mirror of
https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah.git
synced 2026-01-20 09:16:58 +01:00
Compare commits
No commits in common. "main" and "v0.3.1" have entirely different histories.
79 changed files with 6167 additions and 23295 deletions
|
|
@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
|
|||
tests
|
||||
dist
|
||||
build
|
||||
env*
|
||||
*.egg-info
|
||||
models_eynollah*
|
||||
44
.github/workflows/build-docker.yml
vendored
44
.github/workflows/build-docker.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
|||
name: CD
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: [ "main" ]
|
||||
workflow_dispatch: # run manually
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
packages: write
|
||||
contents: read
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# we need tags for docker version tagging
|
||||
fetch-tags: true
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
- # Activate cache export feature to reduce build time of images
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
- name: Login to GitHub Container Registry
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
registry: ghcr.io
|
||||
username: ${{ github.actor }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Log in to Docker Hub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERIO_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERIO_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
- name: Build the Docker image
|
||||
# build both tags at the same time
|
||||
run: make docker DOCKER_TAG="docker.io/ocrd/eynollah -t ghcr.io/qurator-spk/eynollah"
|
||||
- name: Test the Docker image
|
||||
run: docker run --rm ocrd/eynollah ocrd-eynollah-segment -h
|
||||
- name: Push to Dockerhub
|
||||
run: docker push docker.io/ocrd/eynollah
|
||||
- name: Push to Github Container Registry
|
||||
run: docker push ghcr.io/qurator-spk/eynollah
|
||||
24
.github/workflows/pypi.yml
vendored
24
.github/workflows/pypi.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
|||
name: PyPI CD
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
release:
|
||||
types: [published]
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
pypi-publish:
|
||||
name: upload release to PyPI
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
# IMPORTANT: this permission is mandatory for Trusted Publishing
|
||||
id-token: write
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
- name: Build package
|
||||
run: make build
|
||||
- name: Publish package distributions to PyPI
|
||||
uses: pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish@release/v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
verbose: true
|
||||
79
.github/workflows/test-eynollah.yml
vendored
79
.github/workflows/test-eynollah.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -14,49 +14,15 @@ jobs:
|
|||
python-version: ['3.8', '3.9', '3.10', '3.11']
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: clean up
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
df -h
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /opt/ghc
|
||||
sudo rm -rf "/usr/local/share/boost"
|
||||
sudo rm -rf "$AGENT_TOOLSDIRECTORY"
|
||||
df -h
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache/restore@v4
|
||||
id: seg_model_cache
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache@v4
|
||||
id: model_cache
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: models_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||
key: seg-models
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache/restore@v4
|
||||
id: ocr_model_cache
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: models_ocr_v0_5_1
|
||||
key: ocr-models
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache/restore@v4
|
||||
id: bin_model_cache
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: default-2021-03-09
|
||||
key: bin-models
|
||||
path: models_eynollah
|
||||
key: ${{ runner.os }}-models
|
||||
- name: Download models
|
||||
if: steps.seg_model_cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' || steps.bin_model_cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' || steps.ocr_model_cache.outputs.cache-hit != true
|
||||
if: steps.model_cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
|
||||
run: make models
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache/save@v4
|
||||
if: steps.seg_model_cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: models_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||
key: seg-models
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache/save@v4
|
||||
if: steps.ocr_model_cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: models_ocr_v0_5_1
|
||||
key: ocr-models
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache/save@v4
|
||||
if: steps.bin_model_cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: default-2021-03-09
|
||||
key: bin-models
|
||||
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
|
|
@ -64,36 +30,7 @@ jobs:
|
|||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
make install-dev EXTRAS=OCR,plotting
|
||||
make deps-test EXTRAS=OCR,plotting
|
||||
ls -l models_*
|
||||
- name: Lint with ruff
|
||||
uses: astral-sh/ruff-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
src: "./src"
|
||||
pip install .
|
||||
pip install -r requirements-test.txt
|
||||
- name: Test with pytest
|
||||
run: make coverage PYTEST_ARGS="-vv --junitxml=pytest.xml"
|
||||
- name: Get coverage results
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
coverage report --format=markdown >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
coverage html
|
||||
coverage json
|
||||
coverage xml
|
||||
- name: Store coverage results
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: coverage-report_${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
path: |
|
||||
htmlcov
|
||||
pytest.xml
|
||||
coverage.xml
|
||||
coverage.json
|
||||
- name: Upload coverage results
|
||||
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
files: coverage.xml
|
||||
fail_ci_if_error: false
|
||||
- name: Test standalone CLI
|
||||
run: make smoke-test
|
||||
- name: Test OCR-D CLI
|
||||
run: make ocrd-test
|
||||
run: make test
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
6
.gitignore
vendored
6
.gitignore
vendored
|
|
@ -2,12 +2,6 @@
|
|||
__pycache__
|
||||
sbb_newspapers_org_image/pylint.log
|
||||
models_eynollah*
|
||||
models_ocr*
|
||||
models_layout*
|
||||
default-2021-03-09
|
||||
output.html
|
||||
/build
|
||||
/dist
|
||||
*.tif
|
||||
*.sw?
|
||||
TAGS
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
187
CHANGELOG.md
187
CHANGELOG.md
|
|
@ -5,188 +5,6 @@ Versioned according to [Semantic Versioning](http://semver.org/).
|
|||
|
||||
## Unreleased
|
||||
|
||||
## [0.6.0] - 2025-10-17
|
||||
|
||||
Added:
|
||||
|
||||
* `eynollah-training` CLI and docs for training the models, #187, #193, https://github.com/qurator-spk/sbb_pixelwise_segmentation/tree/unifying-training-models
|
||||
|
||||
Fixed:
|
||||
|
||||
* `join_polygons` always returning Polygon, not MultiPolygon, #203
|
||||
|
||||
## [0.6.0rc2] - 2025-10-14
|
||||
|
||||
Fixed:
|
||||
|
||||
* Prevent OOM GPU error by avoiding loading the `region_fl` model, #199
|
||||
* XML output: encoding should be `utf-8`, not `utf8`, #196, #197
|
||||
|
||||
## [0.6.0rc1] - 2025-10-10
|
||||
|
||||
Fixed:
|
||||
|
||||
* continue processing when no columns detected but text regions exist
|
||||
* convert marginalia to main text if no main text is present
|
||||
* reset deskewing angle to 0° when text covers <30% image area and detected angle >45°
|
||||
* :fire: polygons: avoid invalid paths (use `Polygon.buffer()` instead of dilation etc.)
|
||||
* `return_boxes_of_images_by_order_of_reading_new`: avoid Numpy.dtype mismatch, simplify
|
||||
* `return_boxes_of_images_by_order_of_reading_new`: log any exceptions instead of ignoring
|
||||
* `filter_contours_without_textline_inside`: avoid removing from duplicate lists twice
|
||||
* `get_marginals`: exit early if no peaks found to avoid spurious overlap mask
|
||||
* `get_smallest_skew`: after shifting search range of rotation angle, use overall best result
|
||||
* Dockerfile: fix CUDA installation (cuDNN contested between Torch and TF due to extra OCR)
|
||||
* OCR: re-instate missing methods and fix `utils_ocr` function calls
|
||||
* mbreorder/enhancement CLIs: missing imports
|
||||
* :fire: writer: `SeparatorRegion` needs `SeparatorRegionType` (not `ImageRegionType`), f458e3e
|
||||
* tests: switch from `pytest-subtests` to `parametrize` so we can use `pytest-isolate`
|
||||
(so CUDA memory gets freed between tests if running on GPU)
|
||||
|
||||
Added:
|
||||
* :fire: `layout` CLI: new option `--model_version` to override default choices
|
||||
* test coverage for OCR options in `layout`
|
||||
* test coverage for table detection in `layout`
|
||||
* CI linting with ruff
|
||||
|
||||
Changed:
|
||||
|
||||
* polygons: slightly widen for regions and lines, increase for separators
|
||||
* various refactorings, some code style and identifier improvements
|
||||
* deskewing/multiprocessing: switch back to ProcessPoolExecutor (faster),
|
||||
but use shared memory if necessary, and switch back from `loky` to stdlib,
|
||||
and shutdown in `del()` instead of `atexit`
|
||||
* :fire: OCR: switch CNN-RNN model to `20250930` version compatible with TF 2.12 on CPU, too
|
||||
* OCR: allow running `-tr` without `-fl`, too
|
||||
* :fire: writer: use `@type='heading'` instead of `'header'` for headings
|
||||
* :fire: performance gains via refactoring (simplification, less copy-code, vectorization,
|
||||
avoiding unused calculations, avoiding unnecessary 3-channel image operations)
|
||||
* :fire: heuristic reading order detection: many improvements
|
||||
- contour vs splitter box matching:
|
||||
* contour must be contained in box exactly instead of heuristics
|
||||
* make fallback center matching, center must be contained in box
|
||||
- original vs deskewed contour matching:
|
||||
* same min-area filter on both sides
|
||||
* similar area score in addition to center proximity
|
||||
* avoid duplicate and missing mappings by allowing N:M
|
||||
matches and splitting+joining where necessary
|
||||
* CI: update+improve model caching
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [0.5.0] - 2025-09-26
|
||||
|
||||
Fixed:
|
||||
|
||||
* restoring the contour in the original image caused an error due to an empty tuple, #154
|
||||
* removed NumPy warnings calculating sigma, mean, (fixed issue #158)
|
||||
* fixed bug in `separate_lines.py`, #124
|
||||
* Drop capitals are now handled separately from their corresponding textline
|
||||
* Marginals are now divided into left and right. Their reading order is written first for left marginals, then for right marginals, and within each side from top to bottom
|
||||
* Added a new page extraction model. Instead of bounding boxes, it outputs page contours in the XML file, improving results for skewed pages
|
||||
* Improved reading order for cases where a textline is segmented into multiple smaller textlines
|
||||
|
||||
Changed
|
||||
|
||||
* CLIs: read only allowed filename suffixes (image or XML) with `--dir_in`
|
||||
* CLIs: make all output option required, and `-i` / `-di` required but mutually exclusive
|
||||
* ocr CLI: drop redundant `-brb` in favour of just `-dib`
|
||||
* APIs: move all input/output path options from class (kwarg and attribute) ro `run` kwarg
|
||||
* layout textlines: polygonal also without `-cl`
|
||||
|
||||
Added:
|
||||
|
||||
* `eynollah machine-based-reading-order` CLI to run reading order detection, #175
|
||||
* `eynollah enhancement` CLI to run image enhancement, #175
|
||||
* Improved models for page extraction and reading order detection, #175
|
||||
* For the lightweight version (layout and textline detection), thresholds are now assigned to the artificial class. Users can apply these thresholds to improve detection of isolated textlines and regions. To counteract the drawback of thresholding, the skeleton of the artificial class is used to keep lines as thin as possible (resolved issues #163 and #161)
|
||||
* Added and integrated a trained CNN-RNN OCR models
|
||||
* Added and integrated a trained TrOCR model
|
||||
* Improved OCR detection to support vertical and curved textlines
|
||||
* Introduced a new machine-based reading order model with rotation augmentation
|
||||
* Optimized reading order speed by clustering text regions that belong to the same block, maintaining top-to-bottom order
|
||||
* Implemented text merging across textlines based on hyphenation when a line ends with a hyphen
|
||||
* Integrated image enhancement as a separate use case
|
||||
* Added reading order functionality on the layout level as a separate use case
|
||||
* CNN-RNN OCR models provide confidence scores for predictions
|
||||
* Added OCR visualization: predicted OCR can be overlaid on an image of the same size as the input
|
||||
* Introduced a threshold value for CNN-RNN OCR models, allowing users to filter out low-confidence textline predictions
|
||||
* For OCR, users can specify a single model by name instead of always using the default model
|
||||
* Under the OCR use case, if Ground Truth XMLs and images are available, textline image and corresponding text extraction can now be performed
|
||||
|
||||
Merged PRs:
|
||||
|
||||
* better machine based reading order + layout and textline + ocr by @vahidrezanezhad in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/175
|
||||
* CI: pypi by @kba in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/154
|
||||
* CI: Use most recent actions/setup-python@v5 by @kba in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/157
|
||||
* update docker by @bertsky in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/159
|
||||
* Ocrd fixes by @kba in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/167
|
||||
* Updating readme for eynollah use cases cli by @kba in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/166
|
||||
* OCR-D processor: expose reading_order_machine_based by @bertsky in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/171
|
||||
* prepare release v0.5.0: fix logging by @bertsky in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/180
|
||||
* mb_ro_on_layout: remove copy-pasta code not actually used by @kba in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/181
|
||||
* prepare release v0.5.0: improve CLI docstring, refactor I/O path options from class to run kwargs, increase test coverage @bertsky in #182
|
||||
* prepare release v0.5.0: fix for OCR doit subtest by @bertsky in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/183
|
||||
* Prepare release v0.5.0 by @kba in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/178
|
||||
* updating eynollah README, how to use it for use cases by @vahidrezanezhad in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/156
|
||||
* add feedback to command line interface by @michalbubula in https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/pull/170
|
||||
|
||||
## [0.4.0] - 2025-04-07
|
||||
|
||||
Fixed:
|
||||
|
||||
* allow empty imports for optional dependencies
|
||||
* avoid Numpy warnings (empty slices etc.)
|
||||
* remove deprecated Numpy types
|
||||
* binarization CLI: make `dir_in` usable again
|
||||
|
||||
Added:
|
||||
|
||||
* Continuous Deployment via Dockerhub and GHCR
|
||||
* CI: also test CLIs and OCR-D
|
||||
* CI: measure code coverage, annotate+upload reports
|
||||
* smoke-test: also check results
|
||||
* smoke-test: also test sbb-binarize
|
||||
* ocrd-test: analog for OCR-D CLI (segment and binarize)
|
||||
* pytest: add asserts, extend coverage, use subtests for various options
|
||||
* pytest: also add binarization
|
||||
* pytest: add `dir_in` mode (segment and binarize)
|
||||
* make install: control optional dependencies via `EXTRAS` variable
|
||||
* OCR-D: expose and describe recently added parameters:
|
||||
- `ignore_page_extraction`
|
||||
- `allow_enhancement`
|
||||
- `textline_light`
|
||||
- `right_to_left`
|
||||
* OCR-D: :fire: integrate ocrd-sbb-binarize
|
||||
* add detection confidence in `TextRegion/Coords/@conf`
|
||||
(but only in light version and not for marginalia)
|
||||
|
||||
Changed:
|
||||
|
||||
* Docker build: simplify, w/ `OCR`, conform to OCR-D spec
|
||||
* OCR-D: :fire: migrate to core v3
|
||||
- initialize+setup only once
|
||||
- restrict number of parallel page workers to 1
|
||||
(conflicts with existing multiprocessing; TF parts not mp-compatible)
|
||||
- do query maximally annotated page image
|
||||
(but filtering existing binarization/cropping/deskewing),
|
||||
rebase (as new `@imageFilename`) if necessary
|
||||
- add behavioural docstring
|
||||
|
||||
* :fire: refactor `Eynollah` API:
|
||||
- no more data (kw)args at init,
|
||||
but kwargs `dir_in` / `image_filename` for `run()`
|
||||
- no more data attributes, but function kwargs
|
||||
(`pcgts`, `image_filename`, `image_pil`, `dir_in`, `override_dpi`)
|
||||
- remove redundant TF session/model loaders
|
||||
(only load once during init)
|
||||
- factor `run_single()` out of `run()` (loop body),
|
||||
expose for independent calls (like OCR-D)
|
||||
- expose `cache_images()`, add `dpi` kwarg, set `self._imgs`
|
||||
- single-image mode writes PAGE file result
|
||||
(just as directory mode does)
|
||||
|
||||
* CLI: assertions (instead of print+exit) for options checks
|
||||
* light mode: fine-tune ratio to better detect a region as header
|
||||
|
||||
## [0.3.1] - 2024-08-27
|
||||
|
||||
Fixed:
|
||||
|
|
@ -307,11 +125,6 @@ Fixed:
|
|||
Initial release
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- link-labels -->
|
||||
[0.6.0]: ../../compare/v0.6.0...v0.6.0rc2
|
||||
[0.6.0rc2]: ../../compare/v0.6.0rc2...v0.6.0rc1
|
||||
[0.6.0rc1]: ../../compare/v0.6.0rc1...v0.5.0
|
||||
[0.5.0]: ../../compare/v0.5.0...v0.4.0
|
||||
[0.4.0]: ../../compare/v0.4.0...v0.3.1
|
||||
[0.3.1]: ../../compare/v0.3.1...v0.3.0
|
||||
[0.3.0]: ../../compare/v0.3.0...v0.2.0
|
||||
[0.2.0]: ../../compare/v0.2.0...v0.1.0
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
49
Dockerfile
49
Dockerfile
|
|
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
|||
ARG DOCKER_BASE_IMAGE
|
||||
FROM $DOCKER_BASE_IMAGE
|
||||
|
||||
ARG VCS_REF
|
||||
ARG BUILD_DATE
|
||||
LABEL \
|
||||
maintainer="https://ocr-d.de/en/contact" \
|
||||
org.label-schema.vcs-ref=$VCS_REF \
|
||||
org.label-schema.vcs-url="https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah" \
|
||||
org.label-schema.build-date=$BUILD_DATE \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.vendor="DFG-Funded Initiative for Optical Character Recognition Development" \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.title="Eynollah" \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.description="" \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.source="https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah" \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.documentation="https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/blob/${VCS_REF}/README.md" \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.revision=$VCS_REF \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.created=$BUILD_DATE \
|
||||
org.opencontainers.image.base.name=ocrd/core-cuda-tf2
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
# set proper locales
|
||||
ENV PYTHONIOENCODING=utf8
|
||||
ENV LANG=C.UTF-8
|
||||
ENV LC_ALL=C.UTF-8
|
||||
|
||||
# avoid HOME/.local/share (hard to predict USER here)
|
||||
# so let XDG_DATA_HOME coincide with fixed system location
|
||||
# (can still be overridden by derived stages)
|
||||
ENV XDG_DATA_HOME /usr/local/share
|
||||
# avoid the need for an extra volume for persistent resource user db
|
||||
# (i.e. XDG_CONFIG_HOME/ocrd/resources.yml)
|
||||
ENV XDG_CONFIG_HOME /usr/local/share/ocrd-resources
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /build/eynollah
|
||||
COPY . .
|
||||
COPY ocrd-tool.json .
|
||||
# prepackage ocrd-tool.json as ocrd-all-tool.json
|
||||
RUN ocrd ocrd-tool ocrd-tool.json dump-tools > $(dirname $(ocrd bashlib filename))/ocrd-all-tool.json
|
||||
# prepackage ocrd-all-module-dir.json
|
||||
RUN ocrd ocrd-tool ocrd-tool.json dump-module-dirs > $(dirname $(ocrd bashlib filename))/ocrd-all-module-dir.json
|
||||
# install everything and reduce image size
|
||||
RUN make install EXTRAS=OCR && rm -rf /build/eynollah
|
||||
# fixup for broken cuDNN installation (Torch pulls in 8.5.0, which is incompatible with Tensorflow)
|
||||
RUN pip install nvidia-cudnn-cu11==8.6.0.163
|
||||
# smoke test
|
||||
RUN eynollah --help
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /data
|
||||
VOLUME /data
|
||||
151
Makefile
151
Makefile
|
|
@ -1,30 +1,5 @@
|
|||
PYTHON ?= python3
|
||||
PIP ?= pip3
|
||||
EXTRAS ?=
|
||||
|
||||
# DOCKER_BASE_IMAGE = artefakt.dev.sbb.berlin:5000/sbb/ocrd_core:v2.68.0
|
||||
DOCKER_BASE_IMAGE ?= docker.io/ocrd/core-cuda-tf2:latest
|
||||
DOCKER_TAG ?= ocrd/eynollah
|
||||
DOCKER ?= docker
|
||||
|
||||
#SEG_MODEL := https://qurator-data.de/eynollah/2021-04-25/models_eynollah.tar.gz
|
||||
#SEG_MODEL := https://qurator-data.de/eynollah/2022-04-05/models_eynollah_renamed.tar.gz
|
||||
# SEG_MODEL := https://qurator-data.de/eynollah/2022-04-05/models_eynollah.tar.gz
|
||||
#SEG_MODEL := https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/releases/download/v0.3.0/models_eynollah.tar.gz
|
||||
#SEG_MODEL := https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/releases/download/v0.3.1/models_eynollah.tar.gz
|
||||
SEG_MODEL := https://zenodo.org/records/17194824/files/models_layout_v0_5_0.tar.gz?download=1
|
||||
SEG_MODELFILE = $(notdir $(patsubst %?download=1,%,$(SEG_MODEL)))
|
||||
SEG_MODELNAME = $(SEG_MODELFILE:%.tar.gz=%)
|
||||
|
||||
BIN_MODEL := https://github.com/qurator-spk/sbb_binarization/releases/download/v0.0.11/saved_model_2021_03_09.zip
|
||||
BIN_MODELFILE = $(notdir $(BIN_MODEL))
|
||||
BIN_MODELNAME := default-2021-03-09
|
||||
|
||||
OCR_MODEL := https://zenodo.org/records/17236998/files/models_ocr_v0_5_1.tar.gz?download=1
|
||||
OCR_MODELFILE = $(notdir $(patsubst %?download=1,%,$(OCR_MODEL)))
|
||||
OCR_MODELNAME = $(OCR_MODELFILE:%.tar.gz=%)
|
||||
|
||||
PYTEST_ARGS ?= -vv --isolate
|
||||
EYNOLLAH_MODELS ?= $(PWD)/models_eynollah
|
||||
export EYNOLLAH_MODELS
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN-EVAL makefile-parser --make-help Makefile
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,126 +7,44 @@ help:
|
|||
@echo ""
|
||||
@echo " Targets"
|
||||
@echo ""
|
||||
@echo " docker Build Docker image"
|
||||
@echo " build Build Python source and binary distribution"
|
||||
@echo " install Install package with pip"
|
||||
@echo " models Download and extract models to $(PWD)/models_eynollah"
|
||||
@echo " install Install with pip"
|
||||
@echo " install-dev Install editable with pip"
|
||||
@echo " deps-test Install test dependencies with pip"
|
||||
@echo " models Download and extract models to $(CURDIR):"
|
||||
@echo " $(BIN_MODELNAME) $(SEG_MODELNAME) $(OCR_MODELNAME)"
|
||||
@echo " smoke-test Run simple CLI check"
|
||||
@echo " ocrd-test Run OCR-D CLI check"
|
||||
@echo " test Run unit tests"
|
||||
@echo ""
|
||||
@echo " Variables"
|
||||
@echo " EXTRAS comma-separated list of features (like 'OCR,plotting') for 'install' [$(EXTRAS)]"
|
||||
@echo " DOCKER_TAG Docker image tag for 'docker' [$(DOCKER_TAG)]"
|
||||
@echo " PYTEST_ARGS pytest args for 'test' (Set to '-s' to see log output during test execution, '-vv' to see individual tests. [$(PYTEST_ARGS)]"
|
||||
@echo " SEG_MODEL URL of 'models' archive to download for segmentation 'test' [$(SEG_MODEL)]"
|
||||
@echo " BIN_MODEL URL of 'models' archive to download for binarization 'test' [$(BIN_MODEL)]"
|
||||
@echo " OCR_MODEL URL of 'models' archive to download for binarization 'test' [$(OCR_MODEL)]"
|
||||
@echo ""
|
||||
|
||||
# END-EVAL
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Download and extract models to $(PWD)/models_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||
models: $(BIN_MODELNAME) $(SEG_MODELNAME) $(OCR_MODELNAME)
|
||||
# Download and extract models to $(PWD)/models_eynollah
|
||||
models: models_eynollah
|
||||
|
||||
# do not download these files if we already have the directories
|
||||
.INTERMEDIATE: $(BIN_MODELFILE) $(SEG_MODELFILE) $(OCR_MODELFILE)
|
||||
models_eynollah: models_eynollah.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar xf models_eynollah_renamed.tar.gz --transform 's/models_eynollah_renamed/models_eynollah/'
|
||||
# tar xf models_eynollah_renamed.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar xf models_eynollah_renamed_savedmodel.tar.gz --transform 's/models_eynollah_renamed_savedmodel/models_eynollah/'
|
||||
tar xf models_eynollah.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
$(BIN_MODELFILE):
|
||||
wget -O $@ $(BIN_MODEL)
|
||||
$(SEG_MODELFILE):
|
||||
wget -O $@ $(SEG_MODEL)
|
||||
$(OCR_MODELFILE):
|
||||
wget -O $@ $(OCR_MODEL)
|
||||
|
||||
$(BIN_MODELNAME): $(BIN_MODELFILE)
|
||||
mkdir $@
|
||||
unzip -d $@ $<
|
||||
$(SEG_MODELNAME): $(SEG_MODELFILE)
|
||||
tar zxf $<
|
||||
$(OCR_MODELNAME): $(OCR_MODELFILE)
|
||||
tar zxf $<
|
||||
|
||||
build:
|
||||
$(PIP) install build
|
||||
$(PYTHON) -m build .
|
||||
models_eynollah.tar.gz:
|
||||
# wget 'https://qurator-data.de/eynollah/2021-04-25/models_eynollah.tar.gz'
|
||||
# wget 'https://qurator-data.de/eynollah/2022-04-05/models_eynollah_renamed.tar.gz'
|
||||
# wget 'https://ocr-d.kba.cloud/2022-04-05.SavedModel.tar.gz'
|
||||
# wget 'https://qurator-data.de/eynollah/2022-04-05/models_eynollah_renamed_savedmodel.tar.gz'
|
||||
wget https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/releases/download/v0.3.0/models_eynollah.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
# Install with pip
|
||||
install:
|
||||
$(PIP) install .$(and $(EXTRAS),[$(EXTRAS)])
|
||||
pip install .
|
||||
|
||||
# Install editable with pip
|
||||
install-dev:
|
||||
$(PIP) install -e .$(and $(EXTRAS),[$(EXTRAS)])
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq (OCR,$(findstring OCR, $(EXTRAS)))
|
||||
deps-test: $(OCR_MODELNAME)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
deps-test: $(BIN_MODELNAME) $(SEG_MODELNAME)
|
||||
$(PIP) install -r requirements-test.txt
|
||||
ifeq (OCR,$(findstring OCR, $(EXTRAS)))
|
||||
ln -rs $(OCR_MODELNAME)/* $(SEG_MODELNAME)/
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
smoke-test: TMPDIR != mktemp -d
|
||||
smoke-test: tests/resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif
|
||||
# layout analysis:
|
||||
eynollah layout -i $< -o $(TMPDIR) -m $(CURDIR)/$(SEG_MODELNAME)
|
||||
fgrep -q http://schema.primaresearch.org/PAGE/gts/pagecontent/2019-07-15 $(TMPDIR)/$(basename $(<F)).xml
|
||||
fgrep -c -e TextRegion -e ImageRegion -e SeparatorRegion $(TMPDIR)/$(basename $(<F)).xml
|
||||
# layout, directory mode (skip one, add one):
|
||||
eynollah layout -di $(<D) -o $(TMPDIR) -m $(CURDIR)/$(SEG_MODELNAME)
|
||||
test -s $(TMPDIR)/euler_rechenkunst01_1738_0025.xml
|
||||
# mbreorder, directory mode (overwrite):
|
||||
eynollah machine-based-reading-order -di $(<D) -o $(TMPDIR) -m $(CURDIR)/$(SEG_MODELNAME)
|
||||
fgrep -q http://schema.primaresearch.org/PAGE/gts/pagecontent/2019-07-15 $(TMPDIR)/$(basename $(<F)).xml
|
||||
fgrep -c -e RegionRefIndexed $(TMPDIR)/$(basename $(<F)).xml
|
||||
# binarize:
|
||||
eynollah binarization -m $(CURDIR)/$(BIN_MODELNAME) -i $< -o $(TMPDIR)/$(<F)
|
||||
test -s $(TMPDIR)/$(<F)
|
||||
@set -x; test "$$(identify -format '%w %h' $<)" = "$$(identify -format '%w %h' $(TMPDIR)/$(<F))"
|
||||
# enhance:
|
||||
eynollah enhancement -m $(CURDIR)/$(SEG_MODELNAME) -sos -i $< -o $(TMPDIR) -O
|
||||
test -s $(TMPDIR)/$(<F)
|
||||
@set -x; test "$$(identify -format '%w %h' $<)" = "$$(identify -format '%w %h' $(TMPDIR)/$(<F))"
|
||||
$(RM) -r $(TMPDIR)
|
||||
|
||||
ocrd-test: export OCRD_MISSING_OUTPUT := ABORT
|
||||
ocrd-test: TMPDIR != mktemp -d
|
||||
ocrd-test: tests/resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif
|
||||
cp $< $(TMPDIR)
|
||||
ocrd workspace -d $(TMPDIR) init
|
||||
ocrd workspace -d $(TMPDIR) add -G OCR-D-IMG -g PHYS_0020 -i OCR-D-IMG_0020 $(<F)
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -w $(TMPDIR) -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-SEG -P models $(CURDIR)/$(SEG_MODELNAME)
|
||||
result=$$(ocrd workspace -d $(TMPDIR) find -G OCR-D-SEG); \
|
||||
fgrep -q http://schema.primaresearch.org/PAGE/gts/pagecontent/2019-07-15 $(TMPDIR)/$$result && \
|
||||
fgrep -c -e TextRegion -e ImageRegion -e SeparatorRegion $(TMPDIR)/$$result
|
||||
ocrd-sbb-binarize -w $(TMPDIR) -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P model $(CURDIR)/$(BIN_MODELNAME)
|
||||
ocrd-sbb-binarize -w $(TMPDIR) -I OCR-D-SEG -O OCR-D-SEG-BIN -P model $(CURDIR)/$(BIN_MODELNAME) -P operation_level region
|
||||
$(RM) -r $(TMPDIR)
|
||||
smoke-test:
|
||||
eynollah -i tests/resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif -o . -m $(PWD)/models_eynollah
|
||||
|
||||
# Run unit tests
|
||||
test: export MODELS_LAYOUT=$(CURDIR)/$(SEG_MODELNAME)
|
||||
test: export MODELS_OCR=$(CURDIR)/$(OCR_MODELNAME)
|
||||
test: export MODELS_BIN=$(CURDIR)/$(BIN_MODELNAME)
|
||||
test:
|
||||
$(PYTHON) -m pytest tests --durations=0 --continue-on-collection-errors $(PYTEST_ARGS)
|
||||
|
||||
coverage:
|
||||
coverage erase
|
||||
$(MAKE) test PYTHON="coverage run"
|
||||
coverage report -m
|
||||
|
||||
# Build docker image
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
$(DOCKER) build \
|
||||
--build-arg DOCKER_BASE_IMAGE=$(DOCKER_BASE_IMAGE) \
|
||||
--build-arg VCS_REF=$$(git rev-parse --short HEAD) \
|
||||
--build-arg BUILD_DATE=$$(date -u +"%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ") \
|
||||
-t $(DOCKER_TAG) .
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: models build install install-dev test smoke-test ocrd-test coverage docker help
|
||||
pytest tests
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
142
README.md
142
README.md
|
|
@ -1,34 +1,29 @@
|
|||
# Eynollah
|
||||
|
||||
> Document Layout Analysis, Binarization and OCR with Deep Learning and Heuristics
|
||||
> Document Layout Analysis with Deep Learning and Heuristics
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://pypi.org/project/eynollah/)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/test-eynollah.yml)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/build-docker.yml)
|
||||
[](https://opensource.org/license/apache-2-0/)
|
||||
[](https://doi.org/10.1145/3604951.3605513)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
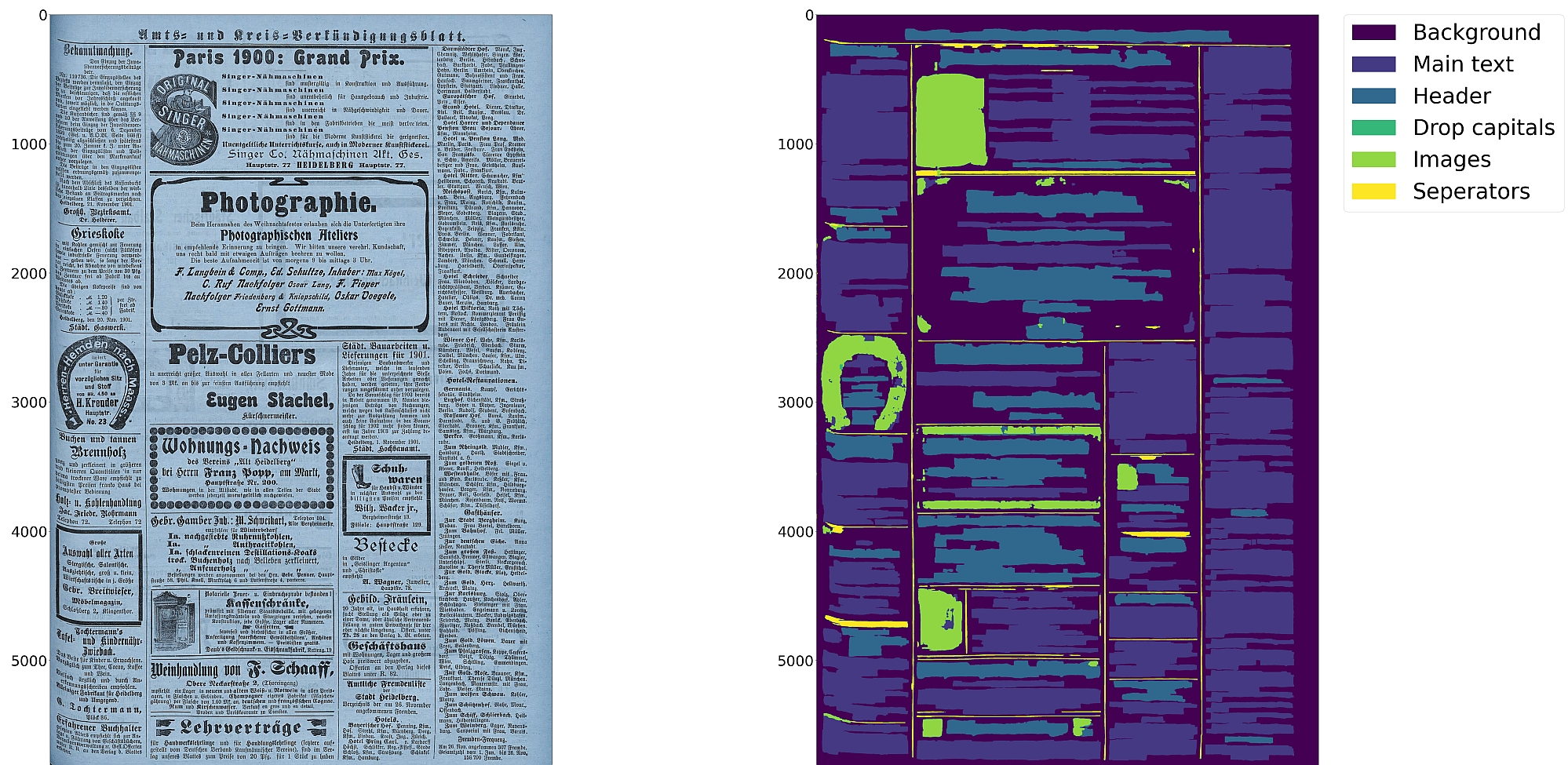
* Support for 10 distinct segmentation classes:
|
||||
* Support for up to 10 segmentation classes:
|
||||
* background, [page border](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyRand.html), [text region](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lytextregion.html#textregionen__textregion_), [text line](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/pagexml/pagecontent_xsd_Complex_Type_pc_TextLineType.html), [header](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyUeberschrift.html), [image](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyBildbereiche.html), [separator](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lySeparatoren.html), [marginalia](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyMarginalie.html), [initial](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyInitiale.html), [table](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyTabellen.html)
|
||||
* Support for various image optimization operations:
|
||||
* cropping (border detection), binarization, deskewing, dewarping, scaling, enhancing, resizing
|
||||
* Textline segmentation to bounding boxes or polygons (contours) including for curved lines and vertical text
|
||||
* Text recognition (OCR) using either CNN-RNN or Transformer models
|
||||
* Detection of reading order (left-to-right or right-to-left) using either heuristics or trainable models
|
||||
* Text line segmentation to bounding boxes or polygons (contours) including for curved lines and vertical text
|
||||
* Detection of reading order (left-to-right or right-to-left)
|
||||
* Output in [PAGE-XML](https://github.com/PRImA-Research-Lab/PAGE-XML)
|
||||
* [OCR-D](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah#use-as-ocr-d-processor) interface
|
||||
|
||||
:warning: Development is focused on achieving the best quality of results for a wide variety of historical
|
||||
documents and therefore processing can be very slow. We aim to improve this, but contributions are welcome.
|
||||
:warning: Development is currently focused on achieving the best possible quality of results for a wide variety of historical documents and therefore processing can be very slow. We aim to improve this, but contributions are welcome.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
Python `3.8-3.11` with Tensorflow `2.12-2.15` on Linux are currently supported.
|
||||
|
||||
Python `3.8-3.11` with Tensorflow `<2.13` on Linux are currently supported.
|
||||
|
||||
For (limited) GPU support the CUDA toolkit needs to be installed. A known working config is CUDA `11` with cuDNN `8.6`.
|
||||
For (limited) GPU support the CUDA toolkit needs to be installed.
|
||||
|
||||
You can either install from PyPI
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,44 +40,19 @@ cd eynollah; pip install -e .
|
|||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can run `make install` or `make install-dev` for editable installation.
|
||||
|
||||
To also install the dependencies for the OCR engines:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install "eynollah[OCR]"
|
||||
# or
|
||||
make install EXTRAS=OCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
Pre-trained models can be downloaded from [qurator-data.de](https://qurator-data.de/eynollah/) or [huggingface](https://huggingface.co/SBB?search_models=eynollah).
|
||||
|
||||
Pretrained models can be downloaded from [zenodo](https://zenodo.org/records/17194824) or [huggingface](https://huggingface.co/SBB?search_models=eynollah).
|
||||
|
||||
For documentation on models, have a look at [`models.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/models.md).
|
||||
Model cards are also provided for our trained models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Training
|
||||
|
||||
In case you want to train your own model with Eynollah, see the
|
||||
documentation in [`train.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/train.md) and use the
|
||||
tools in the [`train` folder](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/train).
|
||||
## Train
|
||||
🚧 **Work in progress**
|
||||
|
||||
In case you want to train your own model, have a look at [`sbb_pixelwise_segmentation`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/sbb_pixelwise_segmentation).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Eynollah supports five use cases: layout analysis (segmentation), binarization,
|
||||
image enhancement, text recognition (OCR), and reading order detection.
