs to be installed. A known working config is CUDA `11` with cuDNN `8.6`.
|
A working config is CUDA `11.8` with cuDNN `8.6`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can either install from PyPI
|
You can either install from PyPI
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -53,23 +52,33 @@ pip install "eynollah[OCR]"
|
||||||
make install EXTRAS=OCR
|
make install EXTRAS=OCR
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
With Docker, use
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
docker pull ghcr.io/qurator-spk/eynollah:latest
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For additional documentation on using Eynollah and Docker, see [`docker.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/docker.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Models
|
## Models
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Pretrained models can be downloaded from [zenodo](https://zenodo.org/records/17194824) or [huggingface](https://huggingface.co/SBB?search_models=eynollah).
|
Pretrained models can be downloaded from [Zenodo](https://zenodo.org/records/17194824) or [Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/SBB?search_models=eynollah).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For documentation on models, have a look at [`models.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/models.md).
|
For documentation on models, have a look at [`models.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/models.md).
|
||||||
Model cards are also provided for our trained models.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Training
|
## Training
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In case you want to train your own model with Eynollah, see the
|
To train your own model with Eynollah, see the documentation in [`train.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/train.md) and use the
|
||||||
documentation in [`train.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/train.md) and use the
|
tools in the [`train`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/train) folder.
|
||||||
tools in the [`train` folder](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/train).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Usage
|
## Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Eynollah supports five use cases: layout analysis (segmentation), binarization,
|
Eynollah supports five use cases:
|
||||||
image enhancement, text recognition (OCR), and reading order detection.
|
1. [layout analysis (segmentation)](#layout-analysis),
|
||||||
|
2. [binarization](#binarization),
|
||||||
|
3. [image enhancement](#image-enhancement),
|
||||||
|
4. [text recognition (OCR)](#ocr), and
|
||||||
|
5. [reading order detection](#reading-order-detection).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Layout Analysis
|
### Layout Analysis
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -114,6 +123,8 @@ If no further option is set, the tool performs layout detection of main regions
|
||||||
and marginals).
|
and marginals).
|
||||||
The best output quality is achieved when RGB images are used as input rather than greyscale or binarized images.
|
The best output quality is achieved when RGB images are used as input rather than greyscale or binarized images.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Additional documentation can be found in [`usage.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/models.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Binarization
|
### Binarization
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The binarization module performs document image binarization using pretrained pixelwise segmentation models.
|
The binarization module performs document image binarization using pretrained pixelwise segmentation models.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -127,9 +138,12 @@ eynollah binarization \
|
||||||
-m <directory containing model files> \
|
-m <directory containing model files> \
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Image Enhancement
|
||||||
|
TODO
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### OCR
|
### OCR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The OCR module performs text recognition using either a CNN-RNN model or a Transformer model.
|
The OCR module performs text recognition using either CNN-RNN or TrOCR models.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The command-line interface for OCR can be called like this:
|
The command-line interface for OCR can be called like this:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -141,7 +155,7 @@ eynollah ocr \
|
||||||
-m <directory containing model files> | --model_name <path to specific model> \
|
-m <directory containing model files> | --model_name <path to specific model> \
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Machine-based-reading-order
|
### Reading Order Detection
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The machine-based reading-order module employs a pretrained model to identify the reading order from layouts represented in PAGE-XML files.
|
The machine-based reading-order module employs a pretrained model to identify the reading order from layouts represented in PAGE-XML files.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -160,36 +174,12 @@ eynollah machine-based-reading-order \
|
||||||
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as [OCR-D](https://ocr-d.de) [processor](https://ocr-d.de/en/spec/cli),
|
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as [OCR-D](https://ocr-d.de) [processor](https://ocr-d.de/en/spec/cli),
|
||||||
formally described in [`ocrd-tool.json`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/src/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json).