|
||||
|
||||
### Layout Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
The layout analysis module is responsible for detecting layout elements, identifying text lines, and determining reading
|
||||
order using either heuristic methods or a [pretrained reading order detection model](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah#machine-based-reading-order).
|
||||
|
||||
Reading order detection can be performed either as part of layout analysis based on image input, or, currently under
|
||||
development, based on pre-existing layout analysis results in PAGE-XML format as input.
|
||||
|
||||
The command-line interface for layout analysis can be called like this:
|
||||
The command-line interface can be called like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah layout \
|
||||
eynollah \
|
||||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||||
-o <output directory> \
|
||||
-m <directory containing model files> \
|
||||
|
|
@ -95,14 +65,12 @@ The following options can be used to further configure the processing:
|
|||
|-------------------|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `-fl` | full layout analysis including all steps and segmentation classes |
|
||||
| `-light` | lighter and faster but simpler method for main region detection and deskewing |
|
||||
| `-tll` | this indicates the light textline and should be passed with light version |
|
||||
| `-tab` | apply table detection |
|
||||
| `-ae` | apply enhancement (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
|
||||
| `-as` | apply scaling |
|
||||
| `-cl` | apply contour detection for curved text lines instead of bounding boxes |
|
||||
| `-ib` | apply binarization (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
|
||||
| `-ep` | enable plotting (MUST always be used with `-sl`, `-sd`, `-sa`, `-si` or `-ae`) |
|
||||
| `-eoi` | extract only images to output directory (other processing will not be done) |
|
||||
| `-ho` | ignore headers for reading order dectection |
|
||||
| `-si <directory>` | save image regions detected to this directory |
|
||||
| `-sd <directory>` | save deskewed image to this directory |
|
||||
|
|
@ -110,83 +78,33 @@ The following options can be used to further configure the processing:
|
|||
| `-sp <directory>` | save cropped page image to this directory |
|
||||
| `-sa <directory>` | save all (plot, enhanced/binary image, layout) to this directory |
|
||||
|
||||
If no further option is set, the tool performs layout detection of main regions (background, text, images, separators
|
||||
and marginals).
|
||||
The best output quality is achieved when RGB images are used as input rather than greyscale or binarized images.
|
||||
|
||||
### Binarization
|
||||
|
||||
The binarization module performs document image binarization using pretrained pixelwise segmentation models.
|
||||
|
||||
The command-line interface for binarization can be called like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah binarization \
|
||||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||||
-o <output directory> \
|
||||
-m <directory containing model files> \
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### OCR
|
||||
|
||||
The OCR module performs text recognition using either a CNN-RNN model or a Transformer model.
|
||||
|
||||
The command-line interface for OCR can be called like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah ocr \
|
||||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||||
-dx <directory of xmls> \
|
||||
-o <output directory> \
|
||||
-m <directory containing model files> | --model_name <path to specific model> \
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Machine-based-reading-order
|
||||
|
||||
The machine-based reading-order module employs a pretrained model to identify the reading order from layouts represented in PAGE-XML files.
|
||||
|
||||
The command-line interface for machine based reading order can be called like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah machine-based-reading-order \
|
||||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||||
-xml <xml file name> | -dx <directory containing xml files> \
|
||||
-m <path to directory containing model files> \
|
||||
-o <output directory>
|
||||
```
|
||||
If no option is set, the tool performs layout detection of main regions (background, text, images, separators and marginals).
|
||||
The best output quality is produced when RGB images are used as input rather than greyscale or binarized images.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Use as OCR-D processor
|
||||
🚧 **Work in progress**
|
||||
|
||||
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as [OCR-D](https://ocr-d.de) [processor](https://ocr-d.de/en/spec/cli),
|
||||
formally described in [`ocrd-tool.json`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/src/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json).
|
||||
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as [OCR-D](https://ocr-d.de) processor.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the source image file group with (preferably) RGB images should be used as input like this:
|
||||
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||
```
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O SEG-LINE -P models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Any image referenced by `@imageFilename` in PAGE-XML is passed on directly to Eynollah as a processor, so that e.g.
|
||||
|
||||
If the input file group is PAGE-XML (from a previous OCR-D workflow step), Eynollah behaves as follows:
|
||||
- existing regions are kept and ignored (i.e. in effect they might overlap segments from Eynollah results)
|
||||
- existing annotation (and respective `AlternativeImage`s) are partially _ignored_:
|
||||
- previous page frame detection (`cropped` images)
|
||||
- previous derotation (`deskewed` images)
|
||||
- previous thresholding (`binarized` images)
|
||||
- if the page-level image nevertheless deviates from the original (`@imageFilename`)
|
||||
(because some other preprocessing step was in effect like `denoised`), then
|
||||
the output PAGE-XML will be based on that as new top-level (`@imageFilename`)
|
||||
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-XYZ -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||||
|
||||
In general, it makes more sense to add other workflow steps **after** Eynollah.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also an OCR-D processor for binarization:
|
||||
|
||||
ocrd-sbb-binarize -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P models default-2021-03-09
|
||||
```
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG-BIN -O SEG-LINE -P models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
uses the original (RGB) image despite any binarization that may have occured in previous OCR-D processing steps
|
||||
|
||||
#### Additional documentation
|
||||
|
||||
Additional documentation is available in the [docs](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs) directory.
|
||||
Please check the [wiki](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/wiki).
|
||||
|
||||
## How to cite
|
||||
If you find this tool useful in your work, please consider citing our paper:
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@inproceedings{hip23rezanezhad,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
165
docs/models.md
165
docs/models.md
|
|
@ -1,165 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# Models documentation
|
||||
|
||||
This suite of 15 models presents a document layout analysis (DLA) system for historical documents implemented by
|
||||
pixel-wise segmentation using a combination of a ResNet50 encoder with various U-Net decoders. In addition, heuristic
|
||||
methods are applied to detect marginals and to determine the reading order of text regions.
|
||||
|
||||
The detection and classification of multiple classes of layout elements such as headings, images, tables etc. as part of
|
||||
DLA is required in order to extract and process them in subsequent steps. Altogether, the combination of image
|
||||
detection, classification and segmentation on the wide variety that can be found in over 400 years of printed cultural
|
||||
heritage makes this a very challenging task. Deep learning models are complemented with heuristics for the detection of
|
||||
text lines, marginals, and reading order. Furthermore, an optional image enhancement step was added in case of documents
|
||||
that either have insufficient pixel density and/or require scaling. Also, a column classifier for the analysis of
|
||||
multi-column documents was added. With these additions, DLA performance was improved, and a high accuracy in the
|
||||
prediction of the reading order is accomplished.
|
||||
|
||||
Two Arabic/Persian terms form the name of the model suite: عين الله, which can be transcribed as "ain'allah" or
|
||||
"eynollah"; it translates into English as "God's Eye" -- it sees (nearly) everything on the document image.
|
||||
|
||||
See the flowchart below for the different stages and how they interact:
|
||||
|
||||
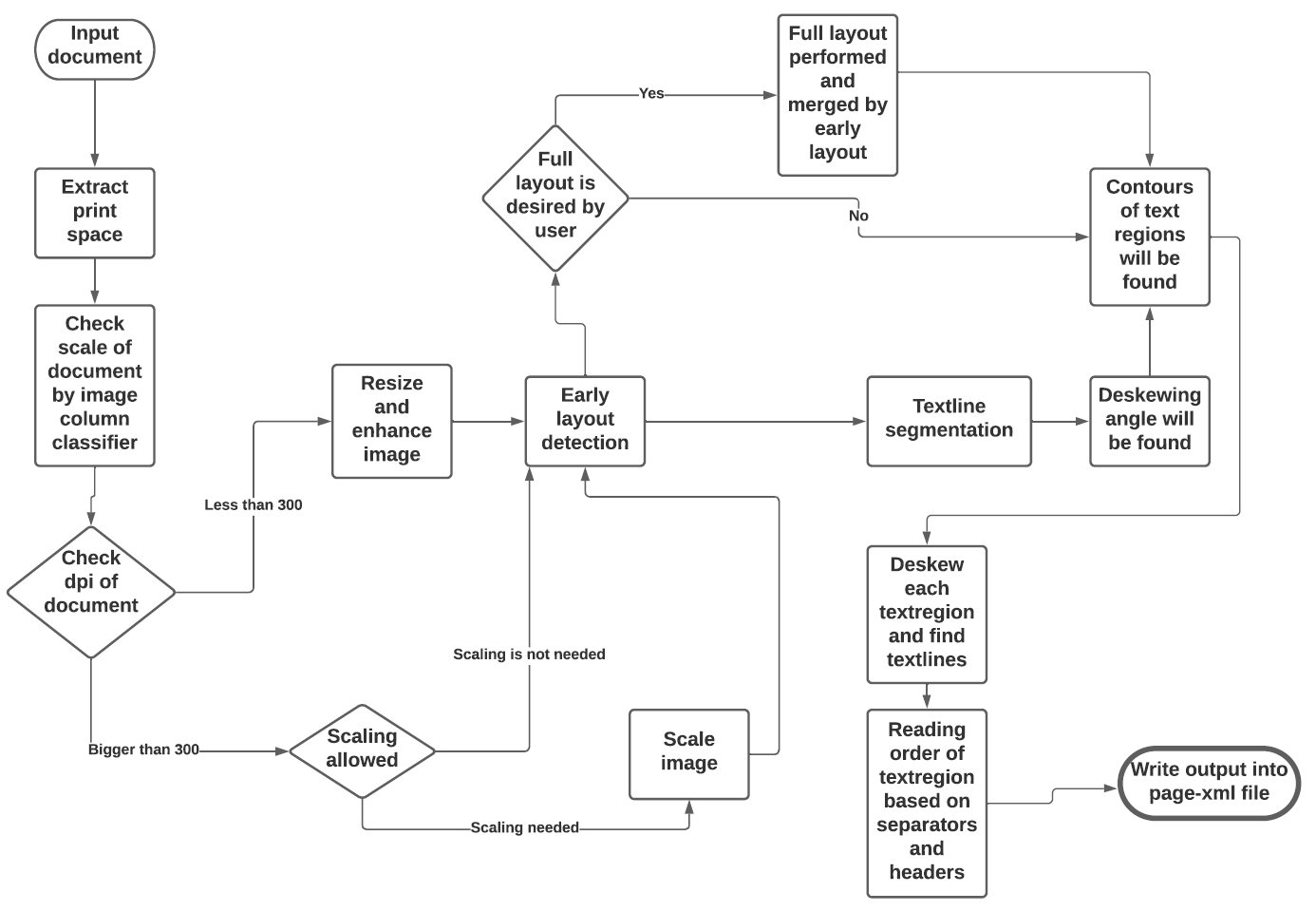
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
|
||||
### Image enhancement
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Image Enhancement](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-enhancement)
|
||||
|
||||
This model addresses image resolution, specifically targeting documents with suboptimal resolution. In instances where
|
||||
the detection of document layout exhibits inadequate performance, the proposed enhancement aims to significantly improve
|
||||
the quality and clarity of the images, thus facilitating enhanced visual interpretation and analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
### Page extraction / border detection
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Page Extraction/Border Detection](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-page-extraction)
|
||||
|
||||
A problem that can negatively affect OCR are black margins around a page caused by document scanning. A deep learning
|
||||
model helps to crop to the page borders by using a pixel-wise segmentation method.
|
||||
|
||||
### Column classification
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Column Classification](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-column-classifier)
|
||||
|
||||
This model is a trained classifier that recognizes the number of columns in a document by use of a training set with
|
||||
manual classification of all documents into six classes with either one, two, three, four, five, or six and more columns
|
||||
respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
### Binarization
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Binarization](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-binarization)
|
||||
|
||||
This model is designed to tackle the intricate task of document image binarization, which involves segmentation of the
|
||||
image into white and black pixels. This process significantly contributes to the overall performance of the layout
|
||||
models, particularly in scenarios where the documents are degraded or exhibit subpar quality. The robust binarization
|
||||
capability of the model enables improved accuracy and reliability in subsequent layout analysis, thereby facilitating
|
||||
enhanced document understanding and interpretation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Main region detection
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Main Region Detection](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-main-regions)
|
||||
|
||||
This model has employed a different set of labels, including an artificial class specifically designed to encompass the
|
||||
text regions. The inclusion of this artificial class facilitates easier isolation of text regions by the model. This
|
||||
approach grants the advantage of training the model using downscaled images, which in turn leads to faster predictions
|
||||
during the inference phase. By incorporating this methodology, improved efficiency is achieved without compromising the
|
||||
model's ability to accurately identify and classify text regions within documents.
|
||||
|
||||
### Main region detection (with scaling augmentation)
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Main Region Detection (with scaling augmentation)](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-main-regions-aug-scaling)
|
||||
|
||||
Utilizing scaling augmentation, this model leverages the capability to effectively segment elements of extremely high or
|
||||
low scales within documents. By harnessing this technique, the tool gains a significant advantage in accurately
|
||||
categorizing and isolating such elements, thereby enhancing its overall performance and enabling precise analysis of
|
||||
documents with varying scale characteristics.
|
||||
|
||||
### Main region detection (with rotation augmentation)
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Main Region Detection (with rotation augmentation)](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-main-regions-aug-rotation)
|
||||
|
||||
This model takes advantage of rotation augmentation. This helps the tool to segment the vertical text regions in a
|
||||
robust way.
|
||||
|
||||
### Main region detection (ensembled)
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Main Region Detection (ensembled)](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-main-regions-ensembled)
|
||||
|
||||
The robustness of this model is attained through an ensembling technique that combines the weights from various epochs.
|
||||
By employing this approach, the model achieves a high level of resilience and stability, effectively leveraging the
|
||||
strengths of multiple epochs to enhance its overall performance and deliver consistent and reliable results.
|
||||
|
||||
### Full region detection (1,2-column documents)
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Full Region Detection (1,2-column documents)](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-full-regions-1column)
|
||||
|
||||
This model deals with documents comprising of one and two columns.
|
||||
|
||||
### Full region detection (3,n-column documents)
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Full Region Detection (3,n-column documents)](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-full-regions-3pluscolumn)
|
||||
|
||||
This model is responsible for detecting headers and drop capitals in documents with three or more columns.
|
||||
|
||||
### Textline detection
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Textline Detection](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-textline)
|
||||
|
||||
The method for textline detection combines deep learning and heuristics. In the deep learning part, an image-to-image
|
||||
model performs binary segmentation of the document into the classes textline vs. background. In the heuristics part,
|
||||
bounding boxes or contours are derived from binary segmentation.
|
||||
|
||||
Skewed documents can heavily affect textline detection accuracy, so robust deskewing is needed. But detecting textlines
|
||||
with rectangle bounding boxes cannot deal with partially curved textlines. To address this, a functionality
|
||||
specifically for documents with curved textlines was included. After finding the contour of a text region and its
|
||||
corresponding textline segmentation, the text region is cut into smaller vertical straps. For each strap, its textline
|
||||
segmentation is first deskewed and then the textlines are separated with the same heuristic method as for finding
|
||||
textline bounding boxes. Later, the strap is rotated back into its original orientation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Textline detection (light)
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Textline Detection Light (simpler but faster method)](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-textline_light)
|
||||
|
||||
The method for textline detection combines deep learning and heuristics. In the deep learning part, an image-to-image
|
||||
model performs binary segmentation of the document into the classes textline vs. background. In the heuristics part,
|
||||
bounding boxes or contours are derived from binary segmentation.
|
||||
|
||||
In the context of this textline model, a distinct labeling approach has been employed to ensure accurate predictions.
|
||||
Specifically, an artificial bounding class has been incorporated alongside the textline classes. This strategic
|
||||
inclusion effectively prevents any spurious connections between adjacent textlines during the prediction phase, thereby
|
||||
enhancing the model's ability to accurately identify and delineate individual textlines within documents. This model
|
||||
eliminates the need for additional heuristics in extracting textline contours.
|
||||
|
||||
### Table detection
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Table Detection](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-tables)
|
||||
|
||||
The objective of this model is to perform table segmentation in historical document images. Due to the pixel-wise
|
||||
segmentation approach employed and the presence of traditional tables predominantly composed of text, the detection of
|
||||
tables required the incorporation of heuristics to achieve reasonable performance. These heuristics were necessary to
|
||||
effectively identify and delineate tables within the historical document images, ensuring accurate segmentation and
|
||||
enabling subsequent analysis and interpretation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Image detection
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Image Detection](https://huggingface.co/SBB/eynollah-image-extraction)
|
||||
|
||||
This model is used for the task of illustration detection only.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reading order detection
|
||||
|
||||
Model card: [Reading Order Detection]()
|
||||
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
|
||||
## Heuristic methods
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, some heuristic methods are employed to further improve the model predictions:
|
||||
|
||||
* After border detection, the largest contour is determined by a bounding box, and the image cropped to these coordinates.
|
||||
* For text region detection, the image is scaled up to make it easier for the model to detect background space between text regions.
|
||||
* A minimum area is defined for text regions in relation to the overall image dimensions, so that very small regions that are noise can be filtered out.
|
||||
* Deskewing is applied on the text region level (due to regions having different degrees of skew) in order to improve the textline segmentation result.
|
||||
* After deskewing, a calculation of the pixel distribution on the X-axis allows the separation of textlines (foreground) and background pixels.
|
||||
* Finally, using the derived coordinates, bounding boxes are determined for each textline.
|
||||
719
docs/train.md
719
docs/train.md
|
|
@ -1,719 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# Training documentation
|
||||
|
||||
This document aims to assist users in preparing training datasets, training models, and
|
||||
performing inference with trained models. We cover various use cases including
|
||||
pixel-wise segmentation, image classification, image enhancement, and
|
||||
machine-based reading order detection. For each use case, we provide guidance
|
||||
on how to generate the corresponding training dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
The following three tasks can all be accomplished using the code in the
|
||||
[`train`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/train) directory:
|
||||
|
||||
* generate training dataset
|
||||
* train a model
|
||||
* inference with the trained model
|
||||
|
||||
## Training, evaluation and output
|
||||
|
||||
The train and evaluation folders should contain subfolders of `images` and `labels`.
|
||||
|
||||
The output folder should be an empty folder where the output model will be written to.
|
||||
|
||||
## Generate training dataset
|
||||
|
||||
The script `generate_gt_for_training.py` is used for generating training datasets. As the results of the following
|
||||
command demonstrates, the dataset generator provides several subcommands:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training generate-gt --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The three most important subcommands are:
|
||||
|
||||
* image-enhancement
|
||||
* machine-based-reading-order
|
||||
* pagexml2label
|
||||
|
||||
### image-enhancement
|
||||
|
||||
Generating a training dataset for image enhancement is quite straightforward. All that is needed is a set of
|
||||
high-resolution images. The training dataset can then be generated using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training image-enhancement \
|
||||
-dis "dir of high resolution images" \
|
||||
-dois "dir where degraded images will be written" \
|
||||
-dols "dir where the corresponding high resolution image will be written as label" \
|
||||
-scs "degrading scales json file"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The scales JSON file is a dictionary with a key named `scales` and values representing scales smaller than 1. Images are
|
||||
downscaled based on these scales and then upscaled again to their original size. This process causes the images to lose
|
||||
resolution at different scales. The degraded images are used as input images, and the original high-resolution images
|
||||
serve as labels. The enhancement model can be trained with this generated dataset. The scales JSON file looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"scales": [0.5, 0.55, 0.6, 0.65, 0.7, 0.75, 0.8, 0.85, 0.9]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### machine-based-reading-order
|
||||
|
||||
For machine-based reading order, we aim to determine the reading priority between two sets of text regions. The model's
|
||||
input is a three-channel image: the first and last channels contain information about each of the two text regions,
|
||||
while the middle channel encodes prominent layout elements necessary for reading order, such as separators and headers.
|
||||
To generate the training dataset, our script requires a page XML file that specifies the image layout with the correct
|
||||
reading order.
|
||||
|
||||
For output images, it is necessary to specify the width and height. Additionally, a minimum text region size can be set
|
||||
to filter out regions smaller than this minimum size. This minimum size is defined as the ratio of the text region area
|
||||
to the image area, with a default value of zero. To run the dataset generator, use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
eynollah-training generate-gt machine-based-reading-order \
|
||||
-dx "dir of GT xml files" \
|
||||
-domi "dir where output images will be written" \
|
||||
"" -docl "dir where the labels will be written" \
|
||||
-ih "height" \
|
||||
-iw "width" \
|
||||
-min "min area ratio"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### pagexml2label
|
||||
|
||||
pagexml2label is designed to generate labels from GT page XML files for various pixel-wise segmentation use cases,
|
||||
including 'layout,' 'textline,' 'printspace,' 'glyph,' and 'word' segmentation.
|
||||
To train a pixel-wise segmentation model, we require images along with their corresponding labels. Our training script
|
||||
expects a PNG image where each pixel corresponds to a label, represented by an integer. The background is always labeled
|
||||
as zero, while other elements are assigned different integers. For instance, if we have ground truth data with four
|
||||
elements including the background, the classes would be labeled as 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
In binary segmentation scenarios such as textline or page extraction, the background is encoded as 0, and the desired
|
||||
element is automatically encoded as 1 in the PNG label.
|
||||
|
||||
To specify the desired use case and the elements to be extracted in the PNG labels, a custom JSON file can be passed.
|
||||
For example, in the case of 'textline' detection, the JSON file would resemble this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"use_case": "textline"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the case of layout segmentation a custom config json file can look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"use_case": "layout",
|
||||
"textregions":{"rest_as_paragraph":1 , "drop-capital": 1, "header":2, "heading":2, "marginalia":3},
|
||||
"imageregion":4,
|
||||
"separatorregion":5,
|
||||
"graphicregions" :{"rest_as_decoration":6 ,"stamp":7}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A possible custom config json file for layout segmentation where the "printspace" is a class:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"use_case": "layout",
|
||||
"textregions":{"rest_as_paragraph":1 , "drop-capital": 1, "header":2, "heading":2, "marginalia":3},
|
||||
"imageregion":4,
|
||||
"separatorregion":5,
|
||||
"graphicregions" :{"rest_as_decoration":6 ,"stamp":7}
|
||||
"printspace_as_class_in_layout" : 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the layout use case, it is beneficial to first understand the structure of the page XML file and its elements.
|
||||
In a given image, the annotations of elements are recorded in a page XML file, including their contours and classes.
|
||||
For an image document, the known regions are 'textregion', 'separatorregion', 'imageregion', 'graphicregion',
|
||||
'noiseregion', and 'tableregion'.
|
||||
|
||||
Text regions and graphic regions also have their own specific types. The known types for text regions are 'paragraph',
|
||||
'header', 'heading', 'marginalia', 'drop-capital', 'footnote', 'footnote-continued', 'signature-mark', 'page-number',
|
||||
and 'catch-word'. The known types for graphic regions are 'handwritten-annotation', 'decoration', 'stamp', and
|
||||
'signature'.
|
||||
Since we don't know all types of text and graphic regions, unknown cases can arise. To handle these, we have defined
|
||||
two additional types, "rest_as_paragraph" and "rest_as_decoration", to ensure that no unknown types are missed.
|
||||
This way, users can extract all known types from the labels and be confident that no unknown types are overlooked.
|
||||
|
||||
In the custom JSON file shown above, "header" and "heading" are extracted as the same class, while "marginalia" is shown
|
||||
as a different class. All other text region types, including "drop-capital," are grouped into the same class. For the
|
||||
graphic region, "stamp" has its own class, while all other types are classified together. "Image region" and "separator
|
||||
region" are also present in the label. However, other regions like "noise region" and "table region" will not be
|
||||
included in the label PNG file, even if they have information in the page XML files, as we chose not to include them.
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training generate-gt pagexml2label \
|
||||
-dx "dir of GT xml files" \
|
||||
-do "dir where output label png files will be written" \
|
||||
-cfg "custom config json file" \
|
||||
-to "output type which has 2d and 3d. 2d is used for training and 3d is just to visualise the labels"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We have also defined an artificial class that can be added to the boundary of text region types or text lines. This key
|
||||
is called "artificial_class_on_boundary." If users want to apply this to certain text regions in the layout use case,
|
||||
the example JSON config file should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"use_case": "layout",
|
||||
"textregions": {
|
||||
"paragraph": 1,
|
||||
"drop-capital": 1,
|
||||
"header": 2,
|
||||
"heading": 2,
|
||||
"marginalia": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"imageregion": 4,
|
||||
"separatorregion": 5,
|
||||
"graphicregions": {
|
||||
"rest_as_decoration": 6
|
||||
},
|
||||
"artificial_class_on_boundary": ["paragraph", "header", "heading", "marginalia"],
|
||||
"artificial_class_label": 7
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This implies that the artificial class label, denoted by 7, will be present on PNG files and will only be added to the
|
||||
elements labeled as "paragraph," "header," "heading," and "marginalia."
|
||||
|
||||
For "textline", "word", and "glyph", the artificial class on the boundaries will be activated only if the
|
||||
"artificial_class_label" key is specified in the config file. Its value should be set as 2 since these elements
|
||||
represent binary cases. For example, if the background and textline are denoted as 0 and 1 respectively, then the
|
||||
artificial class should be assigned the value 2. The example JSON config file should look like this for "textline" use
|
||||
case:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"use_case": "textline",
|
||||
"artificial_class_label": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the coordinates of "PrintSpace" or "Border" are present in the page XML ground truth files, and the user wishes to
|
||||
crop only the print space area, this can be achieved by activating the "-ps" argument. However, it should be noted that
|
||||
in this scenario, since cropping will be applied to the label files, the directory of the original images must be
|
||||
provided to ensure that they are cropped in sync with the labels. This ensures that the correct images and labels
|
||||
required for training are obtained. The command should resemble the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training generate-gt pagexml2label \
|
||||
-dx "dir of GT xml files" \
|
||||
-do "dir where output label png files will be written" \
|
||||
-cfg "custom config json file" \
|
||||
-to "output type which has 2d and 3d. 2d is used for training and 3d is just to visualise the labels" \
|
||||
-ps \
|
||||
-di "dir where the org images are located" \
|
||||
-doi "dir where the cropped output images will be written"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Train a model
|
||||
|
||||
### classification
|
||||
|
||||
For the classification use case, we haven't provided a ground truth generator, as it's unnecessary. For classification,
|
||||
all we require is a training directory with subdirectories, each containing images of its respective classes. We need
|
||||
separate directories for training and evaluation, and the class names (subdirectories) must be consistent across both
|
||||
directories. Additionally, the class names should be specified in the config JSON file, as shown in the following
|
||||
example. If, for instance, we aim to classify "apple" and "orange," with a total of 2 classes, the
|
||||
"classification_classes_name" key in the config file should appear as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "nontransformer",
|
||||
"task": "classification",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 2,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 10,
|
||||
"input_height" : 448,
|
||||
"input_width" : 448,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 4,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"f1_threshold_classification": 0.8,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"classification_classes_name" : {"0":"apple", "1":"orange"},
|
||||
"dir_train": "./train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "./eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "./output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The "dir_train" should be like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── train # train directory
|
||||
├── apple # directory of images for apple class
|
||||
└── orange # directory of images for orange class
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And the "dir_eval" the same structure as train directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── eval # evaluation directory
|
||||
├── apple # directory of images for apple class
|
||||
└── orange # directory of images for orange class
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The classification model can be trained using the following command line:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training train with config_classification.json
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As evident in the example JSON file above, for classification, we utilize a "f1_threshold_classification" parameter.
|
||||
This parameter is employed to gather all models with an evaluation f1 score surpassing this threshold. Subsequently,
|
||||
an ensemble of these model weights is executed, and a model is saved in the output directory as "model_ens_avg".
|
||||
Additionally, the weight of the best model based on the evaluation f1 score is saved as "model_best".
|
||||
|
||||
### reading order
|
||||
An example config json file for machine based reading order should be like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "nontransformer",
|
||||
"task": "reading_order",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 1,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 5,
|
||||
"input_height" : 672,
|
||||
"input_width" : 448,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 4,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"dir_train": "./train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "./eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "./output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The "dir_train" should be like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── train # train directory
|
||||
├── images # directory of images
|
||||
└── labels # directory of labels
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And the "dir_eval" the same structure as train directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── eval # evaluation directory
|
||||
├── images # directory of images
|
||||
└── labels # directory of labels
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The classification model can be trained like the classification case command line.
|
||||
|
||||
### Segmentation (Textline, Binarization, Page extraction and layout) and enhancement
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameter configuration for segmentation or enhancement usecases
|
||||
|
||||
The following parameter configuration can be applied to all segmentation use cases and enhancements. The augmentation,
|
||||
its sub-parameters, and continued training are defined only for segmentation use cases and enhancements, not for
|
||||
classification and machine-based reading order, as you can see in their example config files.
|
||||
|
||||
* `backbone_type`: For segmentation tasks (such as text line, binarization, and layout detection) and enhancement, we
|
||||
offer two backbone options: a "nontransformer" and a "transformer" backbone. For the "transformer" backbone, we first
|
||||
apply a CNN followed by a transformer. In contrast, the "nontransformer" backbone utilizes only a CNN ResNet-50.
|
||||
* `task`: The task parameter can have values such as "segmentation", "enhancement", "classification", and "reading_order".
|
||||
* `patches`: If you want to break input images into smaller patches (input size of the model) you need to set this
|
||||
* parameter to `true`. In the case that the model should see the image once, like page extraction, patches should be
|
||||
set to ``false``.
|
||||
* `n_batch`: Number of batches at each iteration.
|
||||
* `n_classes`: Number of classes. In the case of binary classification this should be 2. In the case of reading_order it
|
||||
should set to 1. And for the case of layout detection just the unique number of classes should be given.
|
||||
* `n_epochs`: Number of epochs.
|
||||
* `input_height`: This indicates the height of model's input.
|
||||
* `input_width`: This indicates the width of model's input.
|
||||
* `weight_decay`: Weight decay of l2 regularization of model layers.
|
||||
* `pretraining`: Set to `true` to load pretrained weights of ResNet50 encoder. The downloaded weights should be saved
|
||||
in a folder named "pretrained_model" in the same directory of "train.py" script.
|
||||
* `augmentation`: If you want to apply any kind of augmentation this parameter should first set to `true`.
|
||||
* `flip_aug`: If `true`, different types of filp will be applied on image. Type of flips is given with "flip_index" parameter.
|
||||
* `blur_aug`: If `true`, different types of blurring will be applied on image. Type of blurrings is given with "blur_k" parameter.
|
||||
* `scaling`: If `true`, scaling will be applied on image. Scale of scaling is given with "scales" parameter.
|
||||
* `degrading`: If `true`, degrading will be applied to the image. The amount of degrading is defined with "degrade_scales" parameter.
|
||||
* `brightening`: If `true`, brightening will be applied to the image. The amount of brightening is defined with "brightness" parameter.
|
||||
* `rotation_not_90`: If `true`, rotation (not 90 degree) will be applied on image. Rotation angles are given with "thetha" parameter.
|
||||
* `rotation`: If `true`, 90 degree rotation will be applied on image.
|
||||
* `binarization`: If `true`,Otsu thresholding will be applied to augment the input data with binarized images.
|
||||
* `scaling_bluring`: If `true`, combination of scaling and blurring will be applied on image.
|
||||
* `scaling_binarization`: If `true`, combination of scaling and binarization will be applied on image.
|
||||
* `scaling_flip`: If `true`, combination of scaling and flip will be applied on image.
|
||||
* `flip_index`: Type of flips.
|
||||
* `blur_k`: Type of blurrings.
|
||||
* `scales`: Scales of scaling.
|
||||
* `brightness`: The amount of brightenings.
|
||||
* `thetha`: Rotation angles.
|
||||
* `degrade_scales`: The amount of degradings.
|
||||
* `continue_training`: If `true`, it means that you have already trained a model and you would like to continue the
|
||||
training. So it is needed to providethe dir of trained model with "dir_of_start_model" and index for naming
|
||||
themodels. For example if you have already trained for 3 epochs then your lastindex is 2 and if you want to continue
|
||||
from model_1.h5, you can set `index_start` to 3 to start naming model with index 3.
|
||||
* `weighted_loss`: If `true`, this means that you want to apply weighted categorical_crossentropy as loss fucntion. Be carefull if you set to `true`the parameter "is_loss_soft_dice" should be ``false``
|
||||
* `data_is_provided`: If you have already provided the input data you can set this to `true`. Be sure that the train
|
||||
and eval data are in"dir_output".Since when once we provide training data we resize and augmentthem and then wewrite
|
||||
them in sub-directories train and eval in "dir_output".
|
||||
* `dir_train`: This is the directory of "images" and "labels" (dir_train should include two subdirectories with names of images and labels ) for raw images and labels. Namely they are not prepared (not resized and not augmented) yet for training the model. When we run this tool these raw data will be transformed to suitable size needed for the model and they will be written in "dir_output" in train and eval directories. Each of train and eval include "images" and "labels" sub-directories.
|
||||
* `index_start`: Starting index for saved models in the case that "continue_training" is `true`.
|
||||
* `dir_of_start_model`: Directory containing pretrained model to continue training the model in the case that "continue_training" is `true`.
|
||||
* `transformer_num_patches_xy`: Number of patches for vision transformer in x and y direction respectively.
|
||||
* `transformer_patchsize_x`: Patch size of vision transformer patches in x direction.
|
||||
* `transformer_patchsize_y`: Patch size of vision transformer patches in y direction.
|
||||
* `transformer_projection_dim`: Transformer projection dimension. Default value is 64.
|
||||
* `transformer_mlp_head_units`: Transformer Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) head units. Default value is [128, 64].
|
||||
* `transformer_layers`: transformer layers. Default value is 8.
|
||||
* `transformer_num_heads`: Transformer number of heads. Default value is 4.
|
||||
* `transformer_cnn_first`: We have two types of vision transformers. In one type, a CNN is applied first, followed by a transformer. In the other type, this order is reversed. If transformer_cnn_first is true, it means the CNN will be applied before the transformer. Default value is true.
|
||||
|
||||
In the case of segmentation and enhancement the train and evaluation directory should be as following.
|
||||
|
||||
The "dir_train" should be like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── train # train directory
|
||||
├── images # directory of images
|
||||
└── labels # directory of labels
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And the "dir_eval" the same structure as train directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── eval # evaluation directory
|
||||
├── images # directory of images
|
||||
└── labels # directory of labels
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After configuring the JSON file for segmentation or enhancement, training can be initiated by running the following
|
||||
command, similar to the process for classification and reading order:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
eynollah-training train with config_classification.json`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Binarization
|
||||
|
||||
### Ground truth format
|
||||
|
||||
Lables for each pixel are identified by a number. So if you have a
|
||||
binary case, ``n_classes`` should be set to ``2`` and labels should
|
||||
be ``0`` and ``1`` for each class and pixel.
|
||||
|
||||
In the case of multiclass, just set ``n_classes`` to the number of classes
|
||||
you have and the try to produce the labels by pixels set from ``0 , 1 ,2 .., n_classes-1``.
|
||||
The labels format should be png.
|
||||
Our lables are 3 channel png images but only information of first channel is used.
|
||||
If you have an image label with height and width of 10, for a binary case the first channel should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
Label: [ [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] ]
|
||||
|
||||
This means that you have an image by `10*10*3` and `pixel[0,0]` belongs
|
||||
to class `1` and `pixel[0,1]` belongs to class `0`.
|
||||
|
||||
A small sample of training data for binarization experiment can be found here, [Training data sample](https://qurator-data.de/~vahid.rezanezhad/binarization_training_data_sample/), which contains images and lables folders.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
An example config json file for binarization can be like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "transformer",
|
||||
"task": "binarization",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 2,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 4,
|
||||
"input_height" : 224,
|
||||
"input_width" : 672,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 1,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"patches" : true,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"augmentation" : true,
|
||||
"flip_aug" : false,
|
||||
"blur_aug" : false,
|
||||
"scaling" : true,
|
||||
"degrading": false,
|
||||
"brightening": false,
|
||||
"binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_bluring" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_flip" : false,
|
||||
"rotation": false,
|
||||
"rotation_not_90": false,
|
||||
"transformer_num_patches_xy": [7, 7],
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_x": 3,
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_y": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_projection_dim": 192,
|
||||
"transformer_mlp_head_units": [128, 64],
|
||||
"transformer_layers": 8,
|
||||
"transformer_num_heads": 4,
|
||||
"transformer_cnn_first": true,
|
||||
"blur_k" : ["blur","guass","median"],
|
||||
"scales" : [0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.1, 1.2, 1.4],
|
||||
"brightness" : [1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 2],
|
||||
"degrade_scales" : [0.2, 0.4],
|
||||
"flip_index" : [0, 1, -1],
|
||||
"thetha" : [10, -10],
|
||||
"continue_training": false,
|
||||
"index_start" : 0,
|
||||
"dir_of_start_model" : " ",
|
||||
"weighted_loss": false,
|
||||
"is_loss_soft_dice": false,
|
||||
"data_is_provided": false,
|
||||
"dir_train": "./train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "./eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "./output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Textline
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "nontransformer",
|
||||
"task": "segmentation",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 2,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 4,
|
||||
"input_height" : 448,
|
||||
"input_width" : 224,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 1,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"patches" : true,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"augmentation" : true,
|
||||
"flip_aug" : false,
|
||||
"blur_aug" : false,
|
||||
"scaling" : true,
|
||||
"degrading": false,
|
||||
"brightening": false,
|
||||
"binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_bluring" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_flip" : false,
|
||||
"rotation": false,
|
||||
"rotation_not_90": false,
|
||||
"blur_k" : ["blur","guass","median"],
|
||||
"scales" : [0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.1, 1.2, 1.4],
|
||||
"brightness" : [1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 2],
|
||||
"degrade_scales" : [0.2, 0.4],
|
||||
"flip_index" : [0, 1, -1],
|
||||
"thetha" : [10, -10],
|
||||
"continue_training": false,
|
||||
"index_start" : 0,
|
||||
"dir_of_start_model" : " ",
|
||||
"weighted_loss": false,
|
||||
"is_loss_soft_dice": false,
|
||||
"data_is_provided": false,
|
||||
"dir_train": "./train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "./eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "./output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enhancement
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "nontransformer",
|
||||
"task": "enhancement",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 3,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 4,
|
||||
"input_height" : 448,
|
||||
"input_width" : 224,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 4,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"patches" : true,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"augmentation" : true,
|
||||
"flip_aug" : false,
|
||||
"blur_aug" : false,
|
||||
"scaling" : true,
|
||||
"degrading": false,
|
||||
"brightening": false,
|
||||
"binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_bluring" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_flip" : false,
|
||||
"rotation": false,
|
||||
"rotation_not_90": false,
|
||||
"blur_k" : ["blur","guass","median"],
|
||||
"scales" : [0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.1, 1.2, 1.4],
|
||||
"brightness" : [1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 2],
|
||||
"degrade_scales" : [0.2, 0.4],
|
||||
"flip_index" : [0, 1, -1],
|
||||
"thetha" : [10, -10],
|
||||
"continue_training": false,
|
||||
"index_start" : 0,
|
||||
"dir_of_start_model" : " ",
|
||||
"weighted_loss": false,
|
||||
"is_loss_soft_dice": false,
|
||||
"data_is_provided": false,
|
||||
"dir_train": "./train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "./eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "./output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It's important to mention that the value of n_classes for enhancement should be 3, as the model's output is a 3-channel
|
||||
image.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Page extraction
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "nontransformer",
|
||||
"task": "segmentation",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 2,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 4,
|
||||
"input_height" : 448,
|
||||
"input_width" : 224,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 1,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"patches" : false,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"augmentation" : false,
|
||||
"flip_aug" : false,
|
||||
"blur_aug" : false,
|
||||
"scaling" : true,
|
||||
"degrading": false,
|
||||
"brightening": false,
|
||||
"binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_bluring" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_flip" : false,
|
||||
"rotation": false,
|
||||
"rotation_not_90": false,
|
||||
"blur_k" : ["blur","guass","median"],
|
||||
"scales" : [0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.1, 1.2, 1.4],
|
||||
"brightness" : [1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 2],
|
||||
"degrade_scales" : [0.2, 0.4],
|
||||
"flip_index" : [0, 1, -1],
|
||||
"thetha" : [10, -10],
|
||||
"continue_training": false,
|
||||
"index_start" : 0,
|
||||
"dir_of_start_model" : " ",
|
||||
"weighted_loss": false,
|
||||
"is_loss_soft_dice": false,
|
||||
"data_is_provided": false,
|
||||
"dir_train": "./train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "./eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "./output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For page segmentation (or print space or border segmentation), the model needs to view the input image in its
|
||||
entirety,hence the patches parameter should be set to false.
|
||||
|
||||
#### layout segmentation
|
||||
|
||||
An example config json file for layout segmentation with 5 classes (including background) can be like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "transformer",
|
||||
"task": "segmentation",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 5,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 4,
|
||||
"input_height" : 448,
|
||||
"input_width" : 224,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 1,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"patches" : true,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"augmentation" : true,
|
||||
"flip_aug" : false,
|
||||
"blur_aug" : false,
|
||||
"scaling" : true,
|
||||
"degrading": false,
|
||||
"brightening": false,
|
||||
"binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_bluring" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_flip" : false,
|
||||
"rotation": false,
|
||||
"rotation_not_90": false,
|
||||
"transformer_num_patches_xy": [7, 14],
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_x": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_y": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_projection_dim": 64,
|
||||
"transformer_mlp_head_units": [128, 64],
|
||||
"transformer_layers": 8,
|
||||
"transformer_num_heads": 4,
|
||||
"transformer_cnn_first": true,
|
||||
"blur_k" : ["blur","guass","median"],
|
||||
"scales" : [0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.1, 1.2, 1.4],
|
||||
"brightness" : [1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 2],
|
||||
"degrade_scales" : [0.2, 0.4],
|
||||
"flip_index" : [0, 1, -1],
|
||||
"thetha" : [10, -10],
|
||||
"continue_training": false,
|
||||
"index_start" : 0,
|
||||
"dir_of_start_model" : " ",
|
||||
"weighted_loss": false,
|
||||
"is_loss_soft_dice": false,
|
||||
"data_is_provided": false,
|
||||
"dir_train": "./train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "./eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "./output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Inference with the trained model
|
||||
|
||||
### classification
|
||||
|
||||
For conducting inference with a trained model, you simply need to execute the following command line, specifying the
|
||||
directory of the model and the image on which to perform inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training inference -m "model dir" -i "image"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will straightforwardly return the class of the image.
|
||||
|
||||
### machine based reading order
|
||||
|
||||
To infer the reading order using a reading order model, we need a page XML file containing layout information but
|
||||
without the reading order. We simply need to provide the model directory, the XML file, and the output directory. The
|
||||
new XML file with the added reading order will be written to the output directory with the same name. We need to run:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training inference \
|
||||
-m "model dir" \
|
||||
-xml "page xml file" \
|
||||
-o "output dir to write new xml with reading order"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Segmentation (Textline, Binarization, Page extraction and layout) and enhancement
|
||||
|
||||
For conducting inference with a trained model for segmentation and enhancement you need to run the following command line:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah-training inference \
|
||||
-m "model dir" \
|
||||
-i "image" \
|
||||
-p \
|
||||
-s "output image"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that in the case of page extraction the -p flag is not needed.
|
||||
|
||||
For segmentation or binarization tasks, if a ground truth (GT) label is available, the IoU evaluation metric can be
|
||||
calculated for the output. To do this, you need to provide the GT label using the argument -gt.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# Usage documentation
|
||||
The command-line interface can be called like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
eynollah \
|
||||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||||
-o <output directory> \
|
||||
-m <directory containing model files> \
|
||||
[OPTIONS]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Processing options
|
||||
The following options can be used to further configure the processing:
|
||||
|
||||
| option | description |
|
||||
|-------------------|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `-fl` | full layout analysis including all steps and segmentation classes |
|
||||
| `-light` | lighter and faster but simpler method for main region detection and deskewing |
|
||||
| `-tab` | apply table detection |
|
||||
| `-ae` | apply enhancement (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
|
||||
| `-as` | apply scaling |
|
||||
| `-cl` | apply contour detection for curved text lines instead of bounding boxes |
|
||||
| `-ib` | apply binarization (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
|
||||
| `-ep` | enable plotting (MUST always be used with `-sl`, `-sd`, `-sa`, `-si` or `-ae`) |
|
||||
| `-eoi` | extract only images to output directory (other processing will not be done) |
|
||||
| `-ho` | ignore headers for reading order dectection |
|
||||
| `-si <directory>` | save image regions detected to this directory |
|
||||
| `-sd <directory>` | save deskewed image to this directory |
|
||||
| `-sl <directory>` | save layout prediction as plot to this directory |
|
||||
| `-sp <directory>` | save cropped page image to this directory |
|
||||
| `-sa <directory>` | save all (plot, enhanced/binary image, layout) to this directory |
|
||||
|
||||
If no option is set, the tool performs detection of main regions (background, text, images, separators and marginals).
|
||||
|
||||
### `--full-layout` vs `--no-full-layout`
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the difference in elements detected depending on the `--full-layout`/`--no-full-layout` command line flags:
|
||||
|
||||
| | `--full-layout` | `--no-full-layout` |
|
||||
|--------------------------|-----------------|--------------------|
|
||||
| reading order | x | x |
|
||||
| header regions | x | - |
|
||||
| text regions | x | x |
|
||||
| text regions / text line | x | x |
|
||||
| drop-capitals | x | - |
|
||||
| marginals | x | x |
|
||||
| marginals / text line | x | x |
|
||||
| image region | x | x |
|
||||
|
||||
## Use as OCR-D processor
|
||||
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as [OCR-D](https://ocr-d.de) processor that is described in
|
||||
[`ocrd-tool.json`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/src/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json).
|
||||
|
||||
The source image file group with (preferably) RGB images should be used as input for Eynollah like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O SEG-LINE -P models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Any image referenced by `@imageFilename` in PAGE-XML is passed on directly to Eynollah as a processor, so that e.g.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG-BIN -O SEG-LINE -P models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
uses the original (RGB) image despite any binarization that may have occured in previous OCR-D processing steps.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use with Docker
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
* The best output quality is produced when RGB images are used as input rather than greyscale or binarized images.
|
||||
* If none of the parameters is set to `true`, the tool will perform a layout detection of main regions (background,
|
||||
text, images, separators and marginals). An advantage of this tool is that it tries to extract main text regions
|
||||
separately as much as possible.
|
||||
* If you set `-ae` (**a**llow image **e**nhancement) parameter to `true`, the tool will first check the ppi
|
||||
(pixel-per-inch) of the image and when it is less than 300, the tool will resize it and only then image enhancement will
|
||||
occur. Image enhancement can also take place without this option, but by setting this option to `true`, the layout xml
|
||||
data (e.g. coordinates) will be based on the resized and enhanced image instead of the original image.
|
||||
* For some documents, while the quality is good, their scale is very large, and the performance of tool decreases. In
|
||||
such cases you can set `-as` (**a**llow **s**caling) to `true`. With this option enabled, the tool will try to rescale
|
||||
the image and only then the layout detection process will begin.
|
||||
* If you care about drop capitals (initials) and headings, you can set `-fl` (**f**ull **l**ayout) to `true`. With this
|
||||
setting, the tool can currently distinguish 7 document layout classes/elements.
|
||||
* In cases where the document includes curved headers or curved lines, rectangular bounding boxes for textlines will not
|
||||
be a great option. In such cases it is strongly recommended setting the flag `-cl` (**c**urved **l**ines) to `true` to
|
||||
find contours of curved lines instead of rectangular bounding boxes. Be advised that enabling this option increases the
|
||||
processing time of the tool.
|
||||
* To crop and save image regions inside the document, set the parameter `-si` (**s**ave **i**mages) to true and provide
|
||||
a directory path to store the extracted images.
|
||||
* To extract only images from a document, set the parameter `-eoi` (**e**xtract **o**nly **i**mages). Choosing this
|
||||
option disables any other processing. To save the cropped images add `-ep` and `-si`.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1 +1 @@
|
|||
src/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json
|
||||
qurator/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,6 +3,7 @@ requires = ["setuptools>=61.0", "wheel", "setuptools-ocrd"]
|
|||
|
||||
[project]
|
||||
name = "eynollah"
|
||||
version = "0.3.1"
|
||||
authors = [
|
||||
{name = "Vahid Rezanezhad"},
|
||||
{name = "Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin - Preußischer Kulturbesitz"},
|
||||
|
|
@ -13,11 +14,7 @@ license.file = "LICENSE"
|
|||
requires-python = ">=3.8"
|
||||
keywords = ["document layout analysis", "image segmentation"]
|
||||
|
||||
dynamic = [
|
||||
"dependencies",
|
||||
"optional-dependencies",
|
||||
"version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
dynamic = ["dependencies"]
|
||||
|
||||
classifiers = [
|
||||
"Development Status :: 4 - Beta",
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,10 +27,8 @@ classifiers = [
|
|||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[project.scripts]
|
||||
eynollah = "eynollah.cli:main"
|
||||
eynollah-training = "eynollah.training.cli:main"
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment = "eynollah.ocrd_cli:main"
|
||||
ocrd-sbb-binarize = "eynollah.ocrd_cli_binarization:main"
|
||||
eynollah = "qurator.eynollah.cli:main"
|
||||
ocrd-eynollah-segment = "qurator.eynollah.ocrd_cli:main"
|
||||
|
||||
[project.urls]
|
||||
Homepage = "https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah"
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,38 +36,9 @@ Repository = "https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah.git"
|
|||
|
||||
[tool.setuptools.dynamic]
|
||||
dependencies = {file = ["requirements.txt"]}
|
||||
optional-dependencies.test = {file = ["requirements-test.txt"]}
|
||||
optional-dependencies.OCR = {file = ["requirements-ocr.txt"]}
|
||||
optional-dependencies.plotting = {file = ["requirements-plotting.txt"]}
|
||||
optional-dependencies.training = {file = ["requirements-training.txt"]}
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.setuptools.packages.find]
|
||||
where = ["src"]
|
||||
where = ["qurator"]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.setuptools.package-data]
|
||||
"*" = ["*.json", '*.yml', '*.xml', '*.xsd', '*.ttf']
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.coverage.run]
|
||||
branch = true
|
||||
source = ["eynollah"]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.ruff]
|
||||
line-length = 120
|
||||
# TODO: Reenable and fix after release v0.6.0
|
||||
exclude = ['src/eynollah/training']
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.ruff.lint]
|
||||
ignore = [
|
||||
# disable unused imports
|
||||
"F401",
|
||||
# disable import order
|
||||
"E402",
|
||||
# disable unused variables
|
||||
"F841",
|
||||
# disable bare except
|
||||
"E722",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.ruff.format]
|
||||
quote-style = "preserve"
|
||||
|
||||
"*" = ["*.json", '*.yml', '*.xml', '*.xsd']
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
208
qurator/eynollah/cli.py
Normal file
208
qurator/eynollah/cli.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
|
|||
import sys
|
||||
import click
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import initLogging, setOverrideLogLevel
|
||||
from qurator.eynollah.eynollah import Eynollah
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@click.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--image",
|
||||
"-i",
|
||||
help="image filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory to write output xml data",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of images",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model",
|
||||
"-m",
|
||||
help="directory of models",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_images",
|
||||
"-si",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, images in documents will be cropped and saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_layout",
|
||||
"-sl",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, plot of layout will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_deskewed",
|
||||
"-sd",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, deskewed image will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_all",
|
||||
"-sa",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, all plots needed for documentation will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_page",
|
||||
"-sp",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, page crop of image will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--enable-plotting/--disable-plotting",
|
||||
"-ep/-noep",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="If set, will plot intermediary files and images",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--allow-enhancement/--no-allow-enhancement",
|
||||
"-ae/-noae",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would check that input image need resizing and enhancement or not. If so output of resized and enhanced image and corresponding layout data will be written in out directory",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--curved-line/--no-curvedline",
|
||||
"-cl/-nocl",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to return contoure of textlines instead of rectangle bounding box of textline. This should be taken into account that with this option the tool need more time to do process.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--textline_light/--no-textline_light",
|
||||
"-tll/-notll",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to return contoure of textlines instead of rectangle bounding box of textline with a faster method.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--full-layout/--no-full-layout",
|
||||
"-fl/-nofl",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to return all elements of layout.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--tables/--no-tables",
|
||||
"-tab/-notab",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to detect tables.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--right2left/--left2right",
|
||||
"-r2l/-l2r",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will extract right-to-left reading order.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--input_binary/--input-RGB",
|
||||
"-ib/-irgb",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="in general, eynollah uses RGB as input but if the input document is strongly dark, bright or for any other reason you can turn binarized input on. This option does not mean that you have to provide a binary image, otherwise this means that the tool itself will binarized the RGB input document.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--allow_scaling/--no-allow-scaling",
|
||||
"-as/-noas",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would check the scale and if needed it will scale it to perform better layout detection",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--headers_off/--headers-on",
|
||||
"-ho/-noho",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would ignore headers role in reading order",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--light_version/--original",
|
||||
"-light/-org",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would use lighter version",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--ignore_page_extraction/--extract_page_included",
|
||||
"-ipe/-epi",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would ignore page extraction",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--log-level",
|
||||
"-l",
|
||||
type=click.Choice(['OFF', 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR']),
|
||||
help="Override log level globally to this",
|
||||
)
|
||||
def main(
|
||||
image,
|
||||
out,
|
||||
dir_in,
|
||||
model,
|
||||
save_images,
|
||||
save_layout,
|
||||
save_deskewed,
|
||||
save_all,
|
||||
save_page,
|
||||
enable_plotting,
|
||||
allow_enhancement,
|
||||
curved_line,
|
||||
textline_light,
|
||||
full_layout,
|
||||
tables,
|
||||
right2left,
|
||||
input_binary,
|
||||
allow_scaling,
|
||||
headers_off,
|
||||
light_version,
|
||||
ignore_page_extraction,
|
||||
log_level
|
||||
):
|
||||
if log_level:
|
||||
setOverrideLogLevel(log_level)
|
||||
initLogging()
|
||||
if not enable_plotting and (save_layout or save_deskewed or save_all or save_page or save_images or allow_enhancement):
|
||||
print("Error: You used one of -sl, -sd, -sa, -sp, -si or -ae but did not enable plotting with -ep")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
elif enable_plotting and not (save_layout or save_deskewed or save_all or save_page or save_images or allow_enhancement):
|
||||
print("Error: You used -ep to enable plotting but set none of -sl, -sd, -sa, -sp, -si or -ae")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
if textline_light and not light_version:
|
||||
print('Error: You used -tll to enable light textline detection but -light is not enabled')
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
eynollah = Eynollah(
|
||||
image_filename=image,
|
||||
dir_out=out,
|
||||
dir_in=dir_in,
|
||||
dir_models=model,
|
||||
dir_of_cropped_images=save_images,
|
||||
dir_of_layout=save_layout,
|
||||
dir_of_deskewed=save_deskewed,
|
||||
dir_of_all=save_all,
|
||||
dir_save_page=save_page,
|
||||
enable_plotting=enable_plotting,
|
||||
allow_enhancement=allow_enhancement,
|
||||
curved_line=curved_line,
|
||||
textline_light=textline_light,
|
||||
full_layout=full_layout,
|
||||
tables=tables,
|
||||
right2left=right2left,
|
||||
input_binary=input_binary,
|
||||
allow_scaling=allow_scaling,
|
||||
headers_off=headers_off,
|
||||
light_version=light_version,
|
||||
ignore_page_extraction=ignore_page_extraction,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if dir_in:
|
||||
eynollah.run()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pcgts = eynollah.run()
|
||||
eynollah.writer.write_pagexml(pcgts)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
3112
qurator/eynollah/eynollah.py
Normal file
3112
qurator/eynollah/eynollah.py
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
65
qurator/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json
Normal file
65
qurator/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"version": "0.3.1",
|
||||
"git_url": "https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah",
|
||||
"tools": {
|
||||
"ocrd-eynollah-segment": {
|
||||
"executable": "ocrd-eynollah-segment",
|
||||
"categories": ["Layout analysis"],
|
||||
"description": "Segment page into regions and lines and do reading order detection with eynollah",
|
||||
"input_file_grp": ["OCR-D-IMG", "OCR-D-SEG-PAGE", "OCR-D-GT-SEG-PAGE"],
|
||||
"output_file_grp": ["OCR-D-SEG-LINE"],
|
||||
"steps": ["layout/segmentation/region", "layout/segmentation/line"],
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
"models": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"format": "file",
|
||||
"content-type": "text/directory",
|
||||
"cacheable": true,
|
||||
"description": "Path to directory containing models to be used (See https://qurator-data.de/eynollah)",
|
||||
"required": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dpi": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"format": "float",
|
||||
"description": "pixel density in dots per inch (overrides any meta-data in the images); ignored if <= 0 (with fall-back 230)",
|
||||
"default": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"full_layout": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": true,
|
||||
"description": "Try to detect all element subtypes, including drop-caps and headings"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"tables": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "Try to detect table regions"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"curved_line": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "try to return contour of textlines instead of just rectangle bounding box. Needs more processing time"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"allow_scaling": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "check the resolution against the number of detected columns and if needed, scale the image up or down during layout detection (heuristic to improve quality and performance)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers_off": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "ignore the special role of headings during reading order detection"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"resources": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"description": "models for eynollah (TensorFlow format)",
|
||||
"url": "https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/releases/download/v0.3.0/models_eynollah.tar.gz",
|
||||
"name": "default",
|
||||
"size": 1761991295,
|
||||
"type": "archive",
|
||||
"path_in_archive": "models_eynollah"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,8 +1,5 @@
|
|||
try:
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
plt = mpatches = None
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import os.path
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,7 +9,7 @@ from .utils import crop_image_inside_box
|
|||
from .utils.rotate import rotate_image_different
|
||||
from .utils.resize import resize_image
|
||||
|
||||
class EynollahPlotter:
|
||||
class EynollahPlotter():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Class collecting all the plotting and image writing methods
|
||||
"""
|
||||
68
qurator/eynollah/processor.py
Normal file
68
qurator/eynollah/processor.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
|||
from json import loads
|
||||
from pkg_resources import resource_string
|
||||
from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from os.path import join
|
||||
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from ocrd import Processor
|
||||
from ocrd_modelfactory import page_from_file, exif_from_filename
|
||||
from ocrd_models import OcrdFile, OcrdExif
|
||||
from ocrd_models.ocrd_page import to_xml
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import (
|
||||
getLogger,
|
||||
MIMETYPE_PAGE,
|
||||
assert_file_grp_cardinality,
|
||||
make_file_id
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from .eynollah import Eynollah
|
||||
from .utils.pil_cv2 import pil2cv
|
||||
|
||||
OCRD_TOOL = loads(resource_string(__name__, 'ocrd-tool.json').decode('utf8'))
|
||||
|
||||
class EynollahProcessor(Processor):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
kwargs['ocrd_tool'] = OCRD_TOOL['tools']['ocrd-eynollah-segment']
|
||||
kwargs['version'] = OCRD_TOOL['version']
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def process(self):
|
||||
LOG = getLogger('eynollah')
|
||||
assert_file_grp_cardinality(self.input_file_grp, 1)
|
||||
assert_file_grp_cardinality(self.output_file_grp, 1)
|
||||
for n, input_file in enumerate(self.input_files):
|
||||
page_id = input_file.pageId or input_file.ID
|
||||
LOG.info("INPUT FILE %s (%d/%d) ", page_id, n + 1, len(self.input_files))
|
||||
pcgts = page_from_file(self.workspace.download_file(input_file))
|
||||
LOG.debug('width %s height %s', pcgts.get_Page().imageWidth, pcgts.get_Page().imageHeight)
|
||||
self.add_metadata(pcgts)
|
||||
page = pcgts.get_Page()
|
||||
# XXX loses DPI information
|
||||
# page_image, _, _ = self.workspace.image_from_page(page, page_id, feature_filter='binarized')
|
||||
image_filename = self.workspace.download_file(next(self.workspace.mets.find_files(local_filename=page.imageFilename))).local_filename
|
||||
eynollah_kwargs = {
|
||||
'dir_models': self.resolve_resource(self.parameter['models']),
|
||||
'allow_enhancement': False,
|
||||
'curved_line': self.parameter['curved_line'],
|
||||
'full_layout': self.parameter['full_layout'],
|
||||
'allow_scaling': self.parameter['allow_scaling'],
|
||||
'headers_off': self.parameter['headers_off'],
|
||||
'tables': self.parameter['tables'],
|
||||
'override_dpi': self.parameter['dpi'],
|
||||
'logger': LOG,
|
||||
'pcgts': pcgts,
|
||||
'image_filename': image_filename
|
||||
}
|
||||
Eynollah(**eynollah_kwargs).run()
|
||||
file_id = make_file_id(input_file, self.output_file_grp)
|
||||
pcgts.set_pcGtsId(file_id)
|
||||
self.workspace.add_file(
|
||||
ID=file_id,
|
||||
file_grp=self.output_file_grp,
|
||||
pageId=page_id,
|
||||
mimetype=MIMETYPE_PAGE,
|
||||
local_filename=join(self.output_file_grp, file_id) + '.xml',
|
||||
content=to_xml(pcgts))
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
370
qurator/eynollah/utils/contour.py
Normal file
370
qurator/eynollah/utils/contour.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
|
|||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from shapely import geometry
|
||||
|
||||
from .rotate import rotate_image, rotation_image_new
|
||||
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue, cpu_count
|
||||
from multiprocessing import Pool
|
||||
def contours_in_same_horizon(cy_main_hor):
|
||||
X1 = np.zeros((len(cy_main_hor), len(cy_main_hor)))
|
||||
X2 = np.zeros((len(cy_main_hor), len(cy_main_hor)))
|
||||
|
||||
X1[0::1, :] = cy_main_hor[:]
|
||||
X2 = X1.T
|
||||
|
||||
X_dif = np.abs(X2 - X1)
|
||||
args_help = np.array(range(len(cy_main_hor)))
|
||||
all_args = []
|
||||
for i in range(len(cy_main_hor)):
|
||||
list_h = list(args_help[X_dif[i, :] <= 20])
|
||||
list_h.append(i)
|
||||
if len(list_h) > 1:
|
||||
all_args.append(list(set(list_h)))
|
||||
return np.unique(np.array(all_args, dtype=object))
|
||||
|
||||
def find_contours_mean_y_diff(contours_main):
|
||||
M_main = [cv2.moments(contours_main[j]) for j in range(len(contours_main))]
|
||||
cy_main = [(M_main[j]["m01"] / (M_main[j]["m00"] + 1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main))]
|
||||
return np.mean(np.diff(np.sort(np.array(cy_main))))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_text_region_boxes_by_given_contours(contours):
|
||||
|
||||
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
|
||||
boxes = []
|
||||
contours_new = []
|
||||
for jj in range(len(contours)):
|
||||
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[jj])
|
||||
|
||||
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
|
||||
contours_new.append(contours[jj])
|
||||
|
||||
del contours
|
||||
return boxes, contours_new
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_contours_area_of_image(image, contours, hierarchy, max_area, min_area):
|
||||
found_polygons_early = list()
|
||||
|
||||
for jv,c in enumerate(contours):
|
||||
if len(c) < 3: # A polygon cannot have less than 3 points
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
polygon = geometry.Polygon([point[0] for point in c])
|
||||
area = polygon.area
|
||||
if area >= min_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]) and area <= max_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]) and hierarchy[0][jv][3] == -1: # and hierarchy[0][jv][3]==-1 :
|
||||
found_polygons_early.append(np.array([[point] for point in polygon.exterior.coords], dtype=np.uint))
|
||||
return found_polygons_early
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(image, contours, hierarchy, max_area, min_area):
|
||||
found_polygons_early = list()
|
||||
|
||||
for jv,c in enumerate(contours):
|
||||
if len(c) < 3: # A polygon cannot have less than 3 points
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
polygon = geometry.Polygon([point[0] for point in c])
|
||||
# area = cv2.contourArea(c)
|
||||
area = polygon.area
|
||||
##print(np.prod(thresh.shape[:2]))
|
||||
# Check that polygon has area greater than minimal area
|
||||
# print(hierarchy[0][jv][3],hierarchy )
|
||||
if area >= min_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]) and area <= max_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]): # and hierarchy[0][jv][3]==-1 :
|
||||
# print(c[0][0][1])
|
||||
found_polygons_early.append(np.array([[point] for point in polygon.exterior.coords], dtype=np.int32))
|
||||
return found_polygons_early
|
||||
|
||||
def find_new_features_of_contours(contours_main):
|
||||
|
||||
areas_main = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours_main[j]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
M_main = [cv2.moments(contours_main[j]) for j in range(len(contours_main))]
|
||||
cx_main = [(M_main[j]["m10"] / (M_main[j]["m00"] + 1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main))]
|
||||
cy_main = [(M_main[j]["m01"] / (M_main[j]["m00"] + 1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main))]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
x_min_main = np.array([np.min(contours_main[j][:, 0, 0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
argmin_x_main = np.array([np.argmin(contours_main[j][:, 0, 0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
x_min_from_argmin = np.array([contours_main[j][argmin_x_main[j], 0, 0] for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
y_corr_x_min_from_argmin = np.array([contours_main[j][argmin_x_main[j], 0, 1] for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
x_max_main = np.array([np.max(contours_main[j][:, 0, 0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
y_min_main = np.array([np.min(contours_main[j][:, 0, 1]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
y_max_main = np.array([np.max(contours_main[j][:, 0, 1]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
except:
|
||||
x_min_main = np.array([np.min(contours_main[j][:, 0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
argmin_x_main = np.array([np.argmin(contours_main[j][:, 0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
x_min_from_argmin = np.array([contours_main[j][argmin_x_main[j], 0] for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
y_corr_x_min_from_argmin = np.array([contours_main[j][argmin_x_main[j], 1] for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
x_max_main = np.array([np.max(contours_main[j][:, 0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
y_min_main = np.array([np.min(contours_main[j][:, 1]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
y_max_main = np.array([np.max(contours_main[j][:, 1]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
# dis_x=np.abs(x_max_main-x_min_main)
|
||||
|
||||
return cx_main, cy_main, x_min_main, x_max_main, y_min_main, y_max_main, y_corr_x_min_from_argmin
|
||||
def find_features_of_contours(contours_main):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
areas_main=np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours_main[j]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
M_main=[cv2.moments(contours_main[j]) for j in range(len(contours_main))]
|
||||
cx_main=[(M_main[j]['m10']/(M_main[j]['m00']+1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main))]
|
||||
cy_main=[(M_main[j]['m01']/(M_main[j]['m00']+1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main))]
|
||||
x_min_main=np.array([np.min(contours_main[j][:,0,0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
x_max_main=np.array([np.max(contours_main[j][:,0,0]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
y_min_main=np.array([np.min(contours_main[j][:,0,1]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
y_max_main=np.array([np.max(contours_main[j][:,0,1]) for j in range(len(contours_main))])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return y_min_main, y_max_main
|
||||
def return_parent_contours(contours, hierarchy):
|
||||
contours_parent = [contours[i] for i in range(len(contours)) if hierarchy[0][i][3] == -1]
|
||||
return contours_parent
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_interested_region(region_pre_p, pixel, min_area=0.0002):
|
||||
|
||||
# pixels of images are identified by 5
|
||||
if len(region_pre_p.shape) == 3:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :, 0] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
cnts_images = cnts_images.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
cnts_images = np.repeat(cnts_images[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(cnts_images, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs = return_parent_contours(contours_imgs, hierarchy)
|
||||
contours_imgs = filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(thresh, contours_imgs, hierarchy, max_area=1, min_area=min_area)
|
||||
|
||||
return contours_imgs
|
||||
|
||||
def do_work_of_contours_in_image(queue_of_all_params, contours_per_process, indexes_r_con_per_pro, img, slope_first):
|
||||
cnts_org_per_each_subprocess = []
|
||||
index_by_text_region_contours = []
|
||||
for mv in range(len(contours_per_process)):
|
||||
index_by_text_region_contours.append(indexes_r_con_per_pro[mv])
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[contours_per_process[mv]], color=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first)
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = img_copy.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_copy, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
cnts_org_per_each_subprocess.append(cont_int[0])
|
||||
|
||||
queue_of_all_params.put([ cnts_org_per_each_subprocess, index_by_text_region_contours])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image_multi(cnts, img, slope_first):
|
||||
|
||||
num_cores = cpu_count()
|
||||
queue_of_all_params = Queue()
|
||||
|
||||
processes = []
|
||||
nh = np.linspace(0, len(cnts), num_cores + 1)
|
||||
indexes_by_text_con = np.array(range(len(cnts)))
|
||||
for i in range(num_cores):
|
||||
contours_per_process = cnts[int(nh[i]) : int(nh[i + 1])]
|
||||
indexes_text_con_per_process = indexes_by_text_con[int(nh[i]) : int(nh[i + 1])]
|
||||
|
||||
processes.append(Process(target=do_work_of_contours_in_image, args=(queue_of_all_params, contours_per_process, indexes_text_con_per_process, img,slope_first )))
|
||||
for i in range(num_cores):
|
||||
processes[i].start()
|
||||
cnts_org = []
|
||||
all_index_text_con = []
|
||||
for i in range(num_cores):
|
||||
list_all_par = queue_of_all_params.get(True)
|
||||
contours_for_sub_process = list_all_par[0]
|
||||
indexes_for_sub_process = list_all_par[1]
|
||||
for j in range(len(contours_for_sub_process)):
|
||||
cnts_org.append(contours_for_sub_process[j])
|
||||
all_index_text_con.append(indexes_for_sub_process[j])
|
||||
for i in range(num_cores):
|
||||
processes[i].join()
|
||||
|
||||
print(all_index_text_con)
|
||||
return cnts_org
|
||||
def loop_contour_image(index_l, cnts,img, slope_first):
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[cnts[index_l]], color=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
# print(img.shape,'img')
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first)
|
||||
##print(img_copy.shape,'img_copy')
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = img_copy.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_copy, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
# print(np.shape(cont_int[0]))
|
||||
return cont_int[0]
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image_multi2(cnts, img, slope_first):
|
||||
|
||||
cnts_org = []
|
||||
# print(cnts,'cnts')
|
||||
with Pool(cpu_count()) as p:
|
||||
cnts_org = p.starmap(loop_contour_image, [(index_l,cnts, img,slope_first) for index_l in range(len(cnts))])
|
||||
|
||||
return cnts_org
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image(cnts, img, slope_first):
|
||||
|
||||
cnts_org = []
|
||||
# print(cnts,'cnts')
|
||||
for i in range(len(cnts)):
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[cnts[i]], color=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
# print(img.shape,'img')
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first)
|
||||
##print(img_copy.shape,'img_copy')
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = img_copy.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_copy, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
# print(np.shape(cont_int[0]))
|
||||
cnts_org.append(cont_int[0])
|
||||
|
||||
return cnts_org
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image_light(cnts, img, slope_first):
|
||||
|
||||
h_o = img.shape[0]
|
||||
w_o = img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(img.shape[1]/3.), int(img.shape[0]/3.)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
##cnts = list( (np.array(cnts)/2).astype(np.int16) )
|
||||
#cnts = cnts/2
|
||||
cnts = [(i/ 3).astype(np.int32) for i in cnts]
|
||||
cnts_org = []
|
||||
#print(cnts,'cnts')
|
||||
for i in range(len(cnts)):
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[cnts[i]], color=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
# print(img.shape,'img')
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first)
|
||||
##print(img_copy.shape,'img_copy')
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = img_copy.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_copy, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
# print(np.shape(cont_int[0]))
|
||||
cnts_org.append(cont_int[0]*3)
|
||||
|
||||
return cnts_org
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_interested_textline(region_pre_p, pixel):
|
||||
|
||||
# pixels of images are identified by 5
|
||||
if len(region_pre_p.shape) == 3:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :, 0] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
cnts_images = cnts_images.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
cnts_images = np.repeat(cnts_images[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(cnts_images, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
contours_imgs, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs = return_parent_contours(contours_imgs, hierarchy)
|
||||
contours_imgs = filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(thresh, contours_imgs, hierarchy, max_area=1, min_area=0.000000003)
|
||||
return contours_imgs
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_image(image):
|
||||
|
||||
if len(image.shape) == 2:
|
||||
image = np.repeat(image[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
image = image.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image = image.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
return contours, hierarchy
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_interested_region_by_min_size(region_pre_p, pixel, min_size=0.00003):
|
||||
|
||||
# pixels of images are identified by 5
|
||||
if len(region_pre_p.shape) == 3:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :, 0] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
cnts_images = cnts_images.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
cnts_images = np.repeat(cnts_images[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(cnts_images, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs = return_parent_contours(contours_imgs, hierarchy)
|
||||
contours_imgs = filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(thresh, contours_imgs, hierarchy, max_area=1, min_area=min_size)
|
||||
|
||||
return contours_imgs
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_interested_region_by_size(region_pre_p, pixel, min_area, max_area):
|
||||
|
||||
# pixels of images are identified by 5
|
||||
if len(region_pre_p.shape) == 3:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :, 0] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :] == pixel) * 1
|
||||
cnts_images = cnts_images.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
cnts_images = np.repeat(cnts_images[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(cnts_images, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
contours_imgs, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs = return_parent_contours(contours_imgs, hierarchy)
|
||||
contours_imgs = filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(thresh, contours_imgs, hierarchy, max_area=max_area, min_area=min_area)
|
||||
|
||||
img_ret = np.zeros((region_pre_p.shape[0], region_pre_p.shape[1], 3))
|
||||
img_ret = cv2.fillPoly(img_ret, pts=contours_imgs, color=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
return img_ret[:, :, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ from collections import Counter
|
|||
REGION_ID_TEMPLATE = 'region_%04d'
|
||||
LINE_ID_TEMPLATE = 'region_%04d_line_%04d'
|
||||
|
||||
class EynollahIdCounter:
|
||||
class EynollahIdCounter():
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, region_idx=0, line_idx=0):
|
||||
self._counter = Counter()
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
|
|||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from .contour import (
|
||||
find_center_of_contours,
|
||||
find_new_features_of_contours,
|
||||
return_contours_of_image,
|
||||
return_parent_contours,
|
||||
return_contours_of_interested_region,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,12 +17,11 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
all_found_textline_polygons_h,
|
||||
kernel=None,
|
||||
curved_line=False,
|
||||
textline_light=False,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# print(np.shape(all_found_textline_polygons),np.shape(all_found_textline_polygons[3]),'all_found_textline_polygonsshape')
|
||||
# print(all_found_textline_polygons[3])
|
||||
cx_m, cy_m = find_center_of_contours(contours_only_text_parent)
|
||||
cx_h, cy_h = find_center_of_contours(contours_only_text_parent_h)
|
||||
cx_m, cy_m, _, _, _, _, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(contours_only_text_parent)
|
||||
cx_h, cy_h, _, _, _, _, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(contours_only_text_parent_h)
|
||||
cx_d, cy_d, _, _, y_min_d, y_max_d, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(polygons_of_drop_capitals)
|
||||
|
||||
img_con_all = np.zeros((text_regions_p.shape[0], text_regions_p.shape[1], 3))
|
||||
|
|
@ -79,7 +76,7 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
# region_with_intersected_drop=region_with_intersected_drop/3
|
||||
region_with_intersected_drop = region_with_intersected_drop.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
# print(np.unique(img_con_all_copy[:,:,0]))
|
||||
if curved_line or textline_light:
|
||||
if curved_line:
|
||||
|
||||
if len(region_with_intersected_drop) > 1:
|
||||
sum_pixels_of_intersection = []
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,9 +87,9 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
region_final = region_with_intersected_drop[np.argmax(sum_pixels_of_intersection)] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# print(region_final,'region_final')
|
||||
# cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# cx_t,cy_t ,_, _, _ ,_,_= find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t, _, _, _, _, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# print(all_box_coord[j_cont])
|
||||
# print(cx_t)
|
||||
# print(cy_t)
|
||||
|
|
@ -117,17 +114,12 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
img_textlines = cv2.fillPoly(img_textlines, pts=[polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop]], color=(255, 255, 255))
|
||||
|
||||
img_textlines = img_textlines.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_combined = return_contours_of_interested_region(img_textlines, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
#plt.imshow(img_textlines)
|
||||
#plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
#imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
#ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
#contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
# print(len(contours_combined),'len textlines mixed')
|
||||
areas_cnt_text = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours_combined[j]) for j in range(len(contours_combined))])
|
||||
|
||||
contours_biggest = contours_combined[np.argmax(areas_cnt_text)]
|
||||
|
|
@ -138,13 +130,8 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
# contours_biggest[:,0,1]=contours_biggest[:,0,1]#-all_box_coord[int(region_final)][0]
|
||||
|
||||
# contours_biggest=contours_biggest.reshape(np.shape(contours_biggest)[0],np.shape(contours_biggest)[2])
|
||||
|
||||
if len(contours_combined)==1:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
elif len(contours_combined)==2:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)].insert(arg_min, polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop] )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
|
||||
except:
|
||||
# print('gordun1')
|
||||
|
|
@ -154,9 +141,9 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
|
||||
# areas_main=np.array([cv2.contourArea(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][0][j] ) for j in range(len(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)]))])
|
||||
|
||||
# cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# cx_t,cy_t ,_, _, _ ,_,_= find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t, _, _, _, _, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# print(all_box_coord[j_cont])
|
||||
# print(cx_t)
|
||||
# print(cy_t)
|
||||
|
|
@ -180,13 +167,14 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
|
||||
img_textlines = img_textlines.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
contours_combined = return_contours_of_interested_region(img_textlines, 255, 0)
|
||||
##imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
##ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_textlines)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
##contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
# print(len(contours_combined),'len textlines mixed')
|
||||
areas_cnt_text = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours_combined[j]) for j in range(len(contours_combined))])
|
||||
|
||||
contours_biggest = contours_combined[np.argmax(areas_cnt_text)]
|
||||
|
|
@ -198,18 +186,13 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
# print(np.shape(contours_biggest),'contours_biggest')
|
||||
# print(np.shape(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min]))
|
||||
##contours_biggest=contours_biggest.reshape(np.shape(contours_biggest)[0],np.shape(contours_biggest)[2])
|
||||
if len(contours_combined)==1:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
elif len(contours_combined)==2:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)].insert(arg_min, polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop] )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# print(all_found_textline_polygons[j_cont][0])
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t, _, _, _, _, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# print(all_box_coord[j_cont])
|
||||
# print(cx_t)
|
||||
# print(cy_t)
|
||||
|
|
@ -232,11 +215,10 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
img_textlines = cv2.fillPoly(img_textlines, pts=[polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop]], color=(255, 255, 255))
|
||||
|
||||
img_textlines = img_textlines.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
contours_combined = return_contours_of_interested_region(img_textlines, 255, 0)
|
||||
#imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
#ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
#contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
# print(len(contours_combined),'len textlines mixed')
|
||||
areas_cnt_text = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours_combined[j]) for j in range(len(contours_combined))])
|
||||
|
|
@ -249,12 +231,7 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
contours_biggest[:, 0, 1] = contours_biggest[:, 0, 1] # -all_box_coord[int(region_final)][0]
|
||||
|
||||
##contours_biggest=contours_biggest.reshape(np.shape(contours_biggest)[0],np.shape(contours_biggest)[2])
|
||||
if len(contours_combined)==1:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
elif len(contours_combined)==2:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)].insert(arg_min, polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop] )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
# all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min]=contours_biggest
|
||||
|
||||
except:
|
||||
|
|
@ -262,7 +239,7 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
##cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
##cx_t,cy_t ,_, _, _ ,_,_= find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
###print(all_box_coord[j_cont])
|
||||
###print(cx_t)
|
||||
###print(cy_t)
|
||||
|
|
@ -316,9 +293,9 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
region_final = region_with_intersected_drop[np.argmax(sum_pixels_of_intersection)] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# print(region_final,'region_final')
|
||||
# cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# cx_t,cy_t ,_, _, _ ,_,_= find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t, _, _, _, _, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# print(all_box_coord[j_cont])
|
||||
# print(cx_t)
|
||||
# print(cy_t)
|
||||
|
|
@ -343,12 +320,10 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
img_textlines = cv2.fillPoly(img_textlines, pts=[polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop]], color=(255, 255, 255))
|
||||
|
||||
img_textlines = img_textlines.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
contours_combined = return_contours_of_interested_region(img_textlines, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
#imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
#ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
#contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
# print(len(contours_combined),'len textlines mixed')
|
||||
areas_cnt_text = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours_combined[j]) for j in range(len(contours_combined))])
|
||||
|
|
@ -361,12 +336,8 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
contours_biggest[:, 0, 1] = contours_biggest[:, 0, 1] - all_box_coord[int(region_final)][0]
|
||||
|
||||
contours_biggest = contours_biggest.reshape(np.shape(contours_biggest)[0], np.shape(contours_biggest)[2])
|
||||
if len(contours_combined)==1:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
elif len(contours_combined)==2:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)].insert(arg_min, polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop] )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
|
||||
except:
|
||||
# print('gordun1')
|
||||
|
|
@ -376,12 +347,12 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
|
||||
# areas_main=np.array([cv2.contourArea(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][0][j] ) for j in range(len(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)]))])
|
||||
|
||||
# cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# cx_t,cy_t ,_, _, _ ,_,_= find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
|
||||
# print(cx_t,'print')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# print(all_found_textline_polygons[j_cont][0])
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
cx_t, cy_t, _, _, _, _, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)])
|
||||
# print(all_box_coord[j_cont])
|
||||
# print(cx_t)
|
||||
# print(cy_t)
|
||||
|
|
@ -404,12 +375,10 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
img_textlines = cv2.fillPoly(img_textlines, pts=[polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop]], color=(255, 255, 255))
|
||||
|
||||
img_textlines = img_textlines.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
contours_combined = return_contours_of_interested_region(img_textlines, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
#imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
#ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_textlines, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
#contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
contours_combined, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
# print(len(contours_combined),'len textlines mixed')
|
||||
areas_cnt_text = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours_combined[j]) for j in range(len(contours_combined))])
|
||||
|
|
@ -422,12 +391,7 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
contours_biggest[:, 0, 1] = contours_biggest[:, 0, 1] - all_box_coord[int(region_final)][0]
|
||||
|
||||
contours_biggest = contours_biggest.reshape(np.shape(contours_biggest)[0], np.shape(contours_biggest)[2])
|
||||
if len(contours_combined)==1:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
elif len(contours_combined)==2:
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)].insert(arg_min, polygons_of_drop_capitals[i_drop] )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min] = contours_biggest
|
||||
# all_found_textline_polygons[int(region_final)][arg_min]=contours_biggest
|
||||
|
||||
except:
|
||||
|
|
@ -454,7 +418,7 @@ def adhere_drop_capital_region_into_corresponding_textline(
|
|||
#####try:
|
||||
#####if len(contours_new_parent)==1:
|
||||
######print(all_found_textline_polygons[j_cont][0])
|
||||
#####cx_t, cy_t = find_center_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[j_cont])
|
||||
#####cx_t,cy_t ,_, _, _ ,_,_= find_new_features_of_contours(all_found_textline_polygons[j_cont])
|
||||
######print(all_box_coord[j_cont])
|
||||
######print(cx_t)
|
||||
######print(cy_t)
|
||||
|
|
@ -2,14 +2,17 @@ import numpy as np
|
|||
import cv2
|
||||
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
|
||||
from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter1d
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from .contour import find_new_features_of_contours, return_contours_of_interested_region
|
||||
from .resize import resize_image
|
||||
from .rotate import rotate_image
|
||||
|
||||
def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, light_version=False, kernel=None):
|
||||
def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, kernel=None):
|
||||
mask_marginals=np.zeros((text_with_lines.shape[0],text_with_lines.shape[1]))
|
||||
mask_marginals=mask_marginals.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
text_with_lines=text_with_lines.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
##text_with_lines=cv2.erode(text_with_lines,self.kernel,iterations=3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,12 +28,8 @@ def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, light_ve
|
|||
text_with_lines=resize_image(text_with_lines,int(text_with_lines.shape[0]*1.8),text_with_lines.shape[1])
|
||||
text_with_lines=cv2.erode(text_with_lines,kernel,iterations=7)
|
||||
text_with_lines=resize_image(text_with_lines,text_with_lines_eroded.shape[0],text_with_lines_eroded.shape[1])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if light_version:
|
||||
kernel_hor = np.ones((1, 5), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
text_with_lines = cv2.erode(text_with_lines,kernel_hor,iterations=6)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
text_with_lines_y=text_with_lines.sum(axis=0)
|
||||
text_with_lines_y_eroded=text_with_lines_eroded.sum(axis=0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -43,23 +42,34 @@ def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, light_ve
|
|||
elif thickness_along_y_percent>=30 and thickness_along_y_percent<50:
|
||||
min_textline_thickness=20
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if light_version:
|
||||
min_textline_thickness=45
|
||||
else:
|
||||
min_textline_thickness=40
|
||||
min_textline_thickness=40
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if thickness_along_y_percent>=14:
|
||||
|
||||
text_with_lines_y_rev=-1*text_with_lines_y[:]
|
||||
#print(text_with_lines_y)
|
||||
#print(text_with_lines_y_rev)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#plt.plot(text_with_lines_y)
|
||||
#plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
text_with_lines_y_rev=text_with_lines_y_rev-np.min(text_with_lines_y_rev)
|
||||
|
||||
#plt.plot(text_with_lines_y_rev)
|
||||
#plt.show()
|
||||
sigma_gaus=1
|
||||
region_sum_0= gaussian_filter1d(text_with_lines_y, sigma_gaus)
|
||||
|
||||
region_sum_0_rev=gaussian_filter1d(text_with_lines_y_rev, sigma_gaus)
|
||||
|
||||
#plt.plot(region_sum_0_rev)
|
||||
#plt.show()
|
||||
region_sum_0_updown=region_sum_0[len(region_sum_0)::-1]
|
||||
|
||||
first_nonzero=(next((i for i, x in enumerate(region_sum_0) if x), None))
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,18 +78,44 @@ def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, light_ve
|
|||
|
||||
last_nonzero=len(region_sum_0)-last_nonzero
|
||||
|
||||
##img_sum_0_smooth_rev=-region_sum_0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
mid_point=(last_nonzero+first_nonzero)/2.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
one_third_right=(last_nonzero-mid_point)/3.0
|
||||
one_third_left=(mid_point-first_nonzero)/3.0
|
||||
|
||||
peaks, _ = find_peaks(text_with_lines_y_rev, height=0)
|
||||
peaks=np.array(peaks)
|
||||
peaks=peaks[(peaks>first_nonzero) & (peaks < last_nonzero)]
|
||||
peaks=peaks[region_sum_0[peaks]<min_textline_thickness ]
|
||||
#img_sum_0_smooth_rev=img_sum_0_smooth_rev-np.min(img_sum_0_smooth_rev)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
peaks, _ = find_peaks(text_with_lines_y_rev, height=0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
peaks=np.array(peaks)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#print(region_sum_0[peaks])
|
||||
##plt.plot(region_sum_0)
|
||||
##plt.plot(peaks,region_sum_0[peaks],'*')
|
||||
##plt.show()
|
||||
#print(first_nonzero,last_nonzero,peaks)
|
||||
peaks=peaks[(peaks>first_nonzero) & ((peaks<last_nonzero))]
|
||||
|
||||
#print(first_nonzero,last_nonzero,peaks)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#print(region_sum_0[peaks]<10)
|
||||
####peaks=peaks[region_sum_0[peaks]<25 ]
|
||||
|
||||
#print(region_sum_0[peaks])
|
||||
peaks=peaks[region_sum_0[peaks]<min_textline_thickness ]
|
||||
#print(peaks)
|
||||
#print(first_nonzero,last_nonzero,one_third_right,one_third_left)
|
||||
|
||||
if num_col==1:
|
||||
peaks_right=peaks[peaks>mid_point]
|
||||
peaks_left=peaks[peaks<mid_point]
|
||||
|
|
@ -99,10 +135,11 @@ def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, light_ve
|
|||
except:
|
||||
point_left=first_nonzero
|
||||
|
||||
if point_left == first_nonzero and point_right == last_nonzero:
|
||||
return text_regions
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#print(point_left,point_right)
|
||||
#print(text_regions.shape)
|
||||
if point_right>=mask_marginals.shape[1]:
|
||||
point_right=mask_marginals.shape[1]-1
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,8 +148,10 @@ def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, light_ve
|
|||
except:
|
||||
mask_marginals[:,:]=1
|
||||
|
||||
#print(mask_marginals.shape,point_left,point_right,'nadosh')
|
||||
mask_marginals_rotated=rotate_image(mask_marginals,-slope_deskew)
|
||||
|
||||
#print(mask_marginals_rotated.shape,'nadosh')
|
||||
mask_marginals_rotated_sum=mask_marginals_rotated.sum(axis=0)
|
||||
|
||||
mask_marginals_rotated_sum[mask_marginals_rotated_sum!=0]=1
|
||||
|
|
@ -128,92 +167,73 @@ def get_marginals(text_with_lines, text_regions, num_col, slope_deskew, light_ve
|
|||
if max_point_of_right_marginal>=text_regions.shape[1]:
|
||||
max_point_of_right_marginal=text_regions.shape[1]-1
|
||||
|
||||
if light_version:
|
||||
text_regions_org = np.copy(text_regions)
|
||||
text_regions[text_regions[:,:]==1]=4
|
||||
|
||||
pixel_img=4
|
||||
min_area_text=0.00001
|
||||
|
||||
polygon_mask_marginals_rotated = return_contours_of_interested_region(mask_marginals,1,min_area_text)
|
||||
|
||||
polygon_mask_marginals_rotated = polygon_mask_marginals_rotated[0]
|
||||
|
||||
polygons_of_marginals=return_contours_of_interested_region(text_regions,pixel_img,min_area_text)
|
||||
#print(np.min(index_x_interest) ,np.max(index_x_interest),'minmaxnew')
|
||||
#print(mask_marginals_rotated.shape,text_regions.shape,'mask_marginals_rotated')
|
||||
#plt.imshow(mask_marginals)
|
||||
#plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
cx_text_only,cy_text_only ,x_min_text_only,x_max_text_only, y_min_text_only ,y_max_text_only,y_cor_x_min_main=find_new_features_of_contours(polygons_of_marginals)
|
||||
#plt.imshow(mask_marginals_rotated)
|
||||
#plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions[(text_regions[:,:]==4)]=1
|
||||
text_regions[(mask_marginals_rotated[:,:]!=1) & (text_regions[:,:]==1)]=4
|
||||
|
||||
marginlas_should_be_main_text=[]
|
||||
#plt.imshow(text_regions)
|
||||
#plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left=[]
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right=[]
|
||||
pixel_img=4
|
||||
min_area_text=0.00001
|
||||
polygons_of_marginals=return_contours_of_interested_region(text_regions,pixel_img,min_area_text)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(len(cx_text_only)):
|
||||
results = cv2.pointPolygonTest(polygon_mask_marginals_rotated, (cx_text_only[i], cy_text_only[i]), False)
|
||||
cx_text_only,cy_text_only ,x_min_text_only,x_max_text_only, y_min_text_only ,y_max_text_only,y_cor_x_min_main=find_new_features_of_contours(polygons_of_marginals)
|
||||
|
||||
if results == -1:
|
||||
marginlas_should_be_main_text.append(polygons_of_marginals[i])
|
||||
text_regions[(text_regions[:,:]==4)]=1
|
||||
|
||||
marginlas_should_be_main_text=[]
|
||||
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left=[]
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right=[]
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions_org=cv2.fillPoly(text_regions_org, pts =marginlas_should_be_main_text, color=(4,4))
|
||||
text_regions = np.copy(text_regions_org)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(len(cx_text_only)):
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions[(mask_marginals_rotated[:,:]!=1) & (text_regions[:,:]==1)]=4
|
||||
|
||||
pixel_img=4
|
||||
min_area_text=0.00001
|
||||
|
||||
polygons_of_marginals=return_contours_of_interested_region(text_regions,pixel_img,min_area_text)
|
||||
|
||||
cx_text_only,cy_text_only ,x_min_text_only,x_max_text_only, y_min_text_only ,y_max_text_only,y_cor_x_min_main=find_new_features_of_contours(polygons_of_marginals)
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions[(text_regions[:,:]==4)]=1
|
||||
|
||||
marginlas_should_be_main_text=[]
|
||||
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left=[]
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right=[]
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(len(cx_text_only)):
|
||||
x_width_mar=abs(x_min_text_only[i]-x_max_text_only[i])
|
||||
y_height_mar=abs(y_min_text_only[i]-y_max_text_only[i])
|
||||
|
||||
if x_width_mar>16 and y_height_mar/x_width_mar<18:
|
||||
marginlas_should_be_main_text.append(polygons_of_marginals[i])
|
||||
if x_min_text_only[i]<(mid_point-one_third_left):
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left_new=x_min_text_only[i]
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_left)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left.append(x_min_marginals_left_new)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left[0]=min(x_min_marginals_left[0],x_min_marginals_left_new)
|
||||
x_width_mar=abs(x_min_text_only[i]-x_max_text_only[i])
|
||||
y_height_mar=abs(y_min_text_only[i]-y_max_text_only[i])
|
||||
#print(x_width_mar,y_height_mar,y_height_mar/x_width_mar,'y_height_mar')
|
||||
if x_width_mar>16 and y_height_mar/x_width_mar<18:
|
||||
marginlas_should_be_main_text.append(polygons_of_marginals[i])
|
||||
if x_min_text_only[i]<(mid_point-one_third_left):
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left_new=x_min_text_only[i]
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_left)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left.append(x_min_marginals_left_new)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right_new=x_min_text_only[i]
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_right)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right.append(x_min_marginals_right_new)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right[0]=min(x_min_marginals_right[0],x_min_marginals_right_new)
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left[0]=min(x_min_marginals_left[0],x_min_marginals_left_new)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right_new=x_min_text_only[i]
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_right)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right.append(x_min_marginals_right_new)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right[0]=min(x_min_marginals_right[0],x_min_marginals_right_new)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_left)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left=[0]
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_right)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right=[text_regions.shape[1]-1]
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_left)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_left=[0]
|
||||
if len(x_min_marginals_right)==0:
|
||||
x_min_marginals_right=[text_regions.shape[1]-1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions=cv2.fillPoly(text_regions, pts =marginlas_should_be_main_text, color=(4,4))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#text_regions[:,:int(x_min_marginals_left[0])][text_regions[:,:int(x_min_marginals_left[0])]==1]=0
|
||||
#text_regions[:,int(x_min_marginals_right[0]):][text_regions[:,int(x_min_marginals_right[0]):]==1]=0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions[:,:int(min_point_of_left_marginal)][text_regions[:,:int(min_point_of_left_marginal)]==1]=0
|
||||
text_regions[:,int(max_point_of_right_marginal):][text_regions[:,int(max_point_of_right_marginal):]==1]=0
|
||||
#print(x_min_marginals_left[0],x_min_marginals_right[0],'margo')
|
||||
|
||||
#print(marginlas_should_be_main_text,'marginlas_should_be_main_text')
|
||||
text_regions=cv2.fillPoly(text_regions, pts =marginlas_should_be_main_text, color=(4,4))
|
||||
|
||||
#print(np.unique(text_regions))
|
||||
|
||||
#text_regions[:,:int(x_min_marginals_left[0])][text_regions[:,:int(x_min_marginals_left[0])]==1]=0
|
||||
#text_regions[:,int(x_min_marginals_right[0]):][text_regions[:,int(x_min_marginals_right[0]):]==1]=0
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions[:,:int(min_point_of_left_marginal)][text_regions[:,:int(min_point_of_left_marginal)]==1]=0
|
||||
text_regions[:,int(max_point_of_right_marginal):][text_regions[:,int(max_point_of_right_marginal):]==1]=0
|
||||
|
||||
###text_regions[:,0:point_left][text_regions[:,0:point_left]==1]=4
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
|||
from contextlib import nullcontext
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from ocrd_models import OcrdExif
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,13 +17,12 @@ def pil2cv(img):
|
|||
def check_dpi(img):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if isinstance(img, Image.Image):
|
||||
pil_image = nullcontext(img)
|
||||
pil_image = img
|
||||
elif isinstance(img, str):
|
||||
pil_image = Image.open(img)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pil_image = nullcontext(cv2pil(img))
|
||||
with pil_image:
|
||||
exif = OcrdExif(pil_image)
|
||||
pil_image = cv2pil(img)
|
||||
exif = OcrdExif(pil_image)
|
||||
resolution = exif.resolution
|
||||
if resolution == 1:
|
||||
raise Exception()
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
|
|||
import math
|
||||
|
||||
import imutils
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
def rotatedRectWithMaxArea(w, h, angle):
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,14 +35,14 @@ def rotate_max_area_new(image, rotated, angle):
|
|||
return rotated[y1:y2, x1:x2]
|
||||
|
||||
def rotation_image_new(img, thetha):
|
||||
rotated = rotate_image(img, thetha)
|
||||
rotated = imutils.rotate(img, thetha)
|
||||
return rotate_max_area_new(img, rotated, thetha)
|
||||
|
||||
def rotate_image(img_patch, slope):
|
||||
(h, w) = img_patch.shape[:2]
|
||||
center = (w // 2, h // 2)
|
||||
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, slope, 1.0)
|
||||
return cv2.warpAffine(img_patch, M, (w, h) )
|
||||
return cv2.warpAffine(img_patch, M, (w, h), flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
|
||||
|
||||
def rotate_image_different( img, slope):
|
||||
# img = cv2.imread('images/input.jpg')
|
||||
|
|
@ -60,17 +62,17 @@ def rotate_max_area(image, rotated, rotated_textline, rotated_layout, rotated_ta
|
|||
return rotated[y1:y2, x1:x2], rotated_textline[y1:y2, x1:x2], rotated_layout[y1:y2, x1:x2], rotated_table_prediction[y1:y2, x1:x2]
|
||||
|
||||
def rotation_not_90_func(img, textline, text_regions_p_1, table_prediction, thetha):
|
||||
rotated = rotate_image(img, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_textline = rotate_image(textline, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_layout = rotate_image(text_regions_p_1, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_table_prediction = rotate_image(table_prediction, thetha)
|
||||
rotated = imutils.rotate(img, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_textline = imutils.rotate(textline, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_layout = imutils.rotate(text_regions_p_1, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_table_prediction = imutils.rotate(table_prediction, thetha)
|
||||
return rotate_max_area(img, rotated, rotated_textline, rotated_layout, rotated_table_prediction, thetha)
|
||||
|
||||
def rotation_not_90_func_full_layout(img, textline, text_regions_p_1, text_regions_p_fully, thetha):
|
||||
rotated = rotate_image(img, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_textline = rotate_image(textline, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_layout = rotate_image(text_regions_p_1, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_layout_full = rotate_image(text_regions_p_fully, thetha)
|
||||
rotated = imutils.rotate(img, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_textline = imutils.rotate(textline, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_layout = imutils.rotate(text_regions_p_1, thetha)
|
||||
rotated_layout_full = imutils.rotate(text_regions_p_fully, thetha)
|
||||
return rotate_max_area_full_layout(img, rotated, rotated_textline, rotated_layout, rotated_layout_full, thetha)
|
||||
|
||||
def rotate_max_area_full_layout(image, rotated, rotated_textline, rotated_layout, rotated_layout_full, angle):
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
|
|
@ -46,26 +46,24 @@ def create_page_xml(imageFilename, height, width):
|
|||
))
|
||||
return pcgts
|
||||
|
||||
def xml_reading_order(page, order_of_texts, id_of_marginalia_left, id_of_marginalia_right):
|
||||
def xml_reading_order(page, order_of_texts, id_of_marginalia):
|
||||
region_order = ReadingOrderType()
|
||||
og = OrderedGroupType(id="ro357564684568544579089")
|
||||
page.set_ReadingOrder(region_order)
|
||||
region_order.set_OrderedGroup(og)
|
||||
region_counter = EynollahIdCounter()
|
||||
|
||||
for id_marginal in id_of_marginalia_left:
|
||||
og.add_RegionRefIndexed(RegionRefIndexedType(index=str(region_counter.get('region')), regionRef=id_marginal))
|
||||
for idx_textregion, _ in enumerate(order_of_texts):
|
||||
og.add_RegionRefIndexed(RegionRefIndexedType(index=str(region_counter.get('region')), regionRef=region_counter.region_id(order_of_texts[idx_textregion] + 1)))
|
||||
region_counter.inc('region')
|
||||
|
||||
for idx_textregion in order_of_texts:
|
||||
og.add_RegionRefIndexed(RegionRefIndexedType(index=str(region_counter.get('region')), regionRef=region_counter.region_id(idx_textregion + 1)))
|
||||
region_counter.inc('region')
|
||||
|
||||
for id_marginal in id_of_marginalia_right:
|
||||
for id_marginal in id_of_marginalia:
|
||||
og.add_RegionRefIndexed(RegionRefIndexedType(index=str(region_counter.get('region')), regionRef=id_marginal))
|
||||
region_counter.inc('region')
|
||||
|
||||
def order_and_id_of_texts(found_polygons_text_region, found_polygons_text_region_h, indexes_sorted, index_of_types, kind_of_texts, ref_point):
|
||||
def order_and_id_of_texts(found_polygons_text_region, found_polygons_text_region_h, matrix_of_orders, indexes_sorted, index_of_types, kind_of_texts, ref_point):
|
||||
indexes_sorted = np.array(indexes_sorted)
|
||||
index_of_types = np.array(index_of_types)
|
||||
kind_of_texts = np.array(kind_of_texts)
|
||||
|
||||
id_of_texts = []
|
||||
order_of_texts = []
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -74,7 +72,7 @@ def order_and_id_of_texts(found_polygons_text_region, found_polygons_text_region
|
|||
|
||||
index_of_types_2 = index_of_types[kind_of_texts == 2]
|
||||
indexes_sorted_2 = indexes_sorted[kind_of_texts == 2]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
counter = EynollahIdCounter(region_idx=ref_point)
|
||||
for idx_textregion, _ in enumerate(found_polygons_text_region):
|
||||
id_of_texts.append(counter.next_region_id)
|
||||
265
qurator/eynollah/writer.py
Normal file
265
qurator/eynollah/writer.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,265 @@
|
|||
# pylint: disable=too-many-locals,wrong-import-position,too-many-lines,too-many-statements,chained-comparison,fixme,broad-except,c-extension-no-member
|
||||
# pylint: disable=import-error
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
import os.path
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils.xml import create_page_xml, xml_reading_order
|
||||
from .utils.counter import EynollahIdCounter
|
||||
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import getLogger
|
||||
from ocrd_models.ocrd_page import (
|
||||
BorderType,
|
||||
CoordsType,
|
||||
PcGtsType,
|
||||
TextLineType,
|
||||
TextRegionType,
|
||||
ImageRegionType,
|
||||
TableRegionType,
|
||||
SeparatorRegionType,
|
||||
to_xml
|
||||
)
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
class EynollahXmlWriter():
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *, dir_out, image_filename, curved_line,textline_light, pcgts=None):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger('eynollah.writer')
|
||||
self.counter = EynollahIdCounter()
|
||||
self.dir_out = dir_out
|
||||
self.image_filename = image_filename
|
||||
self.curved_line = curved_line
|
||||
self.textline_light = textline_light
|
||||
self.pcgts = pcgts
|
||||
self.scale_x = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
self.scale_y = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
self.height_org = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
self.width_org = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def image_filename_stem(self):
|
||||
return Path(Path(self.image_filename).name).stem
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_page_coords(self, cont_page):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter calculate_page_coords')
|
||||
points_page_print = ""
|
||||
for _, contour in enumerate(cont_page[0]):
|
||||
if len(contour) == 2:
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[0]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_page_print += ','
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[1]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[0][0]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_page_print += ','
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[0][1] ) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_page_print = points_page_print + ' '
|
||||
return points_page_print[:-1]
|
||||
|
||||
def serialize_lines_in_marginal(self, marginal_region, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals, marginal_idx, page_coord, all_box_coord_marginals, slopes_marginals, counter):
|
||||
for j in range(len(all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx])):
|
||||
coords = CoordsType()
|
||||
textline = TextLineType(id=counter.next_line_id, Coords=coords)
|
||||
marginal_region.add_TextLine(textline)
|
||||
points_co = ''
|
||||
for l in range(len(all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j])):
|
||||
if not (self.curved_line or self.textline_light):
|
||||
if len(all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l]) == 2:
|
||||
textline_x_coord = max(0, int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][2] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x) )
|
||||
textline_y_coord = max(0, int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][1] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][0] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y) )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
textline_x_coord = max(0, int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0][0] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][2] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x) )
|
||||
textline_y_coord = max(0, int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0][1] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][0] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y) )
|
||||
points_co += str(textline_x_coord)
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(textline_y_coord)
|
||||
if (self.curved_line or self.textline_light) and np.abs(slopes_marginals[marginal_idx]) <= 45:
|
||||
if len(all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l]) == 2:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][1] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0][0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0][1] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
|
||||
elif (self.curved_line or self.textline_light) and np.abs(slopes_marginals[marginal_idx]) > 45:
|
||||
if len(all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l]) == 2:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][2] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][1] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][0] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0][0] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][2] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((all_found_textline_polygons_marginals[marginal_idx][j][l][0][1] + all_box_coord_marginals[marginal_idx][0] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_co += ' '
|
||||
coords.set_points(points_co[:-1])
|
||||
|
||||
def serialize_lines_in_region(self, text_region, all_found_textline_polygons, region_idx, page_coord, all_box_coord, slopes, counter):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter serialize_lines_in_region')
|
||||
for j in range(len(all_found_textline_polygons[region_idx])):
|
||||
coords = CoordsType()
|
||||
textline = TextLineType(id=counter.next_line_id, Coords=coords)
|
||||
text_region.add_TextLine(textline)
|
||||
region_bboxes = all_box_coord[region_idx]
|
||||
points_co = ''
|
||||
for idx_contour_textline, contour_textline in enumerate(all_found_textline_polygons[region_idx][j]):
|
||||
if not (self.curved_line or self.textline_light):
|
||||
if len(contour_textline) == 2:
|
||||
textline_x_coord = max(0, int((contour_textline[0] + region_bboxes[2] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
textline_y_coord = max(0, int((contour_textline[1] + region_bboxes[0] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
textline_x_coord = max(0, int((contour_textline[0][0] + region_bboxes[2] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
textline_y_coord = max(0, int((contour_textline[0][1] + region_bboxes[0] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_co += str(textline_x_coord)
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(textline_y_coord)
|
||||
|
||||
if (self.curved_line or self.textline_light) and np.abs(slopes[region_idx]) <= 45:
|
||||
if len(contour_textline) == 2:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[1] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[0][0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[0][1] + page_coord[0])/self.scale_y))
|
||||
elif (self.curved_line or self.textline_light) and np.abs(slopes[region_idx]) > 45:
|
||||
if len(contour_textline)==2:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[0] + region_bboxes[2] + page_coord[2])/self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[1] + region_bboxes[0] + page_coord[0])/self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[0][0] + region_bboxes[2]+page_coord[2])/self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((contour_textline[0][1] + region_bboxes[0]+page_coord[0])/self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_co += ' '
|
||||
coords.set_points(points_co[:-1])
|
||||
|
||||
def write_pagexml(self, pcgts):
|
||||
out_fname = os.path.join(self.dir_out, self.image_filename_stem) + ".xml"
|
||||
self.logger.info("output filename: '%s'", out_fname)
|
||||
with open(out_fname, 'w') as f:
|
||||
f.write(to_xml(pcgts))
|
||||
|
||||
def build_pagexml_no_full_layout(self, found_polygons_text_region, page_coord, order_of_texts, id_of_texts, all_found_textline_polygons, all_box_coord, found_polygons_text_region_img, found_polygons_marginals, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals, all_box_coord_marginals, slopes, slopes_marginals, cont_page, polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml, found_polygons_tables):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter build_pagexml_no_full_layout')
|
||||
|
||||
# create the file structure
|
||||
pcgts = self.pcgts if self.pcgts else create_page_xml(self.image_filename, self.height_org, self.width_org)
|
||||
page = pcgts.get_Page()
|
||||
page.set_Border(BorderType(Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_page_coords(cont_page))))
|
||||
|
||||
counter = EynollahIdCounter()
|
||||
if len(found_polygons_text_region) > 0:
|
||||
_counter_marginals = EynollahIdCounter(region_idx=len(order_of_texts))
|
||||
id_of_marginalia = [_counter_marginals.next_region_id for _ in found_polygons_marginals]
|
||||
xml_reading_order(page, order_of_texts, id_of_marginalia)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_text_region)):
|
||||
textregion = TextRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, type_='paragraph',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_text_region[mm], page_coord)),
|
||||
)
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(textregion)
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(textregion, all_found_textline_polygons, mm, page_coord, all_box_coord, slopes, counter)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_marginals)):
|
||||
marginal = TextRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, type_='marginalia',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_marginals[mm], page_coord)))
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(marginal)
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_marginal(marginal, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals, mm, page_coord, all_box_coord_marginals, slopes_marginals, counter)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_text_region_img)):
|
||||
img_region = ImageRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, Coords=CoordsType())
|
||||
page.add_ImageRegion(img_region)
|
||||
points_co = ''
|
||||
for lmm in range(len(found_polygons_text_region_img[mm])):
|
||||
points_co += str(int((found_polygons_text_region_img[mm][lmm,0,0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((found_polygons_text_region_img[mm][lmm,0,1] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_co += ' '
|
||||
img_region.get_Coords().set_points(points_co[:-1])
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml)):
|
||||
sep_hor = SeparatorRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, Coords=CoordsType())
|
||||
page.add_SeparatorRegion(sep_hor)
|
||||
points_co = ''
|
||||
for lmm in range(len(polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml[mm])):
|
||||
points_co += str(int((polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml[mm][lmm,0,0] ) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml[mm][lmm,0,1] ) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_co += ' '
|
||||
sep_hor.get_Coords().set_points(points_co[:-1])
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_tables)):
|
||||
tab_region = TableRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, Coords=CoordsType())
|
||||
page.add_TableRegion(tab_region)
|
||||
points_co = ''
|
||||
for lmm in range(len(found_polygons_tables[mm])):
|
||||
points_co += str(int((found_polygons_tables[mm][lmm,0,0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_co += ','
|
||||
points_co += str(int((found_polygons_tables[mm][lmm,0,1] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_co += ' '
|
||||
tab_region.get_Coords().set_points(points_co[:-1])
|
||||
|
||||
return pcgts
|
||||
|
||||
def build_pagexml_full_layout(self, found_polygons_text_region, found_polygons_text_region_h, page_coord, order_of_texts, id_of_texts, all_found_textline_polygons, all_found_textline_polygons_h, all_box_coord, all_box_coord_h, found_polygons_text_region_img, found_polygons_tables, found_polygons_drop_capitals, found_polygons_marginals, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals, all_box_coord_marginals, slopes, slopes_h, slopes_marginals, cont_page, polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter build_pagexml_full_layout')
|
||||
|
||||
# create the file structure
|
||||
pcgts = self.pcgts if self.pcgts else create_page_xml(self.image_filename, self.height_org, self.width_org)
|
||||
page = pcgts.get_Page()
|
||||
page.set_Border(BorderType(Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_page_coords(cont_page))))
|
||||
|
||||
counter = EynollahIdCounter()
|
||||
_counter_marginals = EynollahIdCounter(region_idx=len(order_of_texts))
|
||||
id_of_marginalia = [_counter_marginals.next_region_id for _ in found_polygons_marginals]
|
||||
xml_reading_order(page, order_of_texts, id_of_marginalia)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_text_region)):
|
||||
textregion = TextRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, type_='paragraph',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_text_region[mm], page_coord)))
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(textregion)
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(textregion, all_found_textline_polygons, mm, page_coord, all_box_coord, slopes, counter)
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.debug('len(found_polygons_text_region_h) %s', len(found_polygons_text_region_h))
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_text_region_h)):
|
||||
textregion = TextRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, type_='header',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_text_region_h[mm], page_coord)))
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(textregion)
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(textregion, all_found_textline_polygons_h, mm, page_coord, all_box_coord_h, slopes_h, counter)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_marginals)):
|
||||
marginal = TextRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, type_='marginalia',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_marginals[mm], page_coord)))
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(marginal)
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_marginal(marginal, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals, mm, page_coord, all_box_coord_marginals, slopes_marginals, counter)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_drop_capitals)):
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(TextRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, type_='drop-capital',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_drop_capitals[mm], page_coord))))
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_text_region_img)):
|
||||
page.add_ImageRegion(ImageRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_text_region_img[mm], page_coord))))
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml)):
|
||||
page.add_SeparatorRegion(ImageRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(polygons_lines_to_be_written_in_xml[mm], [0 , 0, 0, 0]))))
|
||||
|
||||
for mm in range(len(found_polygons_tables)):
|
||||
page.add_TableRegion(TableRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id, Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(found_polygons_tables[mm], page_coord))))
|
||||
|
||||
return pcgts
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_polygon_coords(self, contour, page_coord):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter calculate_polygon_coords')
|
||||
coords = ''
|
||||
for value_bbox in contour:
|
||||
if len(value_bbox) == 2:
|
||||
coords += str(int((value_bbox[0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
coords += ','
|
||||
coords += str(int((value_bbox[1] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
coords += str(int((value_bbox[0][0] + page_coord[2]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
coords += ','
|
||||
coords += str(int((value_bbox[0][1] + page_coord[0]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
coords=coords + ' '
|
||||
return coords[:-1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
|
|||
torch <= 2.0.1
|
||||
transformers <= 4.30.2
|
||||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
matplotlib
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,2 @@
|
|||
pytest
|
||||
pytest-isolate
|
||||
coverage[toml]
|
||||
black
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
train/requirements.txt
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
|||
# ocrd includes opencv, numpy, shapely, click
|
||||
ocrd >= 3.3.0
|
||||
ocrd >= 2.23.3
|
||||
numpy <1.24.0
|
||||
scikit-learn >= 0.23.2
|
||||
tensorflow < 2.13
|
||||
numba <= 0.58.1
|
||||
scikit-image
|
||||
biopython
|
||||
tensorflow == 2.12.1
|
||||
imutils >= 0.5.3
|
||||
matplotlib
|
||||
setuptools >= 50
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
27
setup.py
Normal file
27
setup.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||
from setuptools import setup, find_namespace_packages
|
||||
from json import load
|
||||
|
||||
install_requires = open('requirements.txt').read().split('\n')
|
||||
with open('ocrd-tool.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
|
||||
version = load(f)['version']
|
||||
|
||||
setup(
|
||||
name='eynollah',
|
||||
version=version,
|
||||
long_description=open('README.md').read(),
|
||||
long_description_content_type='text/markdown',
|
||||
author='Vahid Rezanezhad',
|
||||
url='https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah',
|
||||
license='Apache License 2.0',
|
||||
packages=find_namespace_packages(include=['qurator']),
|
||||
install_requires=install_requires,
|
||||
package_data={
|
||||
'': ['*.json']
|
||||
},
|
||||
entry_points={
|
||||
'console_scripts': [
|
||||
'eynollah=qurator.eynollah.cli:main',
|
||||
'ocrd-eynollah-segment=qurator.eynollah.ocrd_cli:main',
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
|
@ -1,579 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import sys
|
||||
import click
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import initLogging, getLevelName, getLogger
|
||||
from eynollah.eynollah import Eynollah, Eynollah_ocr
|
||||
from eynollah.sbb_binarize import SbbBinarizer
|
||||
from eynollah.image_enhancer import Enhancer
|
||||
from eynollah.mb_ro_on_layout import machine_based_reading_order_on_layout
|
||||
|
||||
@click.group()
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--input",
|
||||
"-i",
|
||||
help="PAGE-XML input filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of PAGE-XML input files (instead of --input)",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory for output images",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model",
|
||||
"-m",
|
||||
help="directory of models",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--log_level",
|
||||
"-l",
|
||||
type=click.Choice(['OFF', 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR']),
|
||||
help="Override log level globally to this",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def machine_based_reading_order(input, dir_in, out, model, log_level):
|
||||
assert bool(input) != bool(dir_in), "Either -i (single input) or -di (directory) must be provided, but not both."
|
||||
orderer = machine_based_reading_order_on_layout(model)
|
||||
if log_level:
|
||||
orderer.logger.setLevel(getLevelName(log_level))
|
||||
|
||||
orderer.run(xml_filename=input,
|
||||
dir_in=dir_in,
|
||||
dir_out=out,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option('--patches/--no-patches', default=True, help='by enabling this parameter you let the model to see the image in patches.')
|
||||
@click.option('--model_dir', '-m', type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False), required=True, help='directory containing models for prediction')
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--input-image", "--image",
|
||||
"-i",
|
||||
help="input image filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False)
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of input images (instead of --image)",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--output",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="output image (if using -i) or output image directory (if using -di)",
|
||||
type=click.Path(file_okay=True, dir_okay=True),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--log_level",
|
||||
"-l",
|
||||
type=click.Choice(['OFF', 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR']),
|
||||
help="Override log level globally to this",
|
||||
)
|
||||
def binarization(patches, model_dir, input_image, dir_in, output, log_level):
|
||||
assert bool(input_image) != bool(dir_in), "Either -i (single input) or -di (directory) must be provided, but not both."
|
||||
binarizer = SbbBinarizer(model_dir)
|
||||
if log_level:
|
||||
binarizer.log.setLevel(getLevelName(log_level))
|
||||
binarizer.run(image_path=input_image, use_patches=patches, output=output, dir_in=dir_in)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--image",
|
||||
"-i",
|
||||
help="input image filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory for output PAGE-XML files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--overwrite",
|
||||
"-O",
|
||||
help="overwrite (instead of skipping) if output xml exists",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of input images (instead of --image)",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model",
|
||||
"-m",
|
||||
help="directory of models",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--num_col_upper",
|
||||
"-ncu",
|
||||
help="lower limit of columns in document image",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--num_col_lower",
|
||||
"-ncl",
|
||||
help="upper limit of columns in document image",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_org_scale/--no_save_org_scale",
|
||||
"-sos/-nosos",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will save the enhanced image in org scale.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--log_level",
|
||||
"-l",
|
||||
type=click.Choice(['OFF', 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR']),
|
||||
help="Override log level globally to this",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def enhancement(image, out, overwrite, dir_in, model, num_col_upper, num_col_lower, save_org_scale, log_level):
|
||||
assert bool(image) != bool(dir_in), "Either -i (single input) or -di (directory) must be provided, but not both."
|
||||
initLogging()
|
||||
enhancer = Enhancer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
num_col_upper=num_col_upper,
|
||||
num_col_lower=num_col_lower,
|
||||
save_org_scale=save_org_scale,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if log_level:
|
||||
enhancer.logger.setLevel(getLevelName(log_level))
|
||||
enhancer.run(overwrite=overwrite,
|
||||
dir_in=dir_in,
|
||||
image_filename=image,
|
||||
dir_out=out,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--image",
|
||||
"-i",
|
||||
help="input image filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory for output PAGE-XML files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--overwrite",
|
||||
"-O",
|
||||
help="overwrite (instead of skipping) if output xml exists",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of input images (instead of --image)",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model",
|
||||
"-m",
|
||||
help="directory of models",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model_version",
|
||||
"-mv",
|
||||
help="override default versions of model categories",
|
||||
type=(str, str),
|
||||
multiple=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_images",
|
||||
"-si",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, images in documents will be cropped and saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_layout",
|
||||
"-sl",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, plot of layout will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_deskewed",
|
||||
"-sd",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, deskewed image will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_all",
|
||||
"-sa",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, all plots needed for documentation will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_page",
|
||||
"-sp",
|
||||
help="if a directory is given, page crop of image will be saved there",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--enable-plotting/--disable-plotting",
|
||||
"-ep/-noep",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="If set, will plot intermediary files and images",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--extract_only_images/--disable-extracting_only_images",
|
||||
"-eoi/-noeoi",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="If a directory is given, only images in documents will be cropped and saved there and the other processing will not be done",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--allow-enhancement/--no-allow-enhancement",
|
||||
"-ae/-noae",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would check that input image need resizing and enhancement or not. If so output of resized and enhanced image and corresponding layout data will be written in out directory",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--curved-line/--no-curvedline",
|
||||
"-cl/-nocl",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to return contoure of textlines instead of rectangle bounding box of textline. This should be taken into account that with this option the tool need more time to do process.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--textline_light/--no-textline_light",
|
||||
"-tll/-notll",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to return contoure of textlines instead of rectangle bounding box of textline with a faster method.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--full-layout/--no-full-layout",
|
||||
"-fl/-nofl",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to return all elements of layout.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--tables/--no-tables",
|
||||
"-tab/-notab",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to detect tables.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--right2left/--left2right",
|
||||
"-r2l/-l2r",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will extract right-to-left reading order.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--input_binary/--input-RGB",
|
||||
"-ib/-irgb",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="in general, eynollah uses RGB as input but if the input document is strongly dark, bright or for any other reason you can turn binarized input on. This option does not mean that you have to provide a binary image, otherwise this means that the tool itself will binarized the RGB input document.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--allow_scaling/--no-allow-scaling",
|
||||
"-as/-noas",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would check the scale and if needed it will scale it to perform better layout detection",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--headers_off/--headers-on",
|
||||
"-ho/-noho",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would ignore headers role in reading order",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--light_version/--original",
|
||||
"-light/-org",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would use lighter version",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--ignore_page_extraction/--extract_page_included",
|
||||
"-ipe/-epi",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would ignore page extraction",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--reading_order_machine_based/--heuristic_reading_order",
|
||||
"-romb/-hro",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool would apply machine based reading order detection",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--do_ocr",
|
||||
"-ocr/-noocr",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to do ocr",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--transformer_ocr",
|
||||
"-tr/-notr",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will apply transformer ocr",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--batch_size_ocr",
|
||||
"-bs_ocr",
|
||||
help="number of inference batch size of ocr model. Default b_s for trocr and cnn_rnn models are 2 and 8 respectively",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--num_col_upper",
|
||||
"-ncu",
|
||||
help="lower limit of columns in document image",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--num_col_lower",
|
||||
"-ncl",
|
||||
help="upper limit of columns in document image",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--threshold_art_class_layout",
|
||||
"-tharl",
|
||||
help="threshold of artifical class in the case of layout detection. The default value is 0.1",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--threshold_art_class_textline",
|
||||
"-thart",
|
||||
help="threshold of artifical class in the case of textline detection. The default value is 0.1",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--skip_layout_and_reading_order",
|
||||
"-slro/-noslro",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will ignore layout detection and reading order. It means that textline detection will be done within printspace and contours of textline will be written in xml output file.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
# TODO move to top-level CLI context
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--log_level",
|
||||
"-l",
|
||||
type=click.Choice(['OFF', 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR']),
|
||||
help="Override 'eynollah' log level globally to this",
|
||||
)
|
||||
#
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--setup-logging",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="Setup a basic console logger",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def layout(image, out, overwrite, dir_in, model, model_version, save_images, save_layout, save_deskewed, save_all, extract_only_images, save_page, enable_plotting, allow_enhancement, curved_line, textline_light, full_layout, tables, right2left, input_binary, allow_scaling, headers_off, light_version, reading_order_machine_based, do_ocr, transformer_ocr, batch_size_ocr, num_col_upper, num_col_lower, threshold_art_class_textline, threshold_art_class_layout, skip_layout_and_reading_order, ignore_page_extraction, log_level, setup_logging):
|
||||
if setup_logging:
|
||||
console_handler = logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)
|
||||
console_handler.setLevel(logging.INFO)
|
||||
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(message)s')
|
||||
console_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
|
||||
getLogger('eynollah').addHandler(console_handler)
|
||||
getLogger('eynollah').setLevel(logging.INFO)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
initLogging()
|
||||
assert enable_plotting or not save_layout, "Plotting with -sl also requires -ep"
|
||||
assert enable_plotting or not save_deskewed, "Plotting with -sd also requires -ep"
|
||||
assert enable_plotting or not save_all, "Plotting with -sa also requires -ep"
|
||||
assert enable_plotting or not save_page, "Plotting with -sp also requires -ep"
|
||||
assert enable_plotting or not save_images, "Plotting with -si also requires -ep"
|
||||
assert enable_plotting or not allow_enhancement, "Plotting with -ae also requires -ep"
|
||||
assert not enable_plotting or save_layout or save_deskewed or save_all or save_page or save_images or allow_enhancement, \
|
||||
"Plotting with -ep also requires -sl, -sd, -sa, -sp, -si or -ae"
|
||||
assert textline_light == light_version, "Both light textline detection -tll and light version -light must be set or unset equally"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not allow_enhancement, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside allow_enhancement -ae"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not allow_scaling, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside allow_scaling -as"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not light_version, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside light_version -light"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not curved_line, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside curved_line -cl"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not textline_light, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside textline_light -tll"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not full_layout, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside full_layout -fl"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not tables, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside tables -tab"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not right2left, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside right2left -r2l"
|
||||
assert not extract_only_images or not headers_off, "Image extraction -eoi can not be set alongside headers_off -ho"
|
||||
assert bool(image) != bool(dir_in), "Either -i (single input) or -di (directory) must be provided, but not both."
|
||||
eynollah = Eynollah(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
model_versions=model_version,
|
||||
extract_only_images=extract_only_images,
|
||||
enable_plotting=enable_plotting,
|
||||
allow_enhancement=allow_enhancement,
|
||||
curved_line=curved_line,
|
||||
textline_light=textline_light,
|
||||
full_layout=full_layout,
|
||||
tables=tables,
|
||||
right2left=right2left,
|
||||
input_binary=input_binary,
|
||||
allow_scaling=allow_scaling,
|
||||
headers_off=headers_off,
|
||||
light_version=light_version,
|
||||
ignore_page_extraction=ignore_page_extraction,
|
||||
reading_order_machine_based=reading_order_machine_based,
|
||||
do_ocr=do_ocr,
|
||||
transformer_ocr=transformer_ocr,
|
||||
batch_size_ocr=batch_size_ocr,
|
||||
num_col_upper=num_col_upper,
|
||||
num_col_lower=num_col_lower,
|
||||
skip_layout_and_reading_order=skip_layout_and_reading_order,
|
||||
threshold_art_class_textline=threshold_art_class_textline,
|
||||
threshold_art_class_layout=threshold_art_class_layout,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if log_level:
|
||||
eynollah.logger.setLevel(getLevelName(log_level))
|
||||
eynollah.run(overwrite=overwrite,
|
||||
image_filename=image,
|
||||
dir_in=dir_in,
|
||||
dir_out=out,
|
||||
dir_of_cropped_images=save_images,
|
||||
dir_of_layout=save_layout,
|
||||
dir_of_deskewed=save_deskewed,
|
||||
dir_of_all=save_all,
|
||||
dir_save_page=save_page,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--image",
|
||||
"-i",
|
||||
help="input image filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of input images (instead of --image)",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in_bin",
|
||||
"-dib",
|
||||
help="directory of binarized images (in addition to --dir_in for RGB images; filename stems must match the RGB image files, with '.png' suffix).\nPerform prediction using both RGB and binary images. (This does not necessarily improve results, however it may be beneficial for certain document images.)",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_xmls",
|
||||
"-dx",
|
||||
help="directory of input PAGE-XML files (in addition to --dir_in; filename stems must match the image files, with '.xml' suffix).",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory for output PAGE-XML files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out_image_text",
|
||||
"-doit",
|
||||
help="directory for output images, newly rendered with predicted text",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--overwrite",
|
||||
"-O",
|
||||
help="overwrite (instead of skipping) if output xml exists",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model",
|
||||
"-m",
|
||||
help="directory of models",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model_name",
|
||||
help="Specific model file path to use for OCR",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--tr_ocr",
|
||||
"-trocr/-notrocr",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, transformer ocr will be applied, otherwise cnn_rnn model.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--export_textline_images_and_text",
|
||||
"-etit/-noetit",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, images and text in xml will be exported into output dir. This files can be used for training a OCR engine.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--do_not_mask_with_textline_contour",
|
||||
"-nmtc/-mtc",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, cropped textline images will not be masked with textline contour.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--batch_size",
|
||||
"-bs",
|
||||
help="number of inference batch size. Default b_s for trocr and cnn_rnn models are 2 and 8 respectively",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dataset_abbrevation",
|
||||
"-ds_pref",
|
||||
help="in the case of extracting textline and text from a xml GT file user can add an abbrevation of dataset name to generated dataset",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--min_conf_value_of_textline_text",
|
||||
"-min_conf",
|
||||
help="minimum OCR confidence value. Text lines with a confidence value lower than this threshold will not be included in the output XML file.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--log_level",
|
||||
"-l",
|
||||
type=click.Choice(['OFF', 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR']),
|
||||
help="Override log level globally to this",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def ocr(image, dir_in, dir_in_bin, dir_xmls, out, dir_out_image_text, overwrite, model, model_name, tr_ocr, export_textline_images_and_text, do_not_mask_with_textline_contour, batch_size, dataset_abbrevation, min_conf_value_of_textline_text, log_level):
|
||||
initLogging()
|
||||
|
||||
assert bool(model) != bool(model_name), "Either -m (model directory) or --model_name (specific model name) must be provided."
|
||||
assert not export_textline_images_and_text or not tr_ocr, "Exporting textline and text -etit can not be set alongside transformer ocr -tr_ocr"
|
||||
assert not export_textline_images_and_text or not model, "Exporting textline and text -etit can not be set alongside model -m"
|
||||
assert not export_textline_images_and_text or not batch_size, "Exporting textline and text -etit can not be set alongside batch size -bs"
|
||||
assert not export_textline_images_and_text or not dir_in_bin, "Exporting textline and text -etit can not be set alongside directory of bin images -dib"
|
||||
assert not export_textline_images_and_text or not dir_out_image_text, "Exporting textline and text -etit can not be set alongside directory of images with predicted text -doit"
|
||||
assert bool(image) != bool(dir_in), "Either -i (single image) or -di (directory) must be provided, but not both."
|
||||
eynollah_ocr = Eynollah_ocr(
|
||||
dir_models=model,
|
||||
model_name=model_name,
|
||||
tr_ocr=tr_ocr,
|
||||
export_textline_images_and_text=export_textline_images_and_text,
|
||||
do_not_mask_with_textline_contour=do_not_mask_with_textline_contour,
|
||||
batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
pref_of_dataset=dataset_abbrevation,
|
||||
min_conf_value_of_textline_text=min_conf_value_of_textline_text,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if log_level:
|
||||
eynollah_ocr.logger.setLevel(getLevelName(log_level))
|
||||
eynollah_ocr.run(overwrite=overwrite,
|
||||
dir_in=dir_in,
|
||||
dir_in_bin=dir_in_bin,
|
||||
image_filename=image,
|
||||
dir_xmls=dir_xmls,
|
||||
dir_out_image_text=dir_out_image_text,
|
||||
dir_out=out,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
|
|
@ -1,731 +0,0 @@
|
|||
"""
|
||||
Image enhancer. The output can be written as same scale of input or in new predicted scale.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import Logger
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import getLogger, tf_disable_interactive_logs
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from skimage.morphology import skeletonize
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils.resize import resize_image
|
||||
from .utils.pil_cv2 import pil2cv
|
||||
from .utils import (
|
||||
is_image_filename,
|
||||
crop_image_inside_box
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .eynollah import PatchEncoder, Patches
|
||||
|
||||
DPI_THRESHOLD = 298
|
||||
KERNEL = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Enhancer:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
dir_models : str,
|
||||
num_col_upper : Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
num_col_lower : Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
save_org_scale : bool = False,
|
||||
logger : Optional[Logger] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.input_binary = False
|
||||
self.light_version = False
|
||||
self.save_org_scale = save_org_scale
|
||||
if num_col_upper:
|
||||
self.num_col_upper = int(num_col_upper)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.num_col_upper = num_col_upper
|
||||
if num_col_lower:
|
||||
self.num_col_lower = int(num_col_lower)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.num_col_lower = num_col_lower
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger = logger if logger else getLogger('enhancement')
|
||||
self.dir_models = dir_models
|
||||
self.model_dir_of_binarization = dir_models + "/eynollah-binarization_20210425"
|
||||
self.model_dir_of_enhancement = dir_models + "/eynollah-enhancement_20210425"
|
||||
self.model_dir_of_col_classifier = dir_models + "/eynollah-column-classifier_20210425"
|
||||
self.model_page_dir = dir_models + "/model_eynollah_page_extraction_20250915"
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
for device in tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'):
|
||||
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(device, True)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("no GPU device available")
|
||||
|
||||
self.model_page = self.our_load_model(self.model_page_dir)
|
||||
self.model_classifier = self.our_load_model(self.model_dir_of_col_classifier)
|
||||
self.model_enhancement = self.our_load_model(self.model_dir_of_enhancement)
|
||||
self.model_bin = self.our_load_model(self.model_dir_of_binarization)
|
||||
|
||||
def cache_images(self, image_filename=None, image_pil=None, dpi=None):
|
||||
ret = {}
|
||||
if image_filename:
|
||||
ret['img'] = cv2.imread(image_filename)
|
||||
if self.light_version:
|
||||
self.dpi = 100
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.dpi = 0#check_dpi(image_filename)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ret['img'] = pil2cv(image_pil)
|
||||
if self.light_version:
|
||||
self.dpi = 100
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.dpi = 0#check_dpi(image_pil)
|
||||
ret['img_grayscale'] = cv2.cvtColor(ret['img'], cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
for prefix in ('', '_grayscale'):
|
||||
ret[f'img{prefix}_uint8'] = ret[f'img{prefix}'].astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
self._imgs = ret
|
||||
if dpi is not None:
|
||||
self.dpi = dpi
|
||||
|
||||
def reset_file_name_dir(self, image_filename, dir_out):
|
||||
self.cache_images(image_filename=image_filename)
|
||||
self.output_filename = os.path.join(dir_out, Path(image_filename).stem +'.png')
|
||||
|
||||
def imread(self, grayscale=False, uint8=True):
|
||||
key = 'img'
|
||||
if grayscale:
|
||||
key += '_grayscale'
|
||||
if uint8:
|
||||
key += '_uint8'
|
||||
return self._imgs[key].copy()
|
||||
|
||||
def isNaN(self, num):
|
||||
return num != num
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def our_load_model(model_file):
|
||||
if model_file.endswith('.h5') and Path(model_file[:-3]).exists():
|
||||
# prefer SavedModel over HDF5 format if it exists
|
||||
model_file = model_file[:-3]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
model = load_model(model_file, compile=False)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
model = load_model(model_file, compile=False, custom_objects={
|
||||
"PatchEncoder": PatchEncoder, "Patches": Patches})
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def predict_enhancement(self, img):
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter predict_enhancement")
|
||||
|
||||
img_height_model = self.model_enhancement.layers[-1].output_shape[1]
|
||||
img_width_model = self.model_enhancement.layers[-1].output_shape[2]
|
||||
if img.shape[0] < img_height_model:
|
||||
img = cv2.resize(img, (img.shape[1], img_width_model), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
if img.shape[1] < img_width_model:
|
||||
img = cv2.resize(img, (img_height_model, img.shape[0]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
margin = int(0.1 * img_width_model)
|
||||
width_mid = img_width_model - 2 * margin
|
||||
height_mid = img_height_model - 2 * margin
|
||||
img = img / 255.
|
||||
img_h = img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_w = img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = np.zeros((img_h, img_w, 3))
|
||||
nxf = img_w / float(width_mid)
|
||||
nyf = img_h / float(height_mid)
|
||||
nxf = int(nxf) + 1 if nxf > int(nxf) else int(nxf)
|
||||
nyf = int(nyf) + 1 if nyf > int(nyf) else int(nyf)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(nxf):
|
||||
for j in range(nyf):
|
||||
if i == 0:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + img_width_model
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + img_width_model
|
||||
if j == 0:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + img_height_model
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + img_height_model
|
||||
|
||||
if index_x_u > img_w:
|
||||
index_x_u = img_w
|
||||
index_x_d = img_w - img_width_model
|
||||
if index_y_u > img_h:
|
||||
index_y_u = img_h
|
||||
index_y_d = img_h - img_height_model
|
||||
|
||||
img_patch = img[np.newaxis, index_y_d:index_y_u, index_x_d:index_x_u, :]
|
||||
label_p_pred = self.model_enhancement.predict(img_patch, verbose=0)
|
||||
seg = label_p_pred[0, :, :, :] * 255
|
||||
|
||||
if i == 0 and j == 0:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + 0:index_y_u - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d + 0:index_x_u - margin] = \
|
||||
seg[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
0:-margin or None]
|
||||
elif i == nxf - 1 and j == nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin:index_y_u - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d + margin:index_x_u - 0] = \
|
||||
seg[margin:,
|
||||
margin:]
|
||||
elif i == 0 and j == nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin:index_y_u - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d + 0:index_x_u - margin] = \
|
||||
seg[margin:,
|
||||
0:-margin or None]
|
||||
elif i == nxf - 1 and j == 0:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + 0:index_y_u - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d + margin:index_x_u - 0] = \
|
||||
seg[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:]
|
||||
elif i == 0 and j != 0 and j != nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin:index_y_u - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d + 0:index_x_u - margin] = \
|
||||
seg[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
0:-margin or None]
|
||||
elif i == nxf - 1 and j != 0 and j != nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin:index_y_u - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d + margin:index_x_u - 0] = \
|
||||
seg[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:]
|
||||
elif i != 0 and i != nxf - 1 and j == 0:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + 0:index_y_u - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d + margin:index_x_u - margin] = \
|
||||
seg[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None]
|
||||
elif i != 0 and i != nxf - 1 and j == nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin:index_y_u - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d + margin:index_x_u - margin] = \
|
||||
seg[margin:,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin:index_y_u - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d + margin:index_x_u - margin] = \
|
||||
seg[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None]
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = prediction_true.astype(int)
|
||||
return prediction_true
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_width_height_by_columns(self, img, num_col, width_early, label_p_pred):
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter calculate_width_height_by_columns")
|
||||
if num_col == 1:
|
||||
img_w_new = 2000
|
||||
elif num_col == 2:
|
||||
img_w_new = 2400
|
||||
elif num_col == 3:
|
||||
img_w_new = 3000
|
||||
elif num_col == 4:
|
||||
img_w_new = 4000
|
||||
elif num_col == 5:
|
||||
img_w_new = 5000
|
||||
elif num_col == 6:
|
||||
img_w_new = 6500
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_w_new = width_early
|
||||
img_h_new = img_w_new * img.shape[0] // img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
if img_h_new >= 8000:
|
||||
img_new = np.copy(img)
|
||||
num_column_is_classified = False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_new = resize_image(img, img_h_new, img_w_new)
|
||||
num_column_is_classified = True
|
||||
|
||||
return img_new, num_column_is_classified
|
||||
|
||||
def early_page_for_num_of_column_classification(self,img_bin):
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter early_page_for_num_of_column_classification")
|
||||
if self.input_binary:
|
||||
img = np.copy(img_bin).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img = self.imread()
|
||||
img = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5, 5), 0)
|
||||
img_page_prediction = self.do_prediction(False, img, self.model_page)
|
||||
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_page_prediction, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
thresh = cv2.dilate(thresh, KERNEL, iterations=3)
|
||||
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
if len(contours)>0:
|
||||
cnt_size = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours[j])
|
||||
for j in range(len(contours))])
|
||||
cnt = contours[np.argmax(cnt_size)]
|
||||
box = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
box = [0, 0, img.shape[1], img.shape[0]]
|
||||
cropped_page, page_coord = crop_image_inside_box(box, img)
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.debug("exit early_page_for_num_of_column_classification")
|
||||
return cropped_page, page_coord
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_width_height_by_columns_1_2(self, img, num_col, width_early, label_p_pred):
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter calculate_width_height_by_columns")
|
||||
if num_col == 1:
|
||||
img_w_new = 1000
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_w_new = 1300
|
||||
img_h_new = img_w_new * img.shape[0] // img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
if label_p_pred[0][int(num_col - 1)] < 0.9 and img_w_new < width_early:
|
||||
img_new = np.copy(img)
|
||||
num_column_is_classified = False
|
||||
#elif label_p_pred[0][int(num_col - 1)] < 0.8 and img_h_new >= 8000:
|
||||
elif img_h_new >= 8000:
|
||||
img_new = np.copy(img)
|
||||
num_column_is_classified = False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_new = resize_image(img, img_h_new, img_w_new)
|
||||
num_column_is_classified = True
|
||||
|
||||
return img_new, num_column_is_classified
|
||||
|
||||
def resize_and_enhance_image_with_column_classifier(self, light_version):
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter resize_and_enhance_image_with_column_classifier")
|
||||
dpi = 0#self.dpi
|
||||
self.logger.info("Detected %s DPI", dpi)
|
||||
if self.input_binary:
|
||||
img = self.imread()
|
||||
prediction_bin = self.do_prediction(True, img, self.model_bin, n_batch_inference=5)
|
||||
prediction_bin = 255 * (prediction_bin[:,:,0]==0)
|
||||
prediction_bin = np.repeat(prediction_bin[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
img= np.copy(prediction_bin)
|
||||
img_bin = prediction_bin
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img = self.imread()
|
||||
self.h_org, self.w_org = img.shape[:2]
|
||||
img_bin = None
|
||||
|
||||
width_early = img.shape[1]
|
||||
t1 = time.time()
|
||||
_, page_coord = self.early_page_for_num_of_column_classification(img_bin)
|
||||
|
||||
self.image_page_org_size = img[page_coord[0] : page_coord[1], page_coord[2] : page_coord[3], :]
|
||||
self.page_coord = page_coord
|
||||
|
||||
if self.num_col_upper and not self.num_col_lower:
|
||||
num_col = self.num_col_upper
|
||||
label_p_pred = [np.ones(6)]
|
||||
elif self.num_col_lower and not self.num_col_upper:
|
||||
num_col = self.num_col_lower
|
||||
label_p_pred = [np.ones(6)]
|
||||
elif not self.num_col_upper and not self.num_col_lower:
|
||||
if self.input_binary:
|
||||
img_in = np.copy(img)
|
||||
img_in = img_in / 255.0
|
||||
img_in = cv2.resize(img_in, (448, 448), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
img_in = img_in.reshape(1, 448, 448, 3)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_1ch = self.imread(grayscale=True)
|
||||
width_early = img_1ch.shape[1]
|
||||
img_1ch = img_1ch[page_coord[0] : page_coord[1], page_coord[2] : page_coord[3]]
|
||||
|
||||
img_1ch = img_1ch / 255.0
|
||||
img_1ch = cv2.resize(img_1ch, (448, 448), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
img_in = np.zeros((1, img_1ch.shape[0], img_1ch.shape[1], 3))
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 0] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 1] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 2] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
|
||||
label_p_pred = self.model_classifier.predict(img_in, verbose=0)
|
||||
num_col = np.argmax(label_p_pred[0]) + 1
|
||||
elif (self.num_col_upper and self.num_col_lower) and (self.num_col_upper!=self.num_col_lower):
|
||||
if self.input_binary:
|
||||
img_in = np.copy(img)
|
||||
img_in = img_in / 255.0
|
||||
img_in = cv2.resize(img_in, (448, 448), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
img_in = img_in.reshape(1, 448, 448, 3)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_1ch = self.imread(grayscale=True)
|
||||
width_early = img_1ch.shape[1]
|
||||
img_1ch = img_1ch[page_coord[0] : page_coord[1], page_coord[2] : page_coord[3]]
|
||||
|
||||
img_1ch = img_1ch / 255.0
|
||||
img_1ch = cv2.resize(img_1ch, (448, 448), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
img_in = np.zeros((1, img_1ch.shape[0], img_1ch.shape[1], 3))
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 0] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 1] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 2] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
|
||||
label_p_pred = self.model_classifier.predict(img_in, verbose=0)
|
||||
num_col = np.argmax(label_p_pred[0]) + 1
|
||||
|
||||
if num_col > self.num_col_upper:
|
||||
num_col = self.num_col_upper
|
||||
label_p_pred = [np.ones(6)]
|
||||
if num_col < self.num_col_lower:
|
||||
num_col = self.num_col_lower
|
||||
label_p_pred = [np.ones(6)]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
num_col = self.num_col_upper
|
||||
label_p_pred = [np.ones(6)]
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.info("Found %d columns (%s)", num_col, np.around(label_p_pred, decimals=5))
|
||||
|
||||
if dpi < DPI_THRESHOLD:
|
||||
if light_version and num_col in (1,2):
|
||||
img_new, num_column_is_classified = self.calculate_width_height_by_columns_1_2(
|
||||
img, num_col, width_early, label_p_pred)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_new, num_column_is_classified = self.calculate_width_height_by_columns(
|
||||
img, num_col, width_early, label_p_pred)
|
||||
if light_version:
|
||||
image_res = np.copy(img_new)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image_res = self.predict_enhancement(img_new)
|
||||
is_image_enhanced = True
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
num_column_is_classified = True
|
||||
image_res = np.copy(img)
|
||||
is_image_enhanced = False
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.debug("exit resize_and_enhance_image_with_column_classifier")
|
||||
return is_image_enhanced, img, image_res, num_col, num_column_is_classified, img_bin
|
||||
def do_prediction(
|
||||
self, patches, img, model,
|
||||
n_batch_inference=1, marginal_of_patch_percent=0.1,
|
||||
thresholding_for_some_classes_in_light_version=False,
|
||||
thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version=False, thresholding_for_fl_light_version=False, threshold_art_class_textline=0.1):
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter do_prediction")
|
||||
img_height_model = model.layers[-1].output_shape[1]
|
||||
img_width_model = model.layers[-1].output_shape[2]
|
||||
|
||||
if not patches:
|
||||
img_h_page = img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_w_page = img.shape[1]
|
||||
img = img / float(255.0)
|
||||
img = resize_image(img, img_height_model, img_width_model)
|
||||
|
||||
label_p_pred = model.predict(img[np.newaxis], verbose=0)
|
||||
seg = np.argmax(label_p_pred, axis=3)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
seg_art = label_p_pred[0,:,:,2]
|
||||
|
||||
seg_art[seg_art<threshold_art_class_textline] = 0
|
||||
seg_art[seg_art>0] =1
|
||||
|
||||
skeleton_art = skeletonize(seg_art)
|
||||
skeleton_art = skeleton_art*1
|
||||
|
||||
seg[skeleton_art==1]=2
|
||||
|
||||
if thresholding_for_fl_light_version:
|
||||
seg_header = label_p_pred[0,:,:,2]
|
||||
|
||||
seg_header[seg_header<0.2] = 0
|
||||
seg_header[seg_header>0] =1
|
||||
|
||||
seg[seg_header==1]=2
|
||||
|
||||
seg_color = np.repeat(seg[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
prediction_true = resize_image(seg_color, img_h_page, img_w_page).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
return prediction_true
|
||||
|
||||
if img.shape[0] < img_height_model:
|
||||
img = resize_image(img, img_height_model, img.shape[1])
|
||||
if img.shape[1] < img_width_model:
|
||||
img = resize_image(img, img.shape[0], img_width_model)
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Patch size: %sx%s", img_height_model, img_width_model)
|
||||
margin = int(marginal_of_patch_percent * img_height_model)
|
||||
width_mid = img_width_model - 2 * margin
|
||||
height_mid = img_height_model - 2 * margin
|
||||
img = img / 255.
|
||||
#img = img.astype(np.float16)
|
||||
img_h = img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_w = img.shape[1]
|
||||
prediction_true = np.zeros((img_h, img_w, 3))
|
||||
mask_true = np.zeros((img_h, img_w))
|
||||
nxf = img_w / float(width_mid)
|
||||
nyf = img_h / float(height_mid)
|
||||
nxf = int(nxf) + 1 if nxf > int(nxf) else int(nxf)
|
||||
nyf = int(nyf) + 1 if nyf > int(nyf) else int(nyf)
|
||||
|
||||
list_i_s = []
|
||||
list_j_s = []
|
||||
list_x_u = []
|
||||
list_x_d = []
|
||||
list_y_u = []
|
||||
list_y_d = []
|
||||
|
||||
batch_indexer = 0
|
||||
img_patch = np.zeros((n_batch_inference, img_height_model, img_width_model, 3))
|
||||
for i in range(nxf):
|
||||
for j in range(nyf):
|
||||
if i == 0:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + img_width_model
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + img_width_model
|
||||
if j == 0:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + img_height_model
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + img_height_model
|
||||
if index_x_u > img_w:
|
||||
index_x_u = img_w
|
||||
index_x_d = img_w - img_width_model
|
||||
if index_y_u > img_h:
|
||||
index_y_u = img_h
|
||||
index_y_d = img_h - img_height_model
|
||||
|
||||
list_i_s.append(i)
|
||||
list_j_s.append(j)
|
||||
list_x_u.append(index_x_u)
|
||||
list_x_d.append(index_x_d)
|
||||
list_y_d.append(index_y_d)
|
||||
list_y_u.append(index_y_u)
|
||||
|
||||
img_patch[batch_indexer,:,:,:] = img[index_y_d:index_y_u, index_x_d:index_x_u, :]
|
||||
batch_indexer += 1
|
||||
|
||||
if (batch_indexer == n_batch_inference or
|
||||
# last batch
|
||||
i == nxf - 1 and j == nyf - 1):
|
||||
self.logger.debug("predicting patches on %s", str(img_patch.shape))
|
||||
label_p_pred = model.predict(img_patch, verbose=0)
|
||||
seg = np.argmax(label_p_pred, axis=3)
|
||||
|
||||
if thresholding_for_some_classes_in_light_version:
|
||||
seg_not_base = label_p_pred[:,:,:,4]
|
||||
seg_not_base[seg_not_base>0.03] =1
|
||||
seg_not_base[seg_not_base<1] =0
|
||||
|
||||
seg_line = label_p_pred[:,:,:,3]
|
||||
seg_line[seg_line>0.1] =1
|
||||
seg_line[seg_line<1] =0
|
||||
|
||||
seg_background = label_p_pred[:,:,:,0]
|
||||
seg_background[seg_background>0.25] =1
|
||||
seg_background[seg_background<1] =0
|
||||
|
||||
seg[seg_not_base==1]=4
|
||||
seg[seg_background==1]=0
|
||||
seg[(seg_line==1) & (seg==0)]=3
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
seg_art = label_p_pred[:,:,:,2]
|
||||
|
||||
seg_art[seg_art<threshold_art_class_textline] = 0
|
||||
seg_art[seg_art>0] =1
|
||||
|
||||
##seg[seg_art==1]=2
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_inside_batch = 0
|
||||
for i_batch, j_batch in zip(list_i_s, list_j_s):
|
||||
seg_in = seg[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
seg_in_art = seg_art[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
index_y_u_in = list_y_u[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
index_y_d_in = list_y_d[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
index_x_u_in = list_x_u[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
index_x_d_in = list_x_d[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
if i_batch == 0 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + 0:index_x_u_in - margin] = \
|
||||
seg_in[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
0:-margin or None,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + 0:index_x_u_in - margin, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
0:-margin or None]
|
||||
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - 0] = \
|
||||
seg_in[margin:,
|
||||
margin:,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - 0, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[margin:,
|
||||
margin:]
|
||||
|
||||
elif i_batch == 0 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + 0:index_x_u_in - margin] = \
|
||||
seg_in[margin:,
|
||||
0:-margin or None,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + 0:index_x_u_in - margin, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[margin:,
|
||||
0:-margin or None]
|
||||
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - 0] = \
|
||||
seg_in[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - 0, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:]
|
||||
|
||||
elif i_batch == 0 and j_batch != 0 and j_batch != nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + 0:index_x_u_in - margin] = \
|
||||
seg_in[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
0:-margin or None,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + 0:index_x_u_in - margin, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
0:-margin or None]
|
||||
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch != 0 and j_batch != nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - 0] = \
|
||||
seg_in[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - 0, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:]
|
||||
|
||||
elif i_batch != 0 and i_batch != nxf - 1 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - margin] = \
|
||||
seg_in[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - margin, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[0:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None]
|
||||
|
||||
elif i_batch != 0 and i_batch != nxf - 1 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - margin] = \
|
||||
seg_in[margin:,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - 0,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - margin, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[margin:,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None]
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - margin] = \
|
||||
seg_in[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
np.newaxis]
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin:index_y_u_in - margin,
|
||||
index_x_d_in + margin:index_x_u_in - margin, 1] = \
|
||||
seg_in_art[margin:-margin or None,
|
||||
margin:-margin or None]
|
||||
indexer_inside_batch += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
list_i_s = []
|
||||
list_j_s = []
|
||||
list_x_u = []
|
||||
list_x_d = []
|
||||
list_y_u = []
|
||||
list_y_d = []
|
||||
|
||||
batch_indexer = 0
|
||||
img_patch[:] = 0
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = prediction_true.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
if thresholding_for_artificial_class_in_light_version:
|
||||
kernel_min = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
|
||||
prediction_true[:,:,0][prediction_true[:,:,0]==2] = 0
|
||||
|
||||
skeleton_art = skeletonize(prediction_true[:,:,1])
|
||||
skeleton_art = skeleton_art*1
|
||||
|
||||
skeleton_art = skeleton_art.astype('uint8')
|
||||
|
||||
skeleton_art = cv2.dilate(skeleton_art, kernel_min, iterations=1)
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true[:,:,0][skeleton_art==1]=2
|
||||
#del model
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
return prediction_true
|
||||
|
||||
def run_enhancement(self, light_version):
|
||||
t_in = time.time()
|
||||
self.logger.info("Resizing and enhancing image...")
|
||||
is_image_enhanced, img_org, img_res, num_col_classifier, num_column_is_classified, img_bin = \
|
||||
self.resize_and_enhance_image_with_column_classifier(light_version)
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.info("Image was %senhanced.", '' if is_image_enhanced else 'not ')
|
||||
return img_res, is_image_enhanced, num_col_classifier, num_column_is_classified
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run_single(self):
|
||||
t0 = time.time()
|
||||
img_res, is_image_enhanced, num_col_classifier, num_column_is_classified = self.run_enhancement(light_version=False)
|
||||
|
||||
return img_res
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self,
|
||||
overwrite: bool = False,
|
||||
image_filename: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
dir_in: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
dir_out: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get image and scales, then extract the page of scanned image
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter run")
|
||||
t0_tot = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
if dir_in:
|
||||
ls_imgs = [os.path.join(dir_in, image_filename)
|
||||
for image_filename in filter(is_image_filename,
|
||||
os.listdir(dir_in))]
|
||||
elif image_filename:
|
||||
ls_imgs = [image_filename]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError("run requires either a single image filename or a directory")
|
||||
|
||||
for img_filename in ls_imgs:
|
||||
self.logger.info(img_filename)
|
||||
t0 = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
self.reset_file_name_dir(img_filename, dir_out)
|
||||
#print("text region early -11 in %.1fs", time.time() - t0)
|
||||
|
||||
if os.path.exists(self.output_filename):
|
||||
if overwrite:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("will overwrite existing output file '%s'", self.output_filename)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("will skip input for existing output file '%s'", self.output_filename)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
image_enhanced = self.run_single()
|
||||
if self.save_org_scale:
|
||||
image_enhanced = resize_image(image_enhanced, self.h_org, self.w_org)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(self.output_filename, image_enhanced)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,812 +0,0 @@
|
|||
"""
|
||||
Image enhancer. The output can be written as same scale of input or in new predicted scale.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import Logger
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
|
||||
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import getLogger
|
||||
import statistics
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils.resize import resize_image
|
||||
from .utils.contour import (
|
||||
find_new_features_of_contours,
|
||||
return_contours_of_image,
|
||||
return_parent_contours,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .utils import is_xml_filename
|
||||
from .eynollah import PatchEncoder, Patches
|
||||
|
||||
DPI_THRESHOLD = 298
|
||||
KERNEL = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class machine_based_reading_order_on_layout:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
dir_models : str,
|
||||
logger : Optional[Logger] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.logger = logger if logger else getLogger('mbreorder')
|
||||
self.dir_models = dir_models
|
||||
self.model_reading_order_dir = dir_models + "/model_eynollah_reading_order_20250824"
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
for device in tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'):
|
||||
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(device, True)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("no GPU device available")
|
||||
|
||||
self.model_reading_order = self.our_load_model(self.model_reading_order_dir)
|
||||
self.light_version = True
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def our_load_model(model_file):
|
||||
if model_file.endswith('.h5') and Path(model_file[:-3]).exists():
|
||||
# prefer SavedModel over HDF5 format if it exists
|
||||
model_file = model_file[:-3]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
model = load_model(model_file, compile=False)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
model = load_model(model_file, compile=False, custom_objects={
|
||||
"PatchEncoder": PatchEncoder, "Patches": Patches})
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def read_xml(self, xml_file):
|
||||
tree1 = ET.parse(xml_file, parser = ET.XMLParser(encoding='utf-8'))
|
||||
root1=tree1.getroot()
|
||||
alltags=[elem.tag for elem in root1.iter()]
|
||||
link=alltags[0].split('}')[0]+'}'
|
||||
|
||||
index_tot_regions = []
|
||||
tot_region_ref = []
|
||||
|
||||
for jj in root1.iter(link+'Page'):
|
||||
y_len=int(jj.attrib['imageHeight'])
|
||||
x_len=int(jj.attrib['imageWidth'])
|
||||
|
||||
for jj in root1.iter(link+'RegionRefIndexed'):
|
||||
index_tot_regions.append(jj.attrib['index'])
|
||||
tot_region_ref.append(jj.attrib['regionRef'])
|
||||
|
||||
if (link+'PrintSpace' in alltags) or (link+'Border' in alltags):
|
||||
co_printspace = []
|
||||
if link+'PrintSpace' in alltags:
|
||||
region_tags_printspace = np.unique([x for x in alltags if x.endswith('PrintSpace')])
|
||||
elif link+'Border' in alltags:
|
||||
region_tags_printspace = np.unique([x for x in alltags if x.endswith('Border')])
|
||||
|
||||
for tag in region_tags_printspace:
|
||||
if link+'PrintSpace' in alltags:
|
||||
tag_endings_printspace = ['}PrintSpace','}printspace']
|
||||
elif link+'Border' in alltags:
|
||||
tag_endings_printspace = ['}Border','}border']
|
||||
|
||||
if tag.endswith(tag_endings_printspace[0]) or tag.endswith(tag_endings_printspace[1]):
|
||||
for nn in root1.iter(tag):
|
||||
c_t_in = []
|
||||
sumi = 0
|
||||
for vv in nn.iter():
|
||||
# check the format of coords
|
||||
if vv.tag == link + 'Coords':
|
||||
coords = bool(vv.attrib)
|
||||
if coords:
|
||||
p_h = vv.attrib['points'].split(' ')
|
||||
c_t_in.append(
|
||||
np.array([[int(x.split(',')[0]), int(x.split(',')[1])] for x in p_h]))
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
if vv.tag == link + 'Point':
|
||||
c_t_in.append([int(float(vv.attrib['x'])), int(float(vv.attrib['y']))])
|
||||
sumi += 1
|
||||
elif vv.tag != link + 'Point' and sumi >= 1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
co_printspace.append(np.array(c_t_in))
|
||||
img_printspace = np.zeros( (y_len,x_len,3) )
|
||||
img_printspace=cv2.fillPoly(img_printspace, pts =co_printspace, color=(1,1,1))
|
||||
img_printspace = img_printspace.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img_printspace, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
cnt_size = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contours[j]) for j in range(len(contours))])
|
||||
cnt = contours[np.argmax(cnt_size)]
|
||||
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
|
||||
|
||||
bb_coord_printspace = [x, y, w, h]
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bb_coord_printspace = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
region_tags=np.unique([x for x in alltags if x.endswith('Region')])
|
||||
co_text_paragraph=[]
|
||||
co_text_drop=[]
|
||||
co_text_heading=[]
|
||||
co_text_header=[]
|
||||
co_text_marginalia=[]
|
||||
co_text_catch=[]
|
||||
co_text_page_number=[]
|
||||
co_text_signature_mark=[]
|
||||
co_sep=[]
|
||||
co_img=[]
|
||||
co_table=[]
|
||||
co_graphic=[]
|
||||
co_graphic_text_annotation=[]
|
||||
co_graphic_decoration=[]
|
||||
co_noise=[]
|
||||
|
||||
co_text_paragraph_text=[]
|
||||
co_text_drop_text=[]
|
||||
co_text_heading_text=[]
|
||||
co_text_header_text=[]
|
||||
co_text_marginalia_text=[]
|
||||
co_text_catch_text=[]
|
||||
co_text_page_number_text=[]
|
||||
co_text_signature_mark_text=[]
|
||||
co_sep_text=[]
|
||||
co_img_text=[]
|
||||
co_table_text=[]
|
||||
co_graphic_text=[]
|
||||
co_graphic_text_annotation_text=[]
|
||||
co_graphic_decoration_text=[]
|
||||
co_noise_text=[]
|
||||
|
||||
id_paragraph = []
|
||||
id_header = []
|
||||
id_heading = []
|
||||
id_marginalia = []
|
||||
|
||||
for tag in region_tags:
|
||||
if tag.endswith('}TextRegion') or tag.endswith('}Textregion'):
|
||||
for nn in root1.iter(tag):
|
||||
for child2 in nn:
|
||||
tag2 = child2.tag
|
||||
if tag2.endswith('}TextEquiv') or tag2.endswith('}TextEquiv'):
|
||||
for childtext2 in child2:
|
||||
if childtext2.tag.endswith('}Unicode') or childtext2.tag.endswith('}Unicode'):
|
||||
if "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='drop-capital':
|
||||
co_text_drop_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='heading':
|
||||
co_text_heading_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='signature-mark':
|
||||
co_text_signature_mark_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='header':
|
||||
co_text_header_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
###elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='catch-word':
|
||||
###co_text_catch_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
###elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='page-number':
|
||||
###co_text_page_number_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='marginalia':
|
||||
co_text_marginalia_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
co_text_paragraph_text.append(childtext2.text)
|
||||
c_t_in_drop=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_paragraph=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_heading=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_header=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_page_number=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_signature_mark=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_catch=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_marginalia=[]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sumi=0
|
||||
for vv in nn.iter():
|
||||
# check the format of coords
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Coords':
|
||||
|
||||
coords=bool(vv.attrib)
|
||||
if coords:
|
||||
#print('birda1')
|
||||
p_h=vv.attrib['points'].split(' ')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='drop-capital':
|
||||
|
||||
c_t_in_drop.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='heading':
|
||||
##id_heading.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
c_t_in_heading.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='signature-mark':
|
||||
|
||||
c_t_in_signature_mark.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
#print(c_t_in_paragraph)
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='header':
|
||||
#id_header.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
c_t_in_header.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='catch-word':
|
||||
###c_t_in_catch.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='page-number':
|
||||
|
||||
###c_t_in_page_number.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='marginalia':
|
||||
#id_marginalia.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
|
||||
c_t_in_marginalia.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
#id_paragraph.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
|
||||
c_t_in_paragraph.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Point':
|
||||
if "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='drop-capital':
|
||||
|
||||
c_t_in_drop.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='heading':
|
||||
#id_heading.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
c_t_in_heading.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='signature-mark':
|
||||
|
||||
c_t_in_signature_mark.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='header':
|
||||
#id_header.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
c_t_in_header.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='catch-word':
|
||||
###c_t_in_catch.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
###sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
###elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='page-number':
|
||||
|
||||
###c_t_in_page_number.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
###sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='marginalia':
|
||||
#id_marginalia.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
|
||||
c_t_in_marginalia.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
#id_paragraph.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
c_t_in_paragraph.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
elif vv.tag!=link+'Point' and sumi>=1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_drop)>0:
|
||||
co_text_drop.append(np.array(c_t_in_drop))
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_paragraph)>0:
|
||||
co_text_paragraph.append(np.array(c_t_in_paragraph))
|
||||
id_paragraph.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_heading)>0:
|
||||
co_text_heading.append(np.array(c_t_in_heading))
|
||||
id_heading.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_header)>0:
|
||||
co_text_header.append(np.array(c_t_in_header))
|
||||
id_header.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_page_number)>0:
|
||||
co_text_page_number.append(np.array(c_t_in_page_number))
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_catch)>0:
|
||||
co_text_catch.append(np.array(c_t_in_catch))
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_signature_mark)>0:
|
||||
co_text_signature_mark.append(np.array(c_t_in_signature_mark))
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_marginalia)>0:
|
||||
co_text_marginalia.append(np.array(c_t_in_marginalia))
|
||||
id_marginalia.append(nn.attrib['id'])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif tag.endswith('}GraphicRegion') or tag.endswith('}graphicregion'):
|
||||
for nn in root1.iter(tag):
|
||||
c_t_in=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_text_annotation=[]
|
||||
c_t_in_decoration=[]
|
||||
sumi=0
|
||||
for vv in nn.iter():
|
||||
# check the format of coords
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Coords':
|
||||
coords=bool(vv.attrib)
|
||||
if coords:
|
||||
p_h=vv.attrib['points'].split(' ')
|
||||
|
||||
if "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='handwritten-annotation':
|
||||
c_t_in_text_annotation.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='decoration':
|
||||
c_t_in_decoration.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
c_t_in.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Point':
|
||||
if "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='handwritten-annotation':
|
||||
c_t_in_text_annotation.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
elif "type" in nn.attrib and nn.attrib['type']=='decoration':
|
||||
c_t_in_decoration.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
c_t_in.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_text_annotation)>0:
|
||||
co_graphic_text_annotation.append(np.array(c_t_in_text_annotation))
|
||||
if len(c_t_in_decoration)>0:
|
||||
co_graphic_decoration.append(np.array(c_t_in_decoration))
|
||||
if len(c_t_in)>0:
|
||||
co_graphic.append(np.array(c_t_in))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif tag.endswith('}ImageRegion') or tag.endswith('}imageregion'):
|
||||
for nn in root1.iter(tag):
|
||||
c_t_in=[]
|
||||
sumi=0
|
||||
for vv in nn.iter():
|
||||
# check the format of coords
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Coords':
|
||||
coords=bool(vv.attrib)
|
||||
if coords:
|
||||
p_h=vv.attrib['points'].split(' ')
|
||||
c_t_in.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Point':
|
||||
c_t_in.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
elif vv.tag!=link+'Point' and sumi>=1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
co_img.append(np.array(c_t_in))
|
||||
co_img_text.append(' ')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif tag.endswith('}SeparatorRegion') or tag.endswith('}separatorregion'):
|
||||
for nn in root1.iter(tag):
|
||||
c_t_in=[]
|
||||
sumi=0
|
||||
for vv in nn.iter():
|
||||
# check the format of coords
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Coords':
|
||||
coords=bool(vv.attrib)
|
||||
if coords:
|
||||
p_h=vv.attrib['points'].split(' ')
|
||||
c_t_in.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Point':
|
||||
c_t_in.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
elif vv.tag!=link+'Point' and sumi>=1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
co_sep.append(np.array(c_t_in))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif tag.endswith('}TableRegion') or tag.endswith('}tableregion'):
|
||||
for nn in root1.iter(tag):
|
||||
c_t_in=[]
|
||||
sumi=0
|
||||
for vv in nn.iter():
|
||||
# check the format of coords
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Coords':
|
||||
coords=bool(vv.attrib)
|
||||
if coords:
|
||||
p_h=vv.attrib['points'].split(' ')
|
||||
c_t_in.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Point':
|
||||
c_t_in.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
elif vv.tag!=link+'Point' and sumi>=1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
co_table.append(np.array(c_t_in))
|
||||
co_table_text.append(' ')
|
||||
|
||||
elif tag.endswith('}NoiseRegion') or tag.endswith('}noiseregion'):
|
||||
for nn in root1.iter(tag):
|
||||
c_t_in=[]
|
||||
sumi=0
|
||||
for vv in nn.iter():
|
||||
# check the format of coords
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Coords':
|
||||
coords=bool(vv.attrib)
|
||||
if coords:
|
||||
p_h=vv.attrib['points'].split(' ')
|
||||
c_t_in.append( np.array( [ [ int(x.split(',')[0]) , int(x.split(',')[1]) ] for x in p_h] ) )
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if vv.tag==link+'Point':
|
||||
c_t_in.append([ int(float(vv.attrib['x'])) , int(float(vv.attrib['y'])) ])
|
||||
sumi+=1
|
||||
|
||||
elif vv.tag!=link+'Point' and sumi>=1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
co_noise.append(np.array(c_t_in))
|
||||
co_noise_text.append(' ')
|
||||
|
||||
img = np.zeros( (y_len,x_len,3) )
|
||||
img_poly=cv2.fillPoly(img, pts =co_text_paragraph, color=(1,1,1))
|
||||
|
||||
img_poly=cv2.fillPoly(img, pts =co_text_heading, color=(2,2,2))
|
||||
img_poly=cv2.fillPoly(img, pts =co_text_header, color=(2,2,2))
|
||||
img_poly=cv2.fillPoly(img, pts =co_text_marginalia, color=(3,3,3))
|
||||
img_poly=cv2.fillPoly(img, pts =co_img, color=(4,4,4))
|
||||
img_poly=cv2.fillPoly(img, pts =co_sep, color=(5,5,5))
|
||||
|
||||
return tree1, root1, bb_coord_printspace, id_paragraph, id_header+id_heading, co_text_paragraph, co_text_header+co_text_heading,\
|
||||
tot_region_ref,x_len, y_len,index_tot_regions, img_poly
|
||||
|
||||
def return_indexes_of_contours_loctaed_inside_another_list_of_contours(self, contours, contours_loc, cx_main_loc, cy_main_loc, indexes_loc):
|
||||
indexes_of_located_cont = []
|
||||
center_x_coordinates_of_located = []
|
||||
center_y_coordinates_of_located = []
|
||||
#M_main_tot = [cv2.moments(contours_loc[j])
|
||||
#for j in range(len(contours_loc))]
|
||||
#cx_main_loc = [(M_main_tot[j]["m10"] / (M_main_tot[j]["m00"] + 1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main_tot))]
|
||||
#cy_main_loc = [(M_main_tot[j]["m01"] / (M_main_tot[j]["m00"] + 1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main_tot))]
|
||||
|
||||
for ij in range(len(contours)):
|
||||
results = [cv2.pointPolygonTest(contours[ij], (cx_main_loc[ind], cy_main_loc[ind]), False)
|
||||
for ind in range(len(cy_main_loc)) ]
|
||||
results = np.array(results)
|
||||
indexes_in = np.where((results == 0) | (results == 1))
|
||||
indexes = indexes_loc[indexes_in]# [(results == 0) | (results == 1)]#np.where((results == 0) | (results == 1))
|
||||
|
||||
indexes_of_located_cont.append(indexes)
|
||||
center_x_coordinates_of_located.append(np.array(cx_main_loc)[indexes_in] )
|
||||
center_y_coordinates_of_located.append(np.array(cy_main_loc)[indexes_in] )
|
||||
|
||||
return indexes_of_located_cont, center_x_coordinates_of_located, center_y_coordinates_of_located
|
||||
|
||||
def do_order_of_regions_with_model(self, contours_only_text_parent, contours_only_text_parent_h, text_regions_p):
|
||||
height1 =672#448
|
||||
width1 = 448#224
|
||||
|
||||
height2 =672#448
|
||||
width2= 448#224
|
||||
|
||||
height3 =672#448
|
||||
width3 = 448#224
|
||||
|
||||
inference_bs = 3
|
||||
|
||||
ver_kernel = np.ones((5, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
hor_kernel = np.ones((1, 5), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
min_cont_size_to_be_dilated = 10
|
||||
if len(contours_only_text_parent)>min_cont_size_to_be_dilated and self.light_version:
|
||||
cx_conts, cy_conts, x_min_conts, x_max_conts, y_min_conts, y_max_conts, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(contours_only_text_parent)
|
||||
args_cont_located = np.array(range(len(contours_only_text_parent)))
|
||||
|
||||
diff_y_conts = np.abs(y_max_conts[:]-y_min_conts)
|
||||
diff_x_conts = np.abs(x_max_conts[:]-x_min_conts)
|
||||
|
||||
mean_x = statistics.mean(diff_x_conts)
|
||||
median_x = statistics.median(diff_x_conts)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
diff_x_ratio= diff_x_conts/mean_x
|
||||
|
||||
args_cont_located_excluded = args_cont_located[diff_x_ratio>=1.3]
|
||||
args_cont_located_included = args_cont_located[diff_x_ratio<1.3]
|
||||
|
||||
contours_only_text_parent_excluded = [contours_only_text_parent[ind] for ind in range(len(contours_only_text_parent)) if diff_x_ratio[ind]>=1.3]#contours_only_text_parent[diff_x_ratio>=1.3]
|
||||
contours_only_text_parent_included = [contours_only_text_parent[ind] for ind in range(len(contours_only_text_parent)) if diff_x_ratio[ind]<1.3]#contours_only_text_parent[diff_x_ratio<1.3]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
cx_conts_excluded = [cx_conts[ind] for ind in range(len(cx_conts)) if diff_x_ratio[ind]>=1.3]#cx_conts[diff_x_ratio>=1.3]
|
||||
cx_conts_included = [cx_conts[ind] for ind in range(len(cx_conts)) if diff_x_ratio[ind]<1.3]#cx_conts[diff_x_ratio<1.3]
|
||||
|
||||
cy_conts_excluded = [cy_conts[ind] for ind in range(len(cy_conts)) if diff_x_ratio[ind]>=1.3]#cy_conts[diff_x_ratio>=1.3]
|
||||
cy_conts_included = [cy_conts[ind] for ind in range(len(cy_conts)) if diff_x_ratio[ind]<1.3]#cy_conts[diff_x_ratio<1.3]
|
||||
|
||||
#print(diff_x_ratio, 'ratio')
|
||||
text_regions_p = text_regions_p.astype('uint8')
|
||||
|
||||
if len(contours_only_text_parent_excluded)>0:
|
||||
textregion_par = np.zeros((text_regions_p.shape[0], text_regions_p.shape[1])).astype('uint8')
|
||||
textregion_par = cv2.fillPoly(textregion_par, pts=contours_only_text_parent_included, color=(1,1))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
textregion_par = (text_regions_p[:,:]==1)*1
|
||||
textregion_par = textregion_par.astype('uint8')
|
||||
|
||||
text_regions_p_textregions_dilated = cv2.erode(textregion_par , hor_kernel, iterations=2)
|
||||
text_regions_p_textregions_dilated = cv2.dilate(text_regions_p_textregions_dilated , ver_kernel, iterations=4)
|
||||
text_regions_p_textregions_dilated = cv2.erode(text_regions_p_textregions_dilated , hor_kernel, iterations=1)
|
||||
text_regions_p_textregions_dilated = cv2.dilate(text_regions_p_textregions_dilated , ver_kernel, iterations=5)
|
||||
text_regions_p_textregions_dilated[text_regions_p[:,:]>1] = 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
contours_only_dilated, hir_on_text_dilated = return_contours_of_image(text_regions_p_textregions_dilated)
|
||||
contours_only_dilated = return_parent_contours(contours_only_dilated, hir_on_text_dilated)
|
||||
|
||||
indexes_of_located_cont, center_x_coordinates_of_located, center_y_coordinates_of_located = self.return_indexes_of_contours_loctaed_inside_another_list_of_contours(contours_only_dilated, contours_only_text_parent_included, cx_conts_included, cy_conts_included, args_cont_located_included)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if len(args_cont_located_excluded)>0:
|
||||
for ind in args_cont_located_excluded:
|
||||
indexes_of_located_cont.append(np.array([ind]))
|
||||
contours_only_dilated.append(contours_only_text_parent[ind])
|
||||
center_y_coordinates_of_located.append(0)
|
||||
|
||||
array_list = [np.array([elem]) if isinstance(elem, int) else elem for elem in indexes_of_located_cont]
|
||||
flattened_array = np.concatenate([arr.ravel() for arr in array_list])
|
||||
#print(len( np.unique(flattened_array)), 'indexes_of_located_cont uniques')
|
||||
|
||||
missing_textregions = list( set(np.array(range(len(contours_only_text_parent))) ) - set(np.unique(flattened_array)) )
|
||||
#print(missing_textregions, 'missing_textregions')
|
||||
|
||||
for ind in missing_textregions:
|
||||
indexes_of_located_cont.append(np.array([ind]))
|
||||
contours_only_dilated.append(contours_only_text_parent[ind])
|
||||
center_y_coordinates_of_located.append(0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if contours_only_text_parent_h:
|
||||
for vi in range(len(contours_only_text_parent_h)):
|
||||
indexes_of_located_cont.append(int(vi+len(contours_only_text_parent)))
|
||||
|
||||
array_list = [np.array([elem]) if isinstance(elem, int) else elem for elem in indexes_of_located_cont]
|
||||
flattened_array = np.concatenate([arr.ravel() for arr in array_list])
|
||||
|
||||
y_len = text_regions_p.shape[0]
|
||||
x_len = text_regions_p.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
img_poly = np.zeros((y_len,x_len), dtype='uint8')
|
||||
###img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==1] = 1
|
||||
###img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==2] = 2
|
||||
###img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==3] = 4
|
||||
###img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==6] = 5
|
||||
|
||||
##img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==1] = 1
|
||||
##img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==2] = 2
|
||||
##img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==3] = 3
|
||||
##img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==4] = 4
|
||||
##img_poly[text_regions_p[:,:]==5] = 5
|
||||
|
||||
img_poly = np.copy(text_regions_p)
|
||||
|
||||
img_header_and_sep = np.zeros((y_len,x_len), dtype='uint8')
|
||||
if contours_only_text_parent_h:
|
||||
_, cy_main, x_min_main, x_max_main, y_min_main, y_max_main, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(
|
||||
contours_only_text_parent_h)
|
||||
for j in range(len(cy_main)):
|
||||
img_header_and_sep[int(y_max_main[j]):int(y_max_main[j])+12,
|
||||
int(x_min_main[j]):int(x_max_main[j])] = 1
|
||||
co_text_all_org = contours_only_text_parent + contours_only_text_parent_h
|
||||
if len(contours_only_text_parent)>min_cont_size_to_be_dilated and self.light_version:
|
||||
co_text_all = contours_only_dilated + contours_only_text_parent_h
|
||||
else:
|
||||
co_text_all = contours_only_text_parent + contours_only_text_parent_h
|
||||
else:
|
||||
co_text_all_org = contours_only_text_parent
|
||||
if len(contours_only_text_parent)>min_cont_size_to_be_dilated and self.light_version:
|
||||
co_text_all = contours_only_dilated
|
||||
else:
|
||||
co_text_all = contours_only_text_parent
|
||||
|
||||
if not len(co_text_all):
|
||||
return [], []
|
||||
|
||||
labels_con = np.zeros((int(y_len /6.), int(x_len/6.), len(co_text_all)), dtype=bool)
|
||||
|
||||
co_text_all = [(i/6).astype(int) for i in co_text_all]
|
||||
for i in range(len(co_text_all)):
|
||||
img = labels_con[:,:,i].astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
#img = cv2.resize(img, (int(img.shape[1]/6), int(img.shape[0]/6)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(img, pts=[co_text_all[i]], color=(1,))
|
||||
labels_con[:,:,i] = img
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
labels_con = resize_image(labels_con.astype(np.uint8), height1, width1).astype(bool)
|
||||
img_header_and_sep = resize_image(img_header_and_sep, height1, width1)
|
||||
img_poly = resize_image(img_poly, height3, width3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
input_1 = np.zeros((inference_bs, height1, width1, 3))
|
||||
ordered = [list(range(len(co_text_all)))]
|
||||
index_update = 0
|
||||
#print(labels_con.shape[2],"number of regions for reading order")
|
||||
while index_update>=0:
|
||||
ij_list = ordered.pop(index_update)
|
||||
i = ij_list.pop(0)
|
||||
|
||||
ante_list = []
|
||||
post_list = []
|
||||
tot_counter = 0
|
||||
batch = []
|
||||
for j in ij_list:
|
||||
img1 = labels_con[:,:,i].astype(float)
|
||||
img2 = labels_con[:,:,j].astype(float)
|
||||
img1[img_poly==5] = 2
|
||||
img2[img_poly==5] = 2
|
||||
img1[img_header_and_sep==1] = 3
|
||||
img2[img_header_and_sep==1] = 3
|
||||
|
||||
input_1[len(batch), :, :, 0] = img1 / 3.
|
||||
input_1[len(batch), :, :, 2] = img2 / 3.
|
||||
input_1[len(batch), :, :, 1] = img_poly / 5.
|
||||
|
||||
tot_counter += 1
|
||||
batch.append(j)
|
||||
if tot_counter % inference_bs == 0 or tot_counter == len(ij_list):
|
||||
y_pr = self.model_reading_order.predict(input_1 , verbose=0)
|
||||
for jb, j in enumerate(batch):
|
||||
if y_pr[jb][0]>=0.5:
|
||||
post_list.append(j)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ante_list.append(j)
|
||||
batch = []
|
||||
|
||||
if len(ante_list):
|
||||
ordered.insert(index_update, ante_list)
|
||||
index_update += 1
|
||||
ordered.insert(index_update, [i])
|
||||
if len(post_list):
|
||||
ordered.insert(index_update + 1, post_list)
|
||||
|
||||
index_update = -1
|
||||
for index_next, ij_list in enumerate(ordered):
|
||||
if len(ij_list) > 1:
|
||||
index_update = index_next
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
ordered = [i[0] for i in ordered]
|
||||
|
||||
##id_all_text = np.array(id_all_text)[index_sort]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if len(contours_only_text_parent)>min_cont_size_to_be_dilated and self.light_version:
|
||||
org_contours_indexes = []
|
||||
for ind in range(len(ordered)):
|
||||
region_with_curr_order = ordered[ind]
|
||||
if region_with_curr_order < len(contours_only_dilated):
|
||||
if np.isscalar(indexes_of_located_cont[region_with_curr_order]):
|
||||
org_contours_indexes = org_contours_indexes + [indexes_of_located_cont[region_with_curr_order]]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
arg_sort_located_cont = np.argsort(center_y_coordinates_of_located[region_with_curr_order])
|
||||
org_contours_indexes = org_contours_indexes + list(np.array(indexes_of_located_cont[region_with_curr_order])[arg_sort_located_cont]) ##org_contours_indexes + list (
|
||||
else:
|
||||
org_contours_indexes = org_contours_indexes + [indexes_of_located_cont[region_with_curr_order]]
|
||||
|
||||
region_ids = ['region_%04d' % i for i in range(len(co_text_all_org))]
|
||||
return org_contours_indexes, region_ids
|
||||
else:
|
||||
region_ids = ['region_%04d' % i for i in range(len(co_text_all_org))]
|
||||
return ordered, region_ids
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self,
|
||||
overwrite: bool = False,
|
||||
xml_filename: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
dir_in: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
dir_out: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get image and scales, then extract the page of scanned image
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("enter run")
|
||||
t0_tot = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
if dir_in:
|
||||
ls_xmls = [os.path.join(dir_in, xml_filename)
|
||||
for xml_filename in filter(is_xml_filename,
|
||||
os.listdir(dir_in))]
|
||||
elif xml_filename:
|
||||
ls_xmls = [xml_filename]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError("run requires either a single image filename or a directory")
|
||||
|
||||
for xml_filename in ls_xmls:
|
||||
self.logger.info(xml_filename)
|
||||
t0 = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
file_name = Path(xml_filename).stem
|
||||
(tree_xml, root_xml, bb_coord_printspace, id_paragraph, id_header,
|
||||
co_text_paragraph, co_text_header, tot_region_ref,
|
||||
x_len, y_len, index_tot_regions, img_poly) = self.read_xml(xml_filename)
|
||||
|
||||
id_all_text = id_paragraph + id_header
|
||||
|
||||
order_text_new, id_of_texts_tot = self.do_order_of_regions_with_model(co_text_paragraph, co_text_header, img_poly[:,:,0])
|
||||
|
||||
id_all_text = np.array(id_all_text)[order_text_new]
|
||||
|
||||
alltags=[elem.tag for elem in root_xml.iter()]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
link=alltags[0].split('}')[0]+'}'
|
||||
name_space = alltags[0].split('}')[0]
|
||||
name_space = name_space.split('{')[1]
|
||||
|
||||
page_element = root_xml.find(link+'Page')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
old_ro = root_xml.find(".//{*}ReadingOrder")
|
||||
|
||||
if old_ro is not None:
|
||||
page_element.remove(old_ro)
|
||||
|
||||
#print(old_ro, 'old_ro')
|
||||
ro_subelement = ET.Element('ReadingOrder')
|
||||
|
||||
ro_subelement2 = ET.SubElement(ro_subelement, 'OrderedGroup')
|
||||
ro_subelement2.set('id', "ro357564684568544579089")
|
||||
|
||||
for index, id_text in enumerate(id_all_text):
|
||||
new_element_2 = ET.SubElement(ro_subelement2, 'RegionRefIndexed')
|
||||
new_element_2.set('regionRef', id_all_text[index])
|
||||
new_element_2.set('index', str(index))
|
||||
|
||||
if (link+'PrintSpace' in alltags) or (link+'Border' in alltags):
|
||||
page_element.insert(1, ro_subelement)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
page_element.insert(0, ro_subelement)
|
||||
|
||||
alltags=[elem.tag for elem in root_xml.iter()]
|
||||
|
||||
ET.register_namespace("",name_space)
|
||||
tree_xml.write(os.path.join(dir_out, file_name+'.xml'),
|
||||
xml_declaration=True,
|
||||
method='xml',
|
||||
encoding="utf-8",
|
||||
default_namespace=None)
|
||||
|
||||
#sys.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"version": "0.6.0",
|
||||
"git_url": "https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah",
|
||||
"dockerhub": "ocrd/eynollah",
|
||||
"tools": {
|
||||
"ocrd-eynollah-segment": {
|
||||
"executable": "ocrd-eynollah-segment",
|
||||
"categories": ["Layout analysis"],
|
||||
"description": "Segment page into regions and lines and do reading order detection with eynollah",
|
||||
"input_file_grp_cardinality": 1,
|
||||
"output_file_grp_cardinality": 1,
|
||||
"steps": ["layout/segmentation/region", "layout/segmentation/line"],
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
"models": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"format": "uri",
|
||||
"content-type": "text/directory",
|
||||
"cacheable": true,
|
||||
"description": "Directory containing models to be used (See https://qurator-data.de/eynollah)",
|
||||
"required": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dpi": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"format": "float",
|
||||
"description": "pixel density in dots per inch (overrides any meta-data in the images); ignored if <= 0 (with fall-back 230)",
|
||||
"default": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"full_layout": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": true,
|
||||
"description": "Try to detect all element subtypes, including drop-caps and headings"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"light_version": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": true,
|
||||
"description": "Try to detect all element subtypes in light version (faster+simpler method for main region detection and deskewing)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"textline_light": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": true,
|
||||
"description": "Light version need textline light. If this parameter set to true, this tool will try to return contoure of textlines instead of rectangle bounding box of textline with a faster method."
|
||||
},
|
||||
"tables": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "Try to detect table regions"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"curved_line": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "try to return contour of textlines instead of just rectangle bounding box. Needs more processing time"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ignore_page_extraction": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "if this parameter set to true, this tool would ignore page extraction"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"allow_scaling": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "check the resolution against the number of detected columns and if needed, scale the image up or down during layout detection (heuristic to improve quality and performance)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"allow_enhancement": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "if this parameter set to true, this tool would check that input image need resizing and enhancement or not."
|
||||
},
|
||||
"right_to_left": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "if this parameter set to true, this tool will extract right-to-left reading order."
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers_off": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "ignore the special role of headings during reading order detection"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"reading_order_machine_based": {
|
||||
"type": "boolean",
|
||||
"default": false,
|
||||
"description": "use data-driven (rather than rule-based) reading order detection"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"resources": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "https://zenodo.org/records/17194824/files/models_layout_v0_5_0.tar.gz?download=1",
|
||||
"name": "models_layout_v0_5_0",
|
||||
"type": "archive",
|
||||
"path_in_archive": "models_layout_v0_5_0",
|
||||
"size": 3525684179,
|
||||
"description": "Models for layout detection, reading order detection, textline detection, page extraction, column classification, table detection, binarization, image enhancement",
|
||||
"version_range": ">= v0.5.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"description": "models for eynollah (TensorFlow SavedModel format)",
|
||||
"url": "https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/releases/download/v0.3.1/models_eynollah.tar.gz",
|
||||
"name": "default",
|
||||
"size": 1894627041,
|
||||
"type": "archive",
|
||||
"path_in_archive": "models_eynollah",
|
||||
"version_range": ">= v0.3.0, < v0.5.0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ocrd-sbb-binarize": {
|
||||
"executable": "ocrd-sbb-binarize",
|
||||
"description": "Pixelwise binarization with selectional auto-encoders in Keras",
|
||||
"categories": ["Image preprocessing"],
|
||||
"steps": ["preprocessing/optimization/binarization"],
|
||||
"input_file_grp_cardinality": 1,
|
||||
"output_file_grp_cardinality": 1,
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
"operation_level": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"enum": ["page", "region"],
|
||||
"default": "page",
|
||||
"description": "PAGE XML hierarchy level to operate on"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"model": {
|
||||
"description": "Directory containing HDF5 or SavedModel/ProtoBuf models. Can be an absolute path or a path relative to the OCR-D resource location, the current working directory or the $SBB_BINARIZE_DATA environment variable (if set)",
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"format": "uri",
|
||||
"content-type": "text/directory",
|
||||
"required": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"resources": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "https://github.com/qurator-spk/sbb_binarization/releases/download/v0.0.11/saved_model_2020_01_16.zip",
|
||||
"name": "default",
|
||||
"type": "archive",
|
||||
"path_in_archive": "saved_model_2020_01_16",
|
||||
"size": 563147331,
|
||||
"description": "default models provided by github.com/qurator-spk (SavedModel format)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "https://github.com/qurator-spk/sbb_binarization/releases/download/v0.0.11/saved_model_2021_03_09.zip",
|
||||
"name": "default-2021-03-09",
|
||||
"type": "archive",
|
||||
"path_in_archive": ".",
|
||||
"size": 133230419,
|
||||
"description": "updated default models provided by github.com/qurator-spk (SavedModel format)"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
|
|||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from click import command
|
||||
|
||||
from ocrd import Processor, OcrdPageResult, OcrdPageResultImage
|
||||
from ocrd_models.ocrd_page import OcrdPage, AlternativeImageType
|
||||
from ocrd.decorators import ocrd_cli_options, ocrd_cli_wrap_processor
|
||||
|
||||
from .sbb_binarize import SbbBinarizer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def cv2pil(img):
|
||||
return Image.fromarray(img.astype('uint8'))
|
||||
|
||||
def pil2cv(img):
|
||||
# from ocrd/workspace.py
|
||||
color_conversion = cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR if img.mode in ('1', 'L') else cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR
|
||||
pil_as_np_array = np.array(img).astype('uint8') if img.mode == '1' else np.array(img)
|
||||
return cv2.cvtColor(pil_as_np_array, color_conversion)
|
||||
|
||||
class SbbBinarizeProcessor(Processor):
|
||||
# already employs GPU (without singleton process atm)
|
||||
max_workers = 1
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def executable(self):
|
||||
return 'ocrd-sbb-binarize'
|
||||
|
||||
def setup(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set up the model prior to processing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# resolve relative path via OCR-D ResourceManager
|
||||
model_path = self.resolve_resource(self.parameter['model'])
|
||||
self.binarizer = SbbBinarizer(model_dir=model_path, logger=self.logger)
|
||||
|
||||
def process_page_pcgts(self, *input_pcgts: Optional[OcrdPage], page_id: Optional[str] = None) -> OcrdPageResult:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Binarize images with sbb_binarization (based on selectional auto-encoders).
|
||||
|
||||
For each page of the input file group, open and deserialize input PAGE-XML
|
||||
and its respective images. Then iterate over the element hierarchy down to
|
||||
the requested ``operation_level``.
|
||||
|
||||
For each segment element, retrieve a raw (non-binarized) segment image
|
||||
according to the layout annotation (from an existing ``AlternativeImage``,
|
||||
or by cropping into the higher-level images, and deskewing when applicable).
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the image to the binarizer (which runs in fixed-size windows/patches
|
||||
across the image and stitches the results together).
|
||||
|
||||
Serialize the resulting bilevel image as PNG file and add it to the output
|
||||
file group (with file ID suffix ``.IMG-BIN``) along with the output PAGE-XML
|
||||
(referencing it as new ``AlternativeImage`` for the segment element).
|
||||
|
||||
Produce a new PAGE output file by serialising the resulting hierarchy.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert input_pcgts
|
||||
assert input_pcgts[0]
|
||||
assert self.parameter
|
||||
oplevel = self.parameter['operation_level']
|
||||
pcgts = input_pcgts[0]
|
||||
result = OcrdPageResult(pcgts)
|
||||
page = pcgts.get_Page()
|
||||
page_image, page_xywh, _ = self.workspace.image_from_page(
|
||||
page, page_id, feature_filter='binarized')
|
||||
|
||||
if oplevel == 'page':
|
||||
self.logger.info("Binarizing on 'page' level in page '%s'", page_id)
|
||||
page_image_bin = cv2pil(self.binarizer.run(image=pil2cv(page_image), use_patches=True))
|
||||
# update PAGE (reference the image file):
|
||||
page_image_ref = AlternativeImageType(comments=page_xywh['features'] + ',binarized,clipped')
|
||||
page.add_AlternativeImage(page_image_ref)
|
||||
result.images.append(OcrdPageResultImage(page_image_bin, '.IMG-BIN', page_image_ref))
|
||||
|
||||
elif oplevel == 'region':
|
||||
regions = page.get_AllRegions(['Text', 'Table'], depth=1)
|
||||
if not regions:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Page '%s' contains no text/table regions", page_id)
|
||||
for region in regions:
|
||||
region_image, region_xywh = self.workspace.image_from_segment(
|
||||
region, page_image, page_xywh, feature_filter='binarized')
|
||||
region_image_bin = cv2pil(self.binarizer.run(image=pil2cv(region_image), use_patches=True))
|
||||
# update PAGE (reference the image file):
|
||||
region_image_ref = AlternativeImageType(comments=region_xywh['features'] + ',binarized')
|
||||
region.add_AlternativeImage(region_image_ref)
|
||||
result.images.append(OcrdPageResultImage(region_image_bin, region.id + '.IMG-BIN', region_image_ref))
|
||||
|
||||
elif oplevel == 'line':
|
||||
lines = page.get_AllTextLines()
|
||||
if not lines:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Page '%s' contains no text lines", page_id)
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
line_image, line_xywh = self.workspace.image_from_segment(line, page_image, page_xywh, feature_filter='binarized')
|
||||
line_image_bin = cv2pil(self.binarizer.run(image=pil2cv(line_image), use_patches=True))
|
||||
# update PAGE (reference the image file):
|
||||
line_image_ref = AlternativeImageType(comments=line_xywh['features'] + ',binarized')
|
||||
line.add_AlternativeImage(region_image_ref)
|
||||
result.images.append(OcrdPageResultImage(line_image_bin, line.id + '.IMG-BIN', line_image_ref))
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
@command()
|
||||
@ocrd_cli_options
|
||||
def main(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
return ocrd_cli_wrap_processor(SbbBinarizeProcessor, *args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
|||
from functools import cached_property
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
from ocrd_models import OcrdPage
|
||||
from ocrd import OcrdPageResultImage, Processor, OcrdPageResult
|
||||
|
||||
from .eynollah import Eynollah, EynollahXmlWriter
|
||||
|
||||
class EynollahProcessor(Processor):
|
||||
# already employs background CPU multiprocessing per page
|
||||
# already employs GPU (without singleton process atm)
|
||||
max_workers = 1
|
||||
|
||||
@cached_property
|
||||
def executable(self) -> str:
|
||||
return 'ocrd-eynollah-segment'
|
||||
|
||||
def setup(self) -> None:
|
||||
assert self.parameter
|
||||
if self.parameter['textline_light'] != self.parameter['light_version']:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Error: You must set or unset both parameter 'textline_light' (to enable light textline detection), "
|
||||
"and parameter 'light_version' (faster+simpler method for main region detection and deskewing)")
|
||||
self.eynollah = Eynollah(
|
||||
self.resolve_resource(self.parameter['models']),
|
||||
allow_enhancement=self.parameter['allow_enhancement'],
|
||||
curved_line=self.parameter['curved_line'],
|
||||
right2left=self.parameter['right_to_left'],
|
||||
reading_order_machine_based=self.parameter['reading_order_machine_based'],
|
||||
ignore_page_extraction=self.parameter['ignore_page_extraction'],
|
||||
light_version=self.parameter['light_version'],
|
||||
textline_light=self.parameter['textline_light'],
|
||||
full_layout=self.parameter['full_layout'],
|
||||
allow_scaling=self.parameter['allow_scaling'],
|
||||
headers_off=self.parameter['headers_off'],
|
||||
tables=self.parameter['tables'],
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.eynollah.logger = self.logger
|
||||
self.eynollah.plotter = None
|
||||
|
||||
def shutdown(self):
|
||||
if hasattr(self, 'eynollah'):
|
||||
del self.eynollah
|
||||
|
||||
def process_page_pcgts(self, *input_pcgts: Optional[OcrdPage], page_id: Optional[str] = None) -> OcrdPageResult:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Performs cropping, region and line segmentation with Eynollah.
|
||||
|
||||
For each page, open and deserialize PAGE input file (from existing
|
||||
PAGE file in the input fileGrp, or generated from image file).
|
||||
Retrieve its respective page-level image (ignoring annotation that
|
||||
already added `binarized`, `cropped` or `deskewed` features).
|
||||
|
||||
Set up Eynollah to detect regions and lines, and add each one to the
|
||||
page, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
\b
|
||||
- If ``tables``, try to detect table blocks and add them as TableRegion.
|
||||
- If ``full_layout``, then in addition to paragraphs and marginals, also
|
||||
try to detect drop capitals and headings.
|
||||
- If ``ignore_page_extraction``, then attempt no cropping of the page.
|
||||
- If ``curved_line``, then compute contour polygons for text lines
|
||||
instead of simple bounding boxes.
|
||||
- If ``reading_order_machine_based``, then detect reading order via
|
||||
data-driven model instead of geometrical heuristics.
|
||||
|
||||
Produce a new output file by serialising the resulting hierarchy.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert input_pcgts
|
||||
assert input_pcgts[0]
|
||||
assert self.parameter
|
||||
pcgts = input_pcgts[0]
|
||||
result = OcrdPageResult(pcgts)
|
||||
page = pcgts.get_Page()
|
||||
page_image, _, _ = self.workspace.image_from_page(
|
||||
page, page_id,
|
||||
# avoid any features that would change the coordinate system: cropped,deskewed
|
||||
# (the PAGE builder merely adds regions, so afterwards we would not know which to transform)
|
||||
# also avoid binarization as models usually fare better on grayscale/RGB
|
||||
feature_filter='cropped,deskewed,binarized')
|
||||
if hasattr(page_image, 'filename'):
|
||||
image_filename = page_image.filename
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image_filename = "dummy" # will be replaced by ocrd.Processor.process_page_file
|
||||
result.images.append(OcrdPageResultImage(page_image, '.IMG', page)) # mark as new original
|
||||
# FIXME: mask out already existing regions (incremental segmentation)
|
||||
self.eynollah.cache_images(
|
||||
image_pil=page_image,
|
||||
dpi=self.parameter['dpi'],
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.eynollah.writer = EynollahXmlWriter(
|
||||
dir_out=None,
|
||||
image_filename=image_filename,
|
||||
curved_line=self.eynollah.curved_line,
|
||||
textline_light=self.eynollah.textline_light,
|
||||
pcgts=pcgts)
|
||||
self.eynollah.run_single()
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,378 +0,0 @@
|
|||
"""
|
||||
Tool to load model and binarize a given image.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from glob import glob
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import tf_disable_interactive_logs
|
||||
tf_disable_interactive_logs()
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.keras import backend as tensorflow_backend
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils import is_image_filename
|
||||
|
||||
def resize_image(img_in, input_height, input_width):
|
||||
return cv2.resize(img_in, (input_width, input_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
|
||||
class SbbBinarizer:
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, model_dir, logger=None):
|
||||
self.model_dir = model_dir
|
||||
self.log = logger if logger else logging.getLogger('SbbBinarizer')
|
||||
|
||||
self.start_new_session()
|
||||
|
||||
self.model_files = glob(self.model_dir+"/*/", recursive = True)
|
||||
|
||||
self.models = []
|
||||
for model_file in self.model_files:
|
||||
self.models.append(self.load_model(model_file))
|
||||
|
||||
def start_new_session(self):
|
||||
config = tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()
|
||||
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
|
||||
|
||||
self.session = tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config) # tf.InteractiveSession()
|
||||
tensorflow_backend.set_session(self.session)
|
||||
|
||||
def end_session(self):
|
||||
tensorflow_backend.clear_session()
|
||||
self.session.close()
|
||||
del self.session
|
||||
|
||||
def load_model(self, model_name):
|
||||
model = load_model(os.path.join(self.model_dir, model_name), compile=False)
|
||||
model_height = model.layers[len(model.layers)-1].output_shape[1]
|
||||
model_width = model.layers[len(model.layers)-1].output_shape[2]
|
||||
n_classes = model.layers[len(model.layers)-1].output_shape[3]
|
||||
return model, model_height, model_width, n_classes
|
||||
|
||||
def predict(self, model_in, img, use_patches, n_batch_inference=5):
|
||||
tensorflow_backend.set_session(self.session)
|
||||
model, model_height, model_width, n_classes = model_in
|
||||
|
||||
img_org_h = img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_org_w = img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
if img.shape[0] < model_height and img.shape[1] >= model_width:
|
||||
img_padded = np.zeros(( model_height, img.shape[1], img.shape[2] ))
|
||||
|
||||
index_start_h = int( abs( img.shape[0] - model_height) /2.)
|
||||
index_start_w = 0
|
||||
|
||||
img_padded [ index_start_h: index_start_h+img.shape[0], :, : ] = img[:,:,:]
|
||||
|
||||
elif img.shape[0] >= model_height and img.shape[1] < model_width:
|
||||
img_padded = np.zeros(( img.shape[0], model_width, img.shape[2] ))
|
||||
|
||||
index_start_h = 0
|
||||
index_start_w = int( abs( img.shape[1] - model_width) /2.)
|
||||
|
||||
img_padded [ :, index_start_w: index_start_w+img.shape[1], : ] = img[:,:,:]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
elif img.shape[0] < model_height and img.shape[1] < model_width:
|
||||
img_padded = np.zeros(( model_height, model_width, img.shape[2] ))
|
||||
|
||||
index_start_h = int( abs( img.shape[0] - model_height) /2.)
|
||||
index_start_w = int( abs( img.shape[1] - model_width) /2.)
|
||||
|
||||
img_padded [ index_start_h: index_start_h+img.shape[0], index_start_w: index_start_w+img.shape[1], : ] = img[:,:,:]
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_start_h = 0
|
||||
index_start_w = 0
|
||||
img_padded = np.copy(img)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img = np.copy(img_padded)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if use_patches:
|
||||
|
||||
margin = int(0.1 * model_width)
|
||||
|
||||
width_mid = model_width - 2 * margin
|
||||
height_mid = model_height - 2 * margin
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img = img / float(255.0)
|
||||
|
||||
img_h = img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_w = img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = np.zeros((img_h, img_w, 3))
|
||||
mask_true = np.zeros((img_h, img_w))
|
||||
nxf = img_w / float(width_mid)
|
||||
nyf = img_h / float(height_mid)
|
||||
|
||||
if nxf > int(nxf):
|
||||
nxf = int(nxf) + 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
nxf = int(nxf)
|
||||
|
||||
if nyf > int(nyf):
|
||||
nyf = int(nyf) + 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
nyf = int(nyf)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
list_i_s = []
|
||||
list_j_s = []
|
||||
list_x_u = []
|
||||
list_x_d = []
|
||||
list_y_u = []
|
||||
list_y_d = []
|
||||
|
||||
batch_indexer = 0
|
||||
|
||||
img_patch = np.zeros((n_batch_inference, model_height, model_width,3))
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(nxf):
|
||||
for j in range(nyf):
|
||||
|
||||
if i == 0:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + model_width
|
||||
elif i > 0:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + model_width
|
||||
|
||||
if j == 0:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + model_height
|
||||
elif j > 0:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + model_height
|
||||
|
||||
if index_x_u > img_w:
|
||||
index_x_u = img_w
|
||||
index_x_d = img_w - model_width
|
||||
if index_y_u > img_h:
|
||||
index_y_u = img_h
|
||||
index_y_d = img_h - model_height
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
list_i_s.append(i)
|
||||
list_j_s.append(j)
|
||||
list_x_u.append(index_x_u)
|
||||
list_x_d.append(index_x_d)
|
||||
list_y_d.append(index_y_d)
|
||||
list_y_u.append(index_y_u)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_patch[batch_indexer,:,:,:] = img[index_y_d:index_y_u, index_x_d:index_x_u, :]
|
||||
|
||||
batch_indexer = batch_indexer + 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if batch_indexer == n_batch_inference:
|
||||
|
||||
label_p_pred = model.predict(img_patch,verbose=0)
|
||||
|
||||
seg = np.argmax(label_p_pred, axis=3)
|
||||
|
||||
#print(seg.shape, len(seg), len(list_i_s))
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_inside_batch = 0
|
||||
for i_batch, j_batch in zip(list_i_s, list_j_s):
|
||||
seg_in = seg[indexer_inside_batch,:,:]
|
||||
seg_color = np.repeat(seg_in[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
|
||||
index_y_u_in = list_y_u[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
index_y_d_in = list_y_d[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
index_x_u_in = list_x_u[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
index_x_d_in = list_x_d[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
if i_batch == 0 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[0 : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, 0 : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0 : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + 0 : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - 0, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - 0, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - 0, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - 0, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == 0 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - 0, 0 : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - 0, index_x_d_in + 0 : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[0 : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - 0, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0 : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - 0, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == 0 and j_batch != 0 and j_batch != nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, 0 : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + 0 : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch != 0 and j_batch != nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - 0, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - 0, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch != 0 and i_batch != nxf - 1 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[0 : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0 : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch != 0 and i_batch != nxf - 1 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - 0, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - 0, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
else:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_inside_batch = indexer_inside_batch +1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
list_i_s = []
|
||||
list_j_s = []
|
||||
list_x_u = []
|
||||
list_x_d = []
|
||||
list_y_u = []
|
||||
list_y_d = []
|
||||
|
||||
batch_indexer = 0
|
||||
|
||||
img_patch = np.zeros((n_batch_inference, model_height, model_width,3))
|
||||
|
||||
elif i==(nxf-1) and j==(nyf-1):
|
||||
label_p_pred = model.predict(img_patch,verbose=0)
|
||||
|
||||
seg = np.argmax(label_p_pred, axis=3)
|
||||
|
||||
#print(seg.shape, len(seg), len(list_i_s))
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_inside_batch = 0
|
||||
for i_batch, j_batch in zip(list_i_s, list_j_s):
|
||||
seg_in = seg[indexer_inside_batch,:,:]
|
||||
seg_color = np.repeat(seg_in[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
|
||||
index_y_u_in = list_y_u[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
index_y_d_in = list_y_d[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
index_x_u_in = list_x_u[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
index_x_d_in = list_x_d[indexer_inside_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
if i_batch == 0 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[0 : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, 0 : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0 : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + 0 : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - 0, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - 0, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - 0, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - 0, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == 0 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - 0, 0 : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - 0, index_x_d_in + 0 : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[0 : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - 0, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0 : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - 0, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == 0 and j_batch != 0 and j_batch != nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, 0 : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + 0 : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch == nxf - 1 and j_batch != 0 and j_batch != nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - 0, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - 0, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch != 0 and i_batch != nxf - 1 and j_batch == 0:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[0 : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + 0 : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
elif i_batch != 0 and i_batch != nxf - 1 and j_batch == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - 0, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - 0, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
else:
|
||||
seg_color = seg_color[margin : seg_color.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg_color.shape[1] - margin, :]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d_in + margin : index_y_u_in - margin, index_x_d_in + margin : index_x_u_in - margin, :] = seg_color
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_inside_batch = indexer_inside_batch +1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
list_i_s = []
|
||||
list_j_s = []
|
||||
list_x_u = []
|
||||
list_x_d = []
|
||||
list_y_u = []
|
||||
list_y_d = []
|
||||
|
||||
batch_indexer = 0
|
||||
|
||||
img_patch = np.zeros((n_batch_inference, model_height, model_width,3))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = prediction_true[index_start_h: index_start_h+img_org_h, index_start_w: index_start_w+img_org_w,:]
|
||||
prediction_true = prediction_true.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_h_page = img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_w_page = img.shape[1]
|
||||
img = img / float(255.0)
|
||||
img = resize_image(img, model_height, model_width)
|
||||
|
||||
label_p_pred = model.predict(img.reshape(1, img.shape[0], img.shape[1], img.shape[2]))
|
||||
|
||||
seg = np.argmax(label_p_pred, axis=3)[0]
|
||||
seg_color = np.repeat(seg[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
prediction_true = resize_image(seg_color, img_h_page, img_w_page)
|
||||
prediction_true = prediction_true.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
return prediction_true[:,:,0]
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self, image=None, image_path=None, output=None, use_patches=False, dir_in=None):
|
||||
# print(dir_in,'dir_in')
|
||||
if not dir_in:
|
||||
if (image is not None and image_path is not None) or \
|
||||
(image is None and image_path is None):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Must pass either a opencv2 image or an image_path")
|
||||
if image_path is not None:
|
||||
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
|
||||
img_last = 0
|
||||
for n, (model, model_file) in enumerate(zip(self.models, self.model_files)):
|
||||
self.log.info('Predicting with model %s [%s/%s]' % (model_file, n + 1, len(self.model_files)))
|
||||
|
||||
res = self.predict(model, image, use_patches)
|
||||
|
||||
img_fin = np.zeros((res.shape[0], res.shape[1], 3))
|
||||
res[:, :][res[:, :] == 0] = 2
|
||||
res = res - 1
|
||||
res = res * 255
|
||||
img_fin[:, :, 0] = res
|
||||
img_fin[:, :, 1] = res
|
||||
img_fin[:, :, 2] = res
|
||||
|
||||
img_fin = img_fin.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
img_fin = (res[:, :] == 0) * 255
|
||||
img_last = img_last + img_fin
|
||||
|
||||
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
|
||||
img_last[:, :][img_last[:, :] > 0] = 255
|
||||
img_last = (img_last[:, :] == 0) * 255
|
||||
if output:
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(output, img_last)
|
||||
return img_last
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ls_imgs = list(filter(is_image_filename, os.listdir(dir_in)))
|
||||
for image_name in ls_imgs:
|
||||
image_stem = image_name.split('.')[0]
|
||||
print(image_name,'image_name')
|
||||
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(dir_in,image_name) )
|
||||
img_last = 0
|
||||
for n, (model, model_file) in enumerate(zip(self.models, self.model_files)):
|
||||
self.log.info('Predicting with model %s [%s/%s]' % (model_file, n + 1, len(self.model_files)))
|
||||
|
||||
res = self.predict(model, image, use_patches)
|
||||
|
||||
img_fin = np.zeros((res.shape[0], res.shape[1], 3))
|
||||
res[:, :][res[:, :] == 0] = 2
|
||||
res = res - 1
|
||||
res = res * 255
|
||||
img_fin[:, :, 0] = res
|
||||
img_fin[:, :, 1] = res
|
||||
img_fin[:, :, 2] = res
|
||||
|
||||
img_fin = img_fin.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
img_fin = (res[:, :] == 0) * 255
|
||||
img_last = img_last + img_fin
|
||||
|
||||
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
|
||||
img_last[:, :][img_last[:, :] > 0] = 255
|
||||
img_last = (img_last[:, :] == 0) * 255
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(output, image_stem + '.png'), img_last)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import click
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
|
||||
from .models import resnet50_unet
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def configuration():
|
||||
gpu_options = tf.compat.v1.GPUOptions(allow_growth=True)
|
||||
session = tf.compat.v1.Session(config=tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
|
||||
|
||||
@click.command()
|
||||
def build_model_load_pretrained_weights_and_save():
|
||||
n_classes = 2
|
||||
input_height = 224
|
||||
input_width = 448
|
||||
weight_decay = 1e-6
|
||||
pretraining = False
|
||||
dir_of_weights = 'model_bin_sbb_ens.h5'
|
||||
|
||||
# configuration()
|
||||
|
||||
model = resnet50_unet(n_classes, input_height, input_width, weight_decay, pretraining)
|
||||
model.load_weights(dir_of_weights)
|
||||
model.save('./name_in_another_python_version.h5')
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import os
|
||||
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
|
||||
|
||||
import click
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
from .build_model_load_pretrained_weights_and_save import build_model_load_pretrained_weights_and_save
|
||||
from .generate_gt_for_training import main as generate_gt_cli
|
||||
from .inference import main as inference_cli
|
||||
from .train import ex
|
||||
|
||||
@click.command(context_settings=dict(
|
||||
ignore_unknown_options=True,
|
||||
))
|
||||
@click.argument('SACRED_ARGS', nargs=-1, type=click.UNPROCESSED)
|
||||
def train_cli(sacred_args):
|
||||
ex.run_commandline([sys.argv[0]] + list(sacred_args))
|
||||
|
||||
@click.group('training')
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
main.add_command(build_model_load_pretrained_weights_and_save)
|
||||
main.add_command(generate_gt_cli, 'generate-gt')
|
||||
main.add_command(inference_cli, 'inference')
|
||||
main.add_command(train_cli, 'train')
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,583 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import click
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from eynollah.training.gt_gen_utils import (
|
||||
filter_contours_area_of_image,
|
||||
find_format_of_given_filename_in_dir,
|
||||
find_new_features_of_contours,
|
||||
fit_text_single_line,
|
||||
get_content_of_dir,
|
||||
get_images_of_ground_truth,
|
||||
get_layout_contours_for_visualization,
|
||||
get_textline_contours_and_ocr_text,
|
||||
get_textline_contours_for_visualization,
|
||||
overlay_layout_on_image,
|
||||
read_xml,
|
||||
resize_image,
|
||||
visualize_image_from_contours,
|
||||
visualize_image_from_contours_layout
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.group()
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_xml",
|
||||
"-dx",
|
||||
help="directory of GT page-xml files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_images",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of org images. If print space cropping or scaling is needed for labels it would be great to provide the original images to apply the same function on them. So if -ps is not set true or in config files no columns_width key is given this argumnet can be ignored. File stems in this directory should be the same as those in dir_xml.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out_images",
|
||||
"-doi",
|
||||
help="directory where the output org images after undergoing a process (like print space cropping or scaling) will be written.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out",
|
||||
"-do",
|
||||
help="directory where ground truth label images would be written",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--config",
|
||||
"-cfg",
|
||||
help="config file of prefered layout or use case.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--type_output",
|
||||
"-to",
|
||||
help="this defines how output should be. A 2d image array or a 3d image array encoded with RGB color. Just pass 2d or 3d. The file will be saved one directory up. 2D image array is 3d but only information of one channel would be enough since all channels have the same values.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--printspace",
|
||||
"-ps",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, generated labels and in the case of provided org images cropping will be imposed and cropped labels and images will be written in output directories.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def pagexml2label(dir_xml,dir_out,type_output,config, printspace, dir_images, dir_out_images):
|
||||
if config:
|
||||
with open(config) as f:
|
||||
config_params = json.load(f)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("passed")
|
||||
config_params = None
|
||||
gt_list = get_content_of_dir(dir_xml)
|
||||
get_images_of_ground_truth(gt_list,dir_xml,dir_out,type_output, config, config_params, printspace, dir_images, dir_out_images)
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_imgs",
|
||||
"-dis",
|
||||
help="directory of images with high resolution.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out_images",
|
||||
"-dois",
|
||||
help="directory where degraded images will be written.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out_labels",
|
||||
"-dols",
|
||||
help="directory where original images will be written as labels.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--scales",
|
||||
"-scs",
|
||||
help="json dictionary where the scales are written.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
def image_enhancement(dir_imgs, dir_out_images, dir_out_labels, scales):
|
||||
ls_imgs = os.listdir(dir_imgs)
|
||||
with open(scales) as f:
|
||||
scale_dict = json.load(f)
|
||||
ls_scales = scale_dict['scales']
|
||||
|
||||
for img in tqdm(ls_imgs):
|
||||
img_name = img.split('.')[0]
|
||||
img_type = img.split('.')[1]
|
||||
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(dir_imgs, img))
|
||||
for i, scale in enumerate(ls_scales):
|
||||
height_sc = int(image.shape[0]*scale)
|
||||
width_sc = int(image.shape[1]*scale)
|
||||
|
||||
image_down_scaled = resize_image(image, height_sc, width_sc)
|
||||
image_back_to_org_scale = resize_image(image_down_scaled, image.shape[0], image.shape[1])
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out_images, img_name+'_'+str(i)+'.'+img_type), image_back_to_org_scale)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out_labels, img_name+'_'+str(i)+'.'+img_type), image)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_xml",
|
||||
"-dx",
|
||||
help="directory of GT page-xml files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out_modal_image",
|
||||
"-domi",
|
||||
help="directory where ground truth images would be written",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out_classes",
|
||||
"-docl",
|
||||
help="directory where ground truth classes would be written",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--input_height",
|
||||
"-ih",
|
||||
help="input height",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--input_width",
|
||||
"-iw",
|
||||
help="input width",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--min_area_size",
|
||||
"-min",
|
||||
help="min area size of regions considered for reading order training.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--min_area_early",
|
||||
"-min_early",
|
||||
help="If you have already generated a training dataset using a specific minimum area value and now wish to create a dataset with a smaller minimum area value, you can avoid regenerating the previous dataset by providing the earlier minimum area value. This will ensure that only the missing data is generated.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def machine_based_reading_order(dir_xml, dir_out_modal_image, dir_out_classes, input_height, input_width, min_area_size, min_area_early):
|
||||
xml_files_ind = os.listdir(dir_xml)
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [ind_xml for ind_xml in xml_files_ind if ind_xml.endswith('.xml')]
|
||||
input_height = int(input_height)
|
||||
input_width = int(input_width)
|
||||
min_area = float(min_area_size)
|
||||
if min_area_early:
|
||||
min_area_early = float(min_area_early)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_start= 0#55166
|
||||
max_area = 1
|
||||
#min_area = 0.0001
|
||||
|
||||
for ind_xml in tqdm(xml_files_ind):
|
||||
indexer = 0
|
||||
#print(ind_xml)
|
||||
#print('########################')
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(dir_xml,ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = ind_xml.split('.')[0]
|
||||
_, _, _, file_name, id_paragraph, id_header,co_text_paragraph,co_text_header,tot_region_ref,x_len, y_len,index_tot_regions,img_poly = read_xml(xml_file)
|
||||
|
||||
id_all_text = id_paragraph + id_header
|
||||
co_text_all = co_text_paragraph + co_text_header
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_, cy_main, x_min_main, x_max_main, y_min_main, y_max_main, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(co_text_header)
|
||||
|
||||
img_header_and_sep = np.zeros((y_len,x_len), dtype='uint8')
|
||||
|
||||
for j in range(len(cy_main)):
|
||||
img_header_and_sep[int(y_max_main[j]):int(y_max_main[j])+12,int(x_min_main[j]):int(x_max_main[j]) ] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
texts_corr_order_index = [index_tot_regions[tot_region_ref.index(i)] for i in id_all_text ]
|
||||
texts_corr_order_index_int = [int(x) for x in texts_corr_order_index]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
co_text_all, texts_corr_order_index_int, regions_ar_less_than_early_min = filter_contours_area_of_image(img_poly, co_text_all, texts_corr_order_index_int, max_area, min_area, min_area_early)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
arg_array = np.array(range(len(texts_corr_order_index_int)))
|
||||
|
||||
labels_con = np.zeros((y_len,x_len,len(arg_array)),dtype='uint8')
|
||||
for i in range(len(co_text_all)):
|
||||
img_label = np.zeros((y_len,x_len,3),dtype='uint8')
|
||||
img_label=cv2.fillPoly(img_label, pts =[co_text_all[i]], color=(1,1,1))
|
||||
|
||||
img_label[:,:,0][img_poly[:,:,0]==5] = 2
|
||||
img_label[:,:,0][img_header_and_sep[:,:]==1] = 3
|
||||
|
||||
labels_con[:,:,i] = img_label[:,:,0]
|
||||
|
||||
labels_con = resize_image(labels_con, input_height, input_width)
|
||||
img_poly = resize_image(img_poly, input_height, input_width)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(len(texts_corr_order_index_int)):
|
||||
for j in range(len(texts_corr_order_index_int)):
|
||||
if i!=j:
|
||||
if regions_ar_less_than_early_min:
|
||||
if regions_ar_less_than_early_min[i]==1:
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal = np.zeros((input_height,input_width,3)).astype(np.int8)
|
||||
final_f_name = f_name+'_'+str(indexer+indexer_start)
|
||||
order_class_condition = texts_corr_order_index_int[i]-texts_corr_order_index_int[j]
|
||||
if order_class_condition<0:
|
||||
class_type = 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
class_type = 0
|
||||
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal[:,:,0] = labels_con[:,:,i]
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal[:,:,1] = img_poly[:,:,0]
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal[:,:,2] = labels_con[:,:,j]
|
||||
|
||||
np.save(os.path.join(dir_out_classes,final_f_name+'_missed.npy' ), class_type)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out_modal_image,final_f_name+'_missed.png' ), input_multi_visual_modal)
|
||||
indexer = indexer+1
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal = np.zeros((input_height,input_width,3)).astype(np.int8)
|
||||
final_f_name = f_name+'_'+str(indexer+indexer_start)
|
||||
order_class_condition = texts_corr_order_index_int[i]-texts_corr_order_index_int[j]
|
||||
if order_class_condition<0:
|
||||
class_type = 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
class_type = 0
|
||||
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal[:,:,0] = labels_con[:,:,i]
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal[:,:,1] = img_poly[:,:,0]
|
||||
input_multi_visual_modal[:,:,2] = labels_con[:,:,j]
|
||||
|
||||
np.save(os.path.join(dir_out_classes,final_f_name+'.npy' ), class_type)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out_modal_image,final_f_name+'.png' ), input_multi_visual_modal)
|
||||
indexer = indexer+1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--xml_file",
|
||||
"-xml",
|
||||
help="xml filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_xml",
|
||||
"-dx",
|
||||
help="directory of GT page-xml files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory where plots will be written",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_imgs",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory where the overlayed plots will be written", )
|
||||
|
||||
def visualize_reading_order(xml_file, dir_xml, dir_out, dir_imgs):
|
||||
assert xml_file or dir_xml, "A single xml file -xml or a dir of xml files -dx is required not both of them"
|
||||
|
||||
if dir_xml:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = os.listdir(dir_xml)
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [ind_xml for ind_xml in xml_files_ind if ind_xml.endswith('.xml')]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [xml_file]
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_start= 0#55166
|
||||
#min_area = 0.0001
|
||||
|
||||
for ind_xml in tqdm(xml_files_ind):
|
||||
indexer = 0
|
||||
#print(ind_xml)
|
||||
#print('########################')
|
||||
#xml_file = os.path.join(dir_xml,ind_xml )
|
||||
|
||||
if dir_xml:
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(dir_xml,ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = Path(ind_xml).stem
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = Path(ind_xml).stem
|
||||
print(f_name, 'f_name')
|
||||
|
||||
#f_name = ind_xml.split('.')[0]
|
||||
_, _, _, file_name, id_paragraph, id_header,co_text_paragraph,co_text_header,tot_region_ref,x_len, y_len,index_tot_regions,img_poly = read_xml(xml_file)
|
||||
|
||||
id_all_text = id_paragraph + id_header
|
||||
co_text_all = co_text_paragraph + co_text_header
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
cx_main, cy_main, x_min_main, x_max_main, y_min_main, y_max_main, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(co_text_all)
|
||||
|
||||
texts_corr_order_index = [int(index_tot_regions[tot_region_ref.index(i)]) for i in id_all_text ]
|
||||
#texts_corr_order_index_int = [int(x) for x in texts_corr_order_index]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#cx_ordered = np.array(cx_main)[np.array(texts_corr_order_index)]
|
||||
#cx_ordered = cx_ordered.astype(np.int32)
|
||||
|
||||
cx_ordered = [int(val) for (_, val) in sorted(zip(texts_corr_order_index, cx_main), key=lambda x: \
|
||||
x[0], reverse=False)]
|
||||
#cx_ordered = cx_ordered.astype(np.int32)
|
||||
|
||||
cy_ordered = [int(val) for (_, val) in sorted(zip(texts_corr_order_index, cy_main), key=lambda x: \
|
||||
x[0], reverse=False)]
|
||||
#cy_ordered = cy_ordered.astype(np.int32)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
color = (0, 0, 255)
|
||||
thickness = 20
|
||||
if dir_imgs:
|
||||
layout = np.zeros( (y_len,x_len,3) )
|
||||
layout = cv2.fillPoly(layout, pts =co_text_all, color=(1,1,1))
|
||||
|
||||
img_file_name_with_format = find_format_of_given_filename_in_dir(dir_imgs, f_name)
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(dir_imgs, img_file_name_with_format))
|
||||
|
||||
overlayed = overlay_layout_on_image(layout, img, cx_ordered, cy_ordered, color, thickness)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out, f_name+'.png'), overlayed)
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img = np.zeros( (y_len,x_len,3) )
|
||||
img = cv2.fillPoly(img, pts =co_text_all, color=(255,0,0))
|
||||
for i in range(len(cx_ordered)-1):
|
||||
start_point = (int(cx_ordered[i]), int(cy_ordered[i]))
|
||||
end_point = (int(cx_ordered[i+1]), int(cy_ordered[i+1]))
|
||||
img = cv2.arrowedLine(img, start_point, end_point,
|
||||
color, thickness, tipLength = 0.03)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out, f_name+'.png'), img)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--xml_file",
|
||||
"-xml",
|
||||
help="xml filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_xml",
|
||||
"-dx",
|
||||
help="directory of GT page-xml files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory where plots will be written",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_imgs",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of images where textline segmentation will be overlayed", )
|
||||
|
||||
def visualize_textline_segmentation(xml_file, dir_xml, dir_out, dir_imgs):
|
||||
assert xml_file or dir_xml, "A single xml file -xml or a dir of xml files -dx is required not both of them"
|
||||
if dir_xml:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = os.listdir(dir_xml)
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [ind_xml for ind_xml in xml_files_ind if ind_xml.endswith('.xml')]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [xml_file]
|
||||
|
||||
for ind_xml in tqdm(xml_files_ind):
|
||||
indexer = 0
|
||||
#print(ind_xml)
|
||||
#print('########################')
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(dir_xml,ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = Path(ind_xml).stem
|
||||
|
||||
img_file_name_with_format = find_format_of_given_filename_in_dir(dir_imgs, f_name)
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(dir_imgs, img_file_name_with_format))
|
||||
|
||||
co_tetxlines, y_len, x_len = get_textline_contours_for_visualization(xml_file)
|
||||
|
||||
added_image = visualize_image_from_contours(co_tetxlines, img)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out, f_name+'.png'), added_image)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--xml_file",
|
||||
"-xml",
|
||||
help="xml filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_xml",
|
||||
"-dx",
|
||||
help="directory of GT page-xml files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory where plots will be written",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_imgs",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of images where textline segmentation will be overlayed", )
|
||||
|
||||
def visualize_layout_segmentation(xml_file, dir_xml, dir_out, dir_imgs):
|
||||
assert xml_file or dir_xml, "A single xml file -xml or a dir of xml files -dx is required not both of them"
|
||||
if dir_xml:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = os.listdir(dir_xml)
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [ind_xml for ind_xml in xml_files_ind if ind_xml.endswith('.xml')]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [xml_file]
|
||||
|
||||
for ind_xml in tqdm(xml_files_ind):
|
||||
indexer = 0
|
||||
#print(ind_xml)
|
||||
#print('########################')
|
||||
if dir_xml:
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(dir_xml,ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = Path(ind_xml).stem
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = Path(ind_xml).stem
|
||||
print(f_name, 'f_name')
|
||||
|
||||
img_file_name_with_format = find_format_of_given_filename_in_dir(dir_imgs, f_name)
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(dir_imgs, img_file_name_with_format))
|
||||
|
||||
co_text, co_graphic, co_sep, co_img, co_table, co_noise, y_len, x_len = get_layout_contours_for_visualization(xml_file)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
added_image = visualize_image_from_contours_layout(co_text['paragraph'], co_text['header']+co_text['heading'], co_text['drop-capital'], co_sep, co_img, co_text['marginalia'], co_table, img)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(dir_out, f_name+'.png'), added_image)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@main.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--xml_file",
|
||||
"-xml",
|
||||
help="xml filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_xml",
|
||||
"-dx",
|
||||
help="directory of GT page-xml files",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="directory where plots will be written",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def visualize_ocr_text(xml_file, dir_xml, dir_out):
|
||||
assert xml_file or dir_xml, "A single xml file -xml or a dir of xml files -dx is required not both of them"
|
||||
if dir_xml:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = os.listdir(dir_xml)
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [ind_xml for ind_xml in xml_files_ind if ind_xml.endswith('.xml')]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xml_files_ind = [xml_file]
|
||||
|
||||
font_path = "Charis-7.000/Charis-Regular.ttf" # Make sure this file exists!
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, 40)
|
||||
|
||||
for ind_xml in tqdm(xml_files_ind):
|
||||
indexer = 0
|
||||
#print(ind_xml)
|
||||
#print('########################')
|
||||
if dir_xml:
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(dir_xml,ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = Path(ind_xml).stem
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xml_file = os.path.join(ind_xml )
|
||||
f_name = Path(ind_xml).stem
|
||||
print(f_name, 'f_name')
|
||||
|
||||
co_tetxlines, y_len, x_len, ocr_texts = get_textline_contours_and_ocr_text(xml_file)
|
||||
|
||||
total_bb_coordinates = []
|
||||
|
||||
image_text = Image.new("RGB", (x_len, y_len), "white")
|
||||
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image_text)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for index, cnt in enumerate(co_tetxlines):
|
||||
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
|
||||
#total_bb_coordinates.append([x,y,w,h])
|
||||
|
||||
#fit_text_single_line
|
||||
|
||||
#x_bb = bb_ind[0]
|
||||
#y_bb = bb_ind[1]
|
||||
#w_bb = bb_ind[2]
|
||||
#h_bb = bb_ind[3]
|
||||
if ocr_texts[index]:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
is_vertical = h > 2*w # Check orientation
|
||||
font = fit_text_single_line(draw, ocr_texts[index], font_path, w, int(h*0.4) )
|
||||
|
||||
if is_vertical:
|
||||
|
||||
vertical_font = fit_text_single_line(draw, ocr_texts[index], font_path, h, int(w * 0.8))
|
||||
|
||||
text_img = Image.new("RGBA", (h, w), (255, 255, 255, 0)) # Note: dimensions are swapped
|
||||
text_draw = ImageDraw.Draw(text_img)
|
||||
text_draw.text((0, 0), ocr_texts[index], font=vertical_font, fill="black")
|
||||
|
||||
# Rotate text image by 90 degrees
|
||||
rotated_text = text_img.rotate(90, expand=1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Calculate paste position (centered in bbox)
|
||||
paste_x = x + (w - rotated_text.width) // 2
|
||||
paste_y = y + (h - rotated_text.height) // 2
|
||||
|
||||
image_text.paste(rotated_text, (paste_x, paste_y), rotated_text) # Use rotated image as mask
|
||||
else:
|
||||
text_bbox = draw.textbbox((0, 0), ocr_texts[index], font=font)
|
||||
text_width = text_bbox[2] - text_bbox[0]
|
||||
text_height = text_bbox[3] - text_bbox[1]
|
||||
|
||||
text_x = x + (w - text_width) // 2 # Center horizontally
|
||||
text_y = y + (h - text_height) // 2 # Center vertically
|
||||
|
||||
# Draw the text
|
||||
draw.text((text_x, text_y), ocr_texts[index], fill="black", font=font)
|
||||
image_text.save(os.path.join(dir_out, f_name+'.png'))
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
|
|
@ -1,680 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import sys
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
import json
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.layers import *
|
||||
import click
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.keras import backend as tensorflow_backend
|
||||
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
|
||||
|
||||
from .gt_gen_utils import (
|
||||
filter_contours_area_of_image,
|
||||
find_new_features_of_contours,
|
||||
read_xml,
|
||||
resize_image,
|
||||
update_list_and_return_first_with_length_bigger_than_one
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models import (
|
||||
PatchEncoder,
|
||||
Patches
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings():
|
||||
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
|
||||
|
||||
__doc__=\
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Tool to load model and predict for given image.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
class sbb_predict:
|
||||
def __init__(self,image, dir_in, model, task, config_params_model, patches, save, save_layout, ground_truth, xml_file, out, min_area):
|
||||
self.image=image
|
||||
self.dir_in=dir_in
|
||||
self.patches=patches
|
||||
self.save=save
|
||||
self.save_layout=save_layout
|
||||
self.model_dir=model
|
||||
self.ground_truth=ground_truth
|
||||
self.task=task
|
||||
self.config_params_model=config_params_model
|
||||
self.xml_file = xml_file
|
||||
self.out = out
|
||||
if min_area:
|
||||
self.min_area = float(min_area)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.min_area = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def resize_image(self,img_in,input_height,input_width):
|
||||
return cv2.resize( img_in, ( input_width,input_height) ,interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def color_images(self,seg):
|
||||
ann_u=range(self.n_classes)
|
||||
if len(np.shape(seg))==3:
|
||||
seg=seg[:,:,0]
|
||||
|
||||
seg_img=np.zeros((np.shape(seg)[0],np.shape(seg)[1],3)).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
for c in ann_u:
|
||||
c=int(c)
|
||||
seg_img[:,:,0][seg==c]=c
|
||||
seg_img[:,:,1][seg==c]=c
|
||||
seg_img[:,:,2][seg==c]=c
|
||||
return seg_img
|
||||
|
||||
def otsu_copy_binary(self,img):
|
||||
img_r=np.zeros((img.shape[0],img.shape[1],3))
|
||||
img1=img[:,:,0]
|
||||
|
||||
#print(img.min())
|
||||
#print(img[:,:,0].min())
|
||||
#blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5))
|
||||
#ret3,th3 = cv2.threshold(blur,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
|
||||
retval1, threshold1 = cv2.threshold(img1, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_r[:,:,0]=threshold1
|
||||
img_r[:,:,1]=threshold1
|
||||
img_r[:,:,2]=threshold1
|
||||
#img_r=img_r/float(np.max(img_r))*255
|
||||
return img_r
|
||||
|
||||
def otsu_copy(self,img):
|
||||
img_r=np.zeros((img.shape[0],img.shape[1],3))
|
||||
#img1=img[:,:,0]
|
||||
|
||||
#print(img.min())
|
||||
#print(img[:,:,0].min())
|
||||
#blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5))
|
||||
#ret3,th3 = cv2.threshold(blur,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
|
||||
_, threshold1 = cv2.threshold(img[:,:,0], 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
|
||||
_, threshold2 = cv2.threshold(img[:,:,1], 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
|
||||
_, threshold3 = cv2.threshold(img[:,:,2], 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_r[:,:,0]=threshold1
|
||||
img_r[:,:,1]=threshold2
|
||||
img_r[:,:,2]=threshold3
|
||||
###img_r=img_r/float(np.max(img_r))*255
|
||||
return img_r
|
||||
|
||||
def soft_dice_loss(self,y_true, y_pred, epsilon=1e-6):
|
||||
|
||||
axes = tuple(range(1, len(y_pred.shape)-1))
|
||||
|
||||
numerator = 2. * K.sum(y_pred * y_true, axes)
|
||||
|
||||
denominator = K.sum(K.square(y_pred) + K.square(y_true), axes)
|
||||
return 1.00 - K.mean(numerator / (denominator + epsilon)) # average over classes and batch
|
||||
|
||||
def weighted_categorical_crossentropy(self,weights=None):
|
||||
|
||||
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
labels_floats = tf.cast(y_true, tf.float32)
|
||||
per_pixel_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels_floats,logits=y_pred)
|
||||
|
||||
if weights is not None:
|
||||
weight_mask = tf.maximum(tf.reduce_max(tf.constant(
|
||||
np.array(weights, dtype=np.float32)[None, None, None])
|
||||
* labels_floats, axis=-1), 1.0)
|
||||
per_pixel_loss = per_pixel_loss * weight_mask[:, :, :, None]
|
||||
return tf.reduce_mean(per_pixel_loss)
|
||||
return self.loss
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def IoU(self,Yi,y_predi):
|
||||
## mean Intersection over Union
|
||||
## Mean IoU = TP/(FN + TP + FP)
|
||||
|
||||
IoUs = []
|
||||
Nclass = np.unique(Yi)
|
||||
for c in Nclass:
|
||||
TP = np.sum( (Yi == c)&(y_predi==c) )
|
||||
FP = np.sum( (Yi != c)&(y_predi==c) )
|
||||
FN = np.sum( (Yi == c)&(y_predi != c))
|
||||
IoU = TP/float(TP + FP + FN)
|
||||
if self.n_classes>2:
|
||||
print("class {:02.0f}: #TP={:6.0f}, #FP={:6.0f}, #FN={:5.0f}, IoU={:4.3f}".format(c,TP,FP,FN,IoU))
|
||||
IoUs.append(IoU)
|
||||
if self.n_classes>2:
|
||||
mIoU = np.mean(IoUs)
|
||||
print("_________________")
|
||||
print("Mean IoU: {:4.3f}".format(mIoU))
|
||||
return mIoU
|
||||
elif self.n_classes==2:
|
||||
mIoU = IoUs[1]
|
||||
print("_________________")
|
||||
print("IoU: {:4.3f}".format(mIoU))
|
||||
return mIoU
|
||||
|
||||
def start_new_session_and_model(self):
|
||||
|
||||
config = tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()
|
||||
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
|
||||
|
||||
session = tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config) # tf.InteractiveSession()
|
||||
tensorflow_backend.set_session(session)
|
||||
#tensorflow.keras.layers.custom_layer = PatchEncoder
|
||||
#tensorflow.keras.layers.custom_layer = Patches
|
||||
self.model = load_model(self.model_dir , compile=False,custom_objects = {"PatchEncoder": PatchEncoder, "Patches": Patches})
|
||||
#config = tf.ConfigProto()
|
||||
#config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
|
||||
|
||||
#self.session = tf.InteractiveSession()
|
||||
#keras.losses.custom_loss = self.weighted_categorical_crossentropy
|
||||
#self.model = load_model(self.model_dir , compile=False)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##if self.weights_dir!=None:
|
||||
##self.model.load_weights(self.weights_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.task != 'classification' and self.task != 'reading_order':
|
||||
self.img_height=self.model.layers[len(self.model.layers)-1].output_shape[1]
|
||||
self.img_width=self.model.layers[len(self.model.layers)-1].output_shape[2]
|
||||
self.n_classes=self.model.layers[len(self.model.layers)-1].output_shape[3]
|
||||
|
||||
def visualize_model_output(self, prediction, img, task):
|
||||
if task == "binarization":
|
||||
prediction = prediction * -1
|
||||
prediction = prediction + 1
|
||||
added_image = prediction * 255
|
||||
layout_only = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
unique_classes = np.unique(prediction[:,:,0])
|
||||
rgb_colors = {'0' : [255, 255, 255],
|
||||
'1' : [255, 0, 0],
|
||||
'2' : [255, 125, 0],
|
||||
'3' : [255, 0, 125],
|
||||
'4' : [125, 125, 125],
|
||||
'5' : [125, 125, 0],
|
||||
'6' : [0, 125, 255],
|
||||
'7' : [0, 125, 0],
|
||||
'8' : [125, 125, 125],
|
||||
'9' : [0, 125, 255],
|
||||
'10' : [125, 0, 125],
|
||||
'11' : [0, 255, 0],
|
||||
'12' : [0, 0, 255],
|
||||
'13' : [0, 255, 255],
|
||||
'14' : [255, 125, 125],
|
||||
'15' : [255, 0, 255]}
|
||||
|
||||
layout_only = np.zeros(prediction.shape)
|
||||
|
||||
for unq_class in unique_classes:
|
||||
rgb_class_unique = rgb_colors[str(int(unq_class))]
|
||||
layout_only[:,:,0][prediction[:,:,0]==unq_class] = rgb_class_unique[0]
|
||||
layout_only[:,:,1][prediction[:,:,0]==unq_class] = rgb_class_unique[1]
|
||||
layout_only[:,:,2][prediction[:,:,0]==unq_class] = rgb_class_unique[2]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img = self.resize_image(img, layout_only.shape[0], layout_only.shape[1])
|
||||
|
||||
layout_only = layout_only.astype(np.int32)
|
||||
img = img.astype(np.int32)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
added_image = cv2.addWeighted(img,0.5,layout_only,0.1,0)
|
||||
|
||||
return added_image, layout_only
|
||||
|
||||
def predict(self, image_dir):
|
||||
if self.task == 'classification':
|
||||
classes_names = self.config_params_model['classification_classes_name']
|
||||
img_1ch = img=cv2.imread(image_dir, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
img_1ch = img_1ch / 255.0
|
||||
img_1ch = cv2.resize(img_1ch, (self.config_params_model['input_height'], self.config_params_model['input_width']), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
img_in = np.zeros((1, img_1ch.shape[0], img_1ch.shape[1], 3))
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 0] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 1] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
img_in[0, :, :, 2] = img_1ch[:, :]
|
||||
|
||||
label_p_pred = self.model.predict(img_in, verbose=0)
|
||||
index_class = np.argmax(label_p_pred[0])
|
||||
|
||||
print("Predicted Class: {}".format(classes_names[str(int(index_class))]))
|
||||
elif self.task == 'reading_order':
|
||||
img_height = self.config_params_model['input_height']
|
||||
img_width = self.config_params_model['input_width']
|
||||
|
||||
tree_xml, root_xml, bb_coord_printspace, file_name, id_paragraph, id_header, co_text_paragraph, co_text_header, tot_region_ref, x_len, y_len, index_tot_regions, img_poly = read_xml(self.xml_file)
|
||||
_, cy_main, x_min_main, x_max_main, y_min_main, y_max_main, _ = find_new_features_of_contours(co_text_header)
|
||||
|
||||
img_header_and_sep = np.zeros((y_len,x_len), dtype='uint8')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for j in range(len(cy_main)):
|
||||
img_header_and_sep[int(y_max_main[j]):int(y_max_main[j])+12,int(x_min_main[j]):int(x_max_main[j]) ] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
co_text_all = co_text_paragraph + co_text_header
|
||||
id_all_text = id_paragraph + id_header
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##texts_corr_order_index = [index_tot_regions[tot_region_ref.index(i)] for i in id_all_text ]
|
||||
##texts_corr_order_index_int = [int(x) for x in texts_corr_order_index]
|
||||
texts_corr_order_index_int = list(np.array(range(len(co_text_all))))
|
||||
|
||||
#print(texts_corr_order_index_int)
|
||||
|
||||
max_area = 1
|
||||
#print(np.shape(co_text_all[0]), len( np.shape(co_text_all[0]) ),'co_text_all')
|
||||
#co_text_all = filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(img_poly, co_text_all, _, max_area, min_area)
|
||||
#print(co_text_all,'co_text_all')
|
||||
co_text_all, texts_corr_order_index_int, _ = filter_contours_area_of_image(img_poly, co_text_all, texts_corr_order_index_int, max_area, self.min_area)
|
||||
|
||||
#print(texts_corr_order_index_int)
|
||||
|
||||
#co_text_all = [co_text_all[index] for index in texts_corr_order_index_int]
|
||||
id_all_text = [id_all_text[index] for index in texts_corr_order_index_int]
|
||||
|
||||
labels_con = np.zeros((y_len,x_len,len(co_text_all)),dtype='uint8')
|
||||
for i in range(len(co_text_all)):
|
||||
img_label = np.zeros((y_len,x_len,3),dtype='uint8')
|
||||
img_label=cv2.fillPoly(img_label, pts =[co_text_all[i]], color=(1,1,1))
|
||||
labels_con[:,:,i] = img_label[:,:,0]
|
||||
|
||||
if bb_coord_printspace:
|
||||
#bb_coord_printspace[x,y,w,h,_,_]
|
||||
x = bb_coord_printspace[0]
|
||||
y = bb_coord_printspace[1]
|
||||
w = bb_coord_printspace[2]
|
||||
h = bb_coord_printspace[3]
|
||||
labels_con = labels_con[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]
|
||||
img_poly = img_poly[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]
|
||||
img_header_and_sep = img_header_and_sep[y:y+h, x:x+w]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img3= np.copy(img_poly)
|
||||
labels_con = resize_image(labels_con, img_height, img_width)
|
||||
|
||||
img_header_and_sep = resize_image(img_header_and_sep, img_height, img_width)
|
||||
|
||||
img3= resize_image (img3, img_height, img_width)
|
||||
img3 = img3.astype(np.uint16)
|
||||
|
||||
inference_bs = 1#4
|
||||
|
||||
input_1= np.zeros( (inference_bs, img_height, img_width,3))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
starting_list_of_regions = [list(range(labels_con.shape[2]))]
|
||||
|
||||
index_update = 0
|
||||
index_selected = starting_list_of_regions[0]
|
||||
|
||||
scalibility_num = 0
|
||||
while index_update>=0:
|
||||
ij_list = starting_list_of_regions[index_update]
|
||||
i = ij_list[0]
|
||||
ij_list.pop(0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pr_list = []
|
||||
post_list = []
|
||||
|
||||
batch_counter = 0
|
||||
tot_counter = 1
|
||||
|
||||
tot_iteration = len(ij_list)
|
||||
full_bs_ite= tot_iteration//inference_bs
|
||||
last_bs = tot_iteration % inference_bs
|
||||
|
||||
jbatch_indexer =[]
|
||||
for j in ij_list:
|
||||
img1= np.repeat(labels_con[:,:,i][:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
img2 = np.repeat(labels_con[:,:,j][:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img2[:,:,0][img3[:,:,0]==5] = 2
|
||||
img2[:,:,0][img_header_and_sep[:,:]==1] = 3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img1[:,:,0][img3[:,:,0]==5] = 2
|
||||
img1[:,:,0][img_header_and_sep[:,:]==1] = 3
|
||||
|
||||
#input_1= np.zeros( (height1, width1,3))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jbatch_indexer.append(j)
|
||||
|
||||
input_1[batch_counter,:,:,0] = img1[:,:,0]/3.
|
||||
input_1[batch_counter,:,:,2] = img2[:,:,0]/3.
|
||||
input_1[batch_counter,:,:,1] = img3[:,:,0]/5.
|
||||
#input_1[batch_counter,:,:,:]= np.zeros( (batch_counter, height1, width1,3))
|
||||
batch_counter = batch_counter+1
|
||||
|
||||
#input_1[:,:,0] = img1[:,:,0]/3.
|
||||
#input_1[:,:,2] = img2[:,:,0]/3.
|
||||
#input_1[:,:,1] = img3[:,:,0]/5.
|
||||
|
||||
if batch_counter==inference_bs or ( (tot_counter//inference_bs)==full_bs_ite and tot_counter%inference_bs==last_bs):
|
||||
y_pr = self.model.predict(input_1 , verbose=0)
|
||||
scalibility_num = scalibility_num+1
|
||||
|
||||
if batch_counter==inference_bs:
|
||||
iteration_batches = inference_bs
|
||||
else:
|
||||
iteration_batches = last_bs
|
||||
for jb in range(iteration_batches):
|
||||
if y_pr[jb][0]>=0.5:
|
||||
post_list.append(jbatch_indexer[jb])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pr_list.append(jbatch_indexer[jb])
|
||||
|
||||
batch_counter = 0
|
||||
jbatch_indexer = []
|
||||
|
||||
tot_counter = tot_counter+1
|
||||
|
||||
starting_list_of_regions, index_update = update_list_and_return_first_with_length_bigger_than_one(index_update, i, pr_list, post_list,starting_list_of_regions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
index_sort = [i[0] for i in starting_list_of_regions ]
|
||||
|
||||
id_all_text = np.array(id_all_text)[index_sort]
|
||||
|
||||
alltags=[elem.tag for elem in root_xml.iter()]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
link=alltags[0].split('}')[0]+'}'
|
||||
name_space = alltags[0].split('}')[0]
|
||||
name_space = name_space.split('{')[1]
|
||||
|
||||
page_element = root_xml.find(link+'Page')
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
ro_subelement = ET.SubElement(page_element, 'ReadingOrder')
|
||||
#print(page_element, 'page_element')
|
||||
|
||||
#new_element = ET.Element('ReadingOrder')
|
||||
|
||||
new_element_element = ET.Element('OrderedGroup')
|
||||
new_element_element.set('id', "ro357564684568544579089")
|
||||
|
||||
for index, id_text in enumerate(id_all_text):
|
||||
new_element_2 = ET.Element('RegionRefIndexed')
|
||||
new_element_2.set('regionRef', id_all_text[index])
|
||||
new_element_2.set('index', str(index_sort[index]))
|
||||
|
||||
new_element_element.append(new_element_2)
|
||||
|
||||
ro_subelement.append(new_element_element)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
##ro_subelement = ET.SubElement(page_element, 'ReadingOrder')
|
||||
|
||||
ro_subelement = ET.Element('ReadingOrder')
|
||||
|
||||
ro_subelement2 = ET.SubElement(ro_subelement, 'OrderedGroup')
|
||||
ro_subelement2.set('id', "ro357564684568544579089")
|
||||
|
||||
for index, id_text in enumerate(id_all_text):
|
||||
new_element_2 = ET.SubElement(ro_subelement2, 'RegionRefIndexed')
|
||||
new_element_2.set('regionRef', id_all_text[index])
|
||||
new_element_2.set('index', str(index))
|
||||
|
||||
if (link+'PrintSpace' in alltags) or (link+'Border' in alltags):
|
||||
page_element.insert(1, ro_subelement)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
page_element.insert(0, ro_subelement)
|
||||
|
||||
alltags=[elem.tag for elem in root_xml.iter()]
|
||||
|
||||
ET.register_namespace("",name_space)
|
||||
tree_xml.write(os.path.join(self.out, file_name+'.xml'),xml_declaration=True,method='xml',encoding="utf8",default_namespace=None)
|
||||
#tree_xml.write('library2.xml')
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if self.patches:
|
||||
#def textline_contours(img,input_width,input_height,n_classes,model):
|
||||
|
||||
img=cv2.imread(image_dir)
|
||||
self.img_org = np.copy(img)
|
||||
|
||||
if img.shape[0] < self.img_height:
|
||||
img = self.resize_image(img, self.img_height, img.shape[1])
|
||||
|
||||
if img.shape[1] < self.img_width:
|
||||
img = self.resize_image(img, img.shape[0], self.img_width)
|
||||
|
||||
margin = int(0.1 * self.img_width)
|
||||
width_mid = self.img_width - 2 * margin
|
||||
height_mid = self.img_height - 2 * margin
|
||||
img = img / float(255.0)
|
||||
|
||||
img_h = img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_w = img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = np.zeros((img_h, img_w, 3))
|
||||
nxf = img_w / float(width_mid)
|
||||
nyf = img_h / float(height_mid)
|
||||
|
||||
nxf = int(nxf) + 1 if nxf > int(nxf) else int(nxf)
|
||||
nyf = int(nyf) + 1 if nyf > int(nyf) else int(nyf)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(nxf):
|
||||
for j in range(nyf):
|
||||
if i == 0:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + self.img_width
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_x_d = i * width_mid
|
||||
index_x_u = index_x_d + self.img_width
|
||||
if j == 0:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + self.img_height
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_y_d = j * height_mid
|
||||
index_y_u = index_y_d + self.img_height
|
||||
|
||||
if index_x_u > img_w:
|
||||
index_x_u = img_w
|
||||
index_x_d = img_w - self.img_width
|
||||
if index_y_u > img_h:
|
||||
index_y_u = img_h
|
||||
index_y_d = img_h - self.img_height
|
||||
|
||||
img_patch = img[index_y_d:index_y_u, index_x_d:index_x_u, :]
|
||||
label_p_pred = self.model.predict(img_patch.reshape(1, img_patch.shape[0], img_patch.shape[1], img_patch.shape[2]),
|
||||
verbose=0)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.task == 'enhancement':
|
||||
seg = label_p_pred[0, :, :, :]
|
||||
seg = seg * 255
|
||||
elif self.task == 'segmentation' or self.task == 'binarization':
|
||||
seg = np.argmax(label_p_pred, axis=3)[0]
|
||||
seg = np.repeat(seg[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if i == 0 and j == 0:
|
||||
seg = seg[0 : seg.shape[0] - margin, 0 : seg.shape[1] - margin]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + 0 : index_y_u - margin, index_x_d + 0 : index_x_u - margin, :] = seg
|
||||
elif i == nxf - 1 and j == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg = seg[margin : seg.shape[0] - 0, margin : seg.shape[1] - 0]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin : index_y_u - 0, index_x_d + margin : index_x_u - 0, :] = seg
|
||||
elif i == 0 and j == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg = seg[margin : seg.shape[0] - 0, 0 : seg.shape[1] - margin]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin : index_y_u - 0, index_x_d + 0 : index_x_u - margin, :] = seg
|
||||
elif i == nxf - 1 and j == 0:
|
||||
seg = seg[0 : seg.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg.shape[1] - 0]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + 0 : index_y_u - margin, index_x_d + margin : index_x_u - 0, :] = seg
|
||||
elif i == 0 and j != 0 and j != nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg = seg[margin : seg.shape[0] - margin, 0 : seg.shape[1] - margin]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin : index_y_u - margin, index_x_d + 0 : index_x_u - margin, :] = seg
|
||||
elif i == nxf - 1 and j != 0 and j != nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg = seg[margin : seg.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg.shape[1] - 0]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin : index_y_u - margin, index_x_d + margin : index_x_u - 0, :] = seg
|
||||
elif i != 0 and i != nxf - 1 and j == 0:
|
||||
seg = seg[0 : seg.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg.shape[1] - margin]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + 0 : index_y_u - margin, index_x_d + margin : index_x_u - margin, :] = seg
|
||||
elif i != 0 and i != nxf - 1 and j == nyf - 1:
|
||||
seg = seg[margin : seg.shape[0] - 0, margin : seg.shape[1] - margin]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin : index_y_u - 0, index_x_d + margin : index_x_u - margin, :] = seg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
seg = seg[margin : seg.shape[0] - margin, margin : seg.shape[1] - margin]
|
||||
prediction_true[index_y_d + margin : index_y_u - margin, index_x_d + margin : index_x_u - margin, :] = seg
|
||||
prediction_true = prediction_true.astype(int)
|
||||
prediction_true = cv2.resize(prediction_true, (self.img_org.shape[1], self.img_org.shape[0]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
return prediction_true
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
img=cv2.imread(image_dir)
|
||||
self.img_org = np.copy(img)
|
||||
|
||||
width=self.img_width
|
||||
height=self.img_height
|
||||
|
||||
img=img/255.0
|
||||
img=self.resize_image(img,self.img_height,self.img_width)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
label_p_pred=self.model.predict(
|
||||
img.reshape(1,img.shape[0],img.shape[1],img.shape[2]))
|
||||
|
||||
if self.task == 'enhancement':
|
||||
seg = label_p_pred[0, :, :, :]
|
||||
seg = seg * 255
|
||||
elif self.task == 'segmentation' or self.task == 'binarization':
|
||||
seg = np.argmax(label_p_pred, axis=3)[0]
|
||||
seg = np.repeat(seg[:, :, np.newaxis], 3, axis=2)
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = seg.astype(int)
|
||||
|
||||
prediction_true = cv2.resize(prediction_true, (self.img_org.shape[1], self.img_org.shape[0]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
return prediction_true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
self.start_new_session_and_model()
|
||||
if self.image:
|
||||
res=self.predict(image_dir = self.image)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.task == 'classification' or self.task == 'reading_order':
|
||||
pass
|
||||
elif self.task == 'enhancement':
|
||||
if self.save:
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(self.save,res)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_seg_overlayed, only_layout = self.visualize_model_output(res, self.img_org, self.task)
|
||||
if self.save:
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(self.save,img_seg_overlayed)
|
||||
if self.save_layout:
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(self.save_layout, only_layout)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.ground_truth:
|
||||
gt_img=cv2.imread(self.ground_truth)
|
||||
self.IoU(gt_img[:,:,0],res[:,:,0])
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ls_images = os.listdir(self.dir_in)
|
||||
for ind_image in ls_images:
|
||||
f_name = ind_image.split('.')[0]
|
||||
image_dir = os.path.join(self.dir_in, ind_image)
|
||||
res=self.predict(image_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.task == 'classification' or self.task == 'reading_order':
|
||||
pass
|
||||
elif self.task == 'enhancement':
|
||||
self.save = os.path.join(self.out, f_name+'.png')
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(self.save,res)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_seg_overlayed, only_layout = self.visualize_model_output(res, self.img_org, self.task)
|
||||
self.save = os.path.join(self.out, f_name+'_overlayed.png')
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(self.save,img_seg_overlayed)
|
||||
self.save_layout = os.path.join(self.out, f_name+'_layout.png')
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(self.save_layout, only_layout)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.ground_truth:
|
||||
gt_img=cv2.imread(self.ground_truth)
|
||||
self.IoU(gt_img[:,:,0],res[:,:,0])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@click.command()
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--image",
|
||||
"-i",
|
||||
help="image filename",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--dir_in",
|
||||
"-di",
|
||||
help="directory of images",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--out",
|
||||
"-o",
|
||||
help="output directory where xml with detected reading order will be written.",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--patches/--no-patches",
|
||||
"-p/-nop",
|
||||
is_flag=True,
|
||||
help="if this parameter set to true, this tool will try to do inference in patches.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save",
|
||||
"-s",
|
||||
help="save prediction as a png file in current folder.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--save_layout",
|
||||
"-sl",
|
||||
help="save layout prediction only as a png file in current folder.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--model",
|
||||
"-m",
|
||||
help="directory of models",
|
||||
type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False),
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--ground_truth",
|
||||
"-gt",
|
||||
help="ground truth directory if you want to see the iou of prediction.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--xml_file",
|
||||
"-xml",
|
||||
help="xml file with layout coordinates that reading order detection will be implemented on. The result will be written in the same xml file.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@click.option(
|
||||
"--min_area",
|
||||
"-min",
|
||||
help="min area size of regions considered for reading order detection. The default value is zero and means that all text regions are considered for reading order.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
def main(image, dir_in, model, patches, save, save_layout, ground_truth, xml_file, out, min_area):
|
||||
assert image or dir_in, "Either a single image -i or a dir_in -di is required"
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(model,'config.json')) as f:
|
||||
config_params_model = json.load(f)
|
||||
task = config_params_model['task']
|
||||
if task != 'classification' and task != 'reading_order':
|
||||
if image and not save:
|
||||
print("Error: You used one of segmentation or binarization task with image input but not set -s, you need a filename to save visualized output with -s")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
if dir_in and not out:
|
||||
print("Error: You used one of segmentation or binarization task with dir_in but not set -out")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
x=sbb_predict(image, dir_in, model, task, config_params_model, patches, save, save_layout, ground_truth, xml_file, out, min_area)
|
||||
x.run()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,357 +0,0 @@
|
|||
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def focal_loss(gamma=2., alpha=4.):
|
||||
gamma = float(gamma)
|
||||
alpha = float(alpha)
|
||||
|
||||
def focal_loss_fixed(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
"""Focal loss for multi-classification
|
||||
FL(p_t)=-alpha(1-p_t)^{gamma}ln(p_t)
|
||||
Notice: y_pred is probability after softmax
|
||||
gradient is d(Fl)/d(p_t) not d(Fl)/d(x) as described in paper
|
||||
d(Fl)/d(p_t) * [p_t(1-p_t)] = d(Fl)/d(x)
|
||||
Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection
|
||||
https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002
|
||||
|
||||
Arguments:
|
||||
y_true {tensor} -- ground truth labels, shape of [batch_size, num_cls]
|
||||
y_pred {tensor} -- model's output, shape of [batch_size, num_cls]
|
||||
|
||||
Keyword Arguments:
|
||||
gamma {float} -- (default: {2.0})
|
||||
alpha {float} -- (default: {4.0})
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
[tensor] -- loss.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
epsilon = 1.e-9
|
||||
y_true = tf.convert_to_tensor(y_true, tf.float32)
|
||||
y_pred = tf.convert_to_tensor(y_pred, tf.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
model_out = tf.add(y_pred, epsilon)
|
||||
ce = tf.multiply(y_true, -tf.log(model_out))
|
||||
weight = tf.multiply(y_true, tf.pow(tf.subtract(1., model_out), gamma))
|
||||
fl = tf.multiply(alpha, tf.multiply(weight, ce))
|
||||
reduced_fl = tf.reduce_max(fl, axis=1)
|
||||
return tf.reduce_mean(reduced_fl)
|
||||
|
||||
return focal_loss_fixed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def weighted_categorical_crossentropy(weights=None):
|
||||
""" weighted_categorical_crossentropy
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
* weights<ktensor|nparray|list>: crossentropy weights
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
* weighted categorical crossentropy function
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
labels_floats = tf.cast(y_true, tf.float32)
|
||||
per_pixel_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels_floats, logits=y_pred)
|
||||
|
||||
if weights is not None:
|
||||
weight_mask = tf.maximum(tf.reduce_max(tf.constant(
|
||||
np.array(weights, dtype=np.float32)[None, None, None])
|
||||
* labels_floats, axis=-1), 1.0)
|
||||
per_pixel_loss = per_pixel_loss * weight_mask[:, :, :, None]
|
||||
return tf.reduce_mean(per_pixel_loss)
|
||||
|
||||
return loss
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image_categorical_cross_entropy(y_true, y_pred, weights=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param y_true: tensor of shape (batch_size, height, width) representing the ground truth.
|
||||
:param y_pred: tensor of shape (batch_size, height, width) representing the prediction.
|
||||
:return: The mean cross-entropy on softmaxed tensors.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
labels_floats = tf.cast(y_true, tf.float32)
|
||||
per_pixel_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels_floats, logits=y_pred)
|
||||
|
||||
if weights is not None:
|
||||
weight_mask = tf.maximum(
|
||||
tf.reduce_max(tf.constant(
|
||||
np.array(weights, dtype=np.float32)[None, None, None])
|
||||
* labels_floats, axis=-1), 1.0)
|
||||
per_pixel_loss = per_pixel_loss * weight_mask[:, :, :, None]
|
||||
|
||||
return tf.reduce_mean(per_pixel_loss)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def class_tversky(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
smooth = 1.0 # 1.00
|
||||
|
||||
y_true = K.permute_dimensions(y_true, (3, 1, 2, 0))
|
||||
y_pred = K.permute_dimensions(y_pred, (3, 1, 2, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
y_true_pos = K.batch_flatten(y_true)
|
||||
y_pred_pos = K.batch_flatten(y_pred)
|
||||
true_pos = K.sum(y_true_pos * y_pred_pos, 1)
|
||||
false_neg = K.sum(y_true_pos * (1 - y_pred_pos), 1)
|
||||
false_pos = K.sum((1 - y_true_pos) * y_pred_pos, 1)
|
||||
alpha = 0.2 # 0.5
|
||||
beta = 0.8
|
||||
return (true_pos + smooth) / (true_pos + alpha * false_neg + beta * false_pos + smooth)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def focal_tversky_loss(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
pt_1 = class_tversky(y_true, y_pred)
|
||||
gamma = 1.3 # 4./3.0#1.3#4.0/3.00# 0.75
|
||||
return K.sum(K.pow((1 - pt_1), gamma))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def generalized_dice_coeff2(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
n_el = 1
|
||||
for dim in y_true.shape:
|
||||
n_el *= int(dim)
|
||||
n_cl = y_true.shape[-1]
|
||||
w = K.zeros(shape=(n_cl,))
|
||||
w = (K.sum(y_true, axis=(0, 1, 2))) / n_el
|
||||
w = 1 / (w ** 2 + 0.000001)
|
||||
numerator = y_true * y_pred
|
||||
numerator = w * K.sum(numerator, (0, 1, 2))
|
||||
numerator = K.sum(numerator)
|
||||
denominator = y_true + y_pred
|
||||
denominator = w * K.sum(denominator, (0, 1, 2))
|
||||
denominator = K.sum(denominator)
|
||||
return 2 * numerator / denominator
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def generalized_dice_coeff(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
axes = tuple(range(1, len(y_pred.shape) - 1))
|
||||
Ncl = y_pred.shape[-1]
|
||||
w = K.zeros(shape=(Ncl,))
|
||||
w = K.sum(y_true, axis=axes)
|
||||
w = 1 / (w ** 2 + 0.000001)
|
||||
# Compute gen dice coef:
|
||||
numerator = y_true * y_pred
|
||||
numerator = w * K.sum(numerator, axes)
|
||||
numerator = K.sum(numerator)
|
||||
|
||||
denominator = y_true + y_pred
|
||||
denominator = w * K.sum(denominator, axes)
|
||||
denominator = K.sum(denominator)
|
||||
|
||||
gen_dice_coef = 2 * numerator / denominator
|
||||
|
||||
return gen_dice_coef
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def generalized_dice_loss(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
return 1 - generalized_dice_coeff2(y_true, y_pred)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def soft_dice_loss(y_true, y_pred, epsilon=1e-6):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Soft dice loss calculation for arbitrary batch size, number of classes, and number of spatial dimensions.
|
||||
Assumes the `channels_last` format.
|
||||
|
||||
# Arguments
|
||||
y_true: b x X x Y( x Z...) x c One hot encoding of ground truth
|
||||
y_pred: b x X x Y( x Z...) x c Network output, must sum to 1 over c channel (such as after softmax)
|
||||
epsilon: Used for numerical stability to avoid divide by zero errors
|
||||
|
||||
# References
|
||||
V-Net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
|
||||
https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.04797
|
||||
More details on Dice loss formulation
|
||||
https://mediatum.ub.tum.de/doc/1395260/1395260.pdf (page 72)
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from https://github.com/Lasagne/Recipes/issues/99#issuecomment-347775022
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# skip the batch and class axis for calculating Dice score
|
||||
axes = tuple(range(1, len(y_pred.shape) - 1))
|
||||
|
||||
numerator = 2. * K.sum(y_pred * y_true, axes)
|
||||
|
||||
denominator = K.sum(K.square(y_pred) + K.square(y_true), axes)
|
||||
return 1.00 - K.mean(numerator / (denominator + epsilon)) # average over classes and batch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def seg_metrics(y_true, y_pred, metric_name, metric_type='standard', drop_last=True, mean_per_class=False,
|
||||
verbose=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Compute mean metrics of two segmentation masks, via Keras.
|
||||
|
||||
IoU(A,B) = |A & B| / (| A U B|)
|
||||
Dice(A,B) = 2*|A & B| / (|A| + |B|)
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
y_true: true masks, one-hot encoded.
|
||||
y_pred: predicted masks, either softmax outputs, or one-hot encoded.
|
||||
metric_name: metric to be computed, either 'iou' or 'dice'.
|
||||
metric_type: one of 'standard' (default), 'soft', 'naive'.
|
||||
In the standard version, y_pred is one-hot encoded and the mean
|
||||
is taken only over classes that are present (in y_true or y_pred).
|
||||
The 'soft' version of the metrics are computed without one-hot
|
||||
encoding y_pred.
|
||||
The 'naive' version return mean metrics where absent classes contribute
|
||||
to the class mean as 1.0 (instead of being dropped from the mean).
|
||||
drop_last = True: boolean flag to drop last class (usually reserved
|
||||
for background class in semantic segmentation)
|
||||
mean_per_class = False: return mean along batch axis for each class.
|
||||
verbose = False: print intermediate results such as intersection, union
|
||||
(as number of pixels).
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
IoU/Dice of y_true and y_pred, as a float, unless mean_per_class == True
|
||||
in which case it returns the per-class metric, averaged over the batch.
|
||||
|
||||
Inputs are B*W*H*N tensors, with
|
||||
B = batch size,
|
||||
W = width,
|
||||
H = height,
|
||||
N = number of classes
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
flag_soft = (metric_type == 'soft')
|
||||
flag_naive_mean = (metric_type == 'naive')
|
||||
|
||||
# always assume one or more classes
|
||||
num_classes = K.shape(y_true)[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
if not flag_soft:
|
||||
# get one-hot encoded masks from y_pred (true masks should already be one-hot)
|
||||
y_pred = K.one_hot(K.argmax(y_pred), num_classes)
|
||||
y_true = K.one_hot(K.argmax(y_true), num_classes)
|
||||
|
||||
# if already one-hot, could have skipped above command
|
||||
# keras uses float32 instead of float64, would give error down (but numpy arrays or keras.to_categorical gives float64)
|
||||
y_true = K.cast(y_true, 'float32')
|
||||
y_pred = K.cast(y_pred, 'float32')
|
||||
|
||||
# intersection and union shapes are batch_size * n_classes (values = area in pixels)
|
||||
axes = (1, 2) # W,H axes of each image
|
||||
intersection = K.sum(K.abs(y_true * y_pred), axis=axes)
|
||||
mask_sum = K.sum(K.abs(y_true), axis=axes) + K.sum(K.abs(y_pred), axis=axes)
|
||||
union = mask_sum - intersection # or, np.logical_or(y_pred, y_true) for one-hot
|
||||
|
||||
smooth = .001
|
||||
iou = (intersection + smooth) / (union + smooth)
|
||||
dice = 2 * (intersection + smooth) / (mask_sum + smooth)
|
||||
|
||||
metric = {'iou': iou, 'dice': dice}[metric_name]
|
||||
|
||||
# define mask to be 0 when no pixels are present in either y_true or y_pred, 1 otherwise
|
||||
mask = K.cast(K.not_equal(union, 0), 'float32')
|
||||
|
||||
if drop_last:
|
||||
metric = metric[:, :-1]
|
||||
mask = mask[:, :-1]
|
||||
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print('intersection, union')
|
||||
print(K.eval(intersection), K.eval(union))
|
||||
print(