|
formally described in [`ocrd-tool.json`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/src/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In this case, the source image file group with (preferably) RGB images should be used as input like this:
|
Further documentation on using Eynollah with OCR-D can be found in [`ocrd.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/ocrd.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If the input file group is PAGE-XML (from a previous OCR-D workflow step), Eynollah behaves as follows:
|
|
||||||
- existing regions are kept and ignored (i.e. in effect they might overlap segments from Eynollah results)
|
|
||||||
- existing annotation (and respective `AlternativeImage`s) are partially _ignored_:
|
|
||||||
- previous page frame detection (`cropped` images)
|
|
||||||
- previous derotation (`deskewed` images)
|
|
||||||
- previous thresholding (`binarized` images)
|
|
||||||
- if the page-level image nevertheless deviates from the original (`@imageFilename`)
|
|
||||||
(because some other preprocessing step was in effect like `denoised`), then
|
|
||||||
the output PAGE-XML will be based on that as new top-level (`@imageFilename`)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-XYZ -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In general, it makes more sense to add other workflow steps **after** Eynollah.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
There is also an OCR-D processor for binarization:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ocrd-sbb-binarize -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P models default-2021-03-09
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Additional documentation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Additional documentation is available in the [docs](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs) directory.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## How to cite
|
## How to cite
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bibtex
|
```bibtex
|
||||||
@inproceedings{hip23rezanezhad,
|
@inproceedings{hip23eynollah,
|
||||||
title = {Document Layout Analysis with Deep Learning and Heuristics},
|
title = {Document Layout Analysis with Deep Learning and Heuristics},
|
||||||
author = {Rezanezhad, Vahid and Baierer, Konstantin and Gerber, Mike and Labusch, Kai and Neudecker, Clemens},
|
author = {Rezanezhad, Vahid and Baierer, Konstantin and Gerber, Mike and Labusch, Kai and Neudecker, Clemens},
|
||||||
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Historical Document Imaging and Processing {HIP} 2023,
|
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Historical Document Imaging and Processing {HIP} 2023,
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
24
docs/docker.md
Normal file
24
docs/docker.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||||
|
# 1. ocrd resource manager
|
||||||
|
(just once, to get the models and install them into a named volume for later re-use)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
vol_models=ocrd-resources:/usr/local/share/ocrd-resources
|
||||||
|
docker run --rm -v $vol_models ocrd/eynollah ocrd resmgr download ocrd-eynollah-segment default
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Now, each time you want to use Eynollah, pass the same resources volume again.
|
||||||
|
Also, bind-mount some data directory, e.g. current working directory $PWD (/data is default working directory in the container).
|
||||||
|
Either use standalone CLI (2) or OCR-D CLI (3):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 2. standalone CLI (follow self-help, cf. readme)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah eynollah binarization --help
|
||||||
|
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah eynollah layout --help
|
||||||
|
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah eynollah ocr --help
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 3. OCR-D CLI (follow self-help, cf. readme and https://ocr-d.de/en/spec/cli)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah ocrd-eynollah-segment -h
|
||||||
|
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data ocrd/eynollah ocrd-sbb-binarize -h
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Alternatively, just "log in" to the container once and use the commands there:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
docker run --rm -v $vol_models -v $PWD:/data -it ocrd/eynollah bash
|
||||||
21
docs/ocrd.md
Normal file
21
docs/ocrd.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||||
|
When using Eynollah in OCR-D, the source image file group with (preferably) RGB images should be used as input like this:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If the input file group is PAGE-XML (from a previous OCR-D workflow step), Eynollah behaves as follows:
|
||||||
|
- existing regions are kept and ignored (i.e. in effect they might overlap segments from Eynollah results)
|
||||||
|
- existing annotation (and respective `AlternativeImage`s) are partially _ignored_:
|
||||||
|
- previous page frame detection (`cropped` images)
|
||||||
|
- previous derotation (`deskewed` images)
|
||||||
|
- previous thresholding (`binarized` images)
|
||||||
|
- if the page-level image nevertheless deviates from the original (`@imageFilename`)
|
||||||
|
(because some other preprocessing step was in effect like `denoised`), then
|
||||||
|
the output PAGE-XML will be based on that as new top-level (`@imageFilename`)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-XYZ -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In general, it makes more sense to add other workflow steps **after** Eynollah.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
There is also an OCR-D processor for binarization:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ocrd-sbb-binarize -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P models default-2021-03-09
|
||||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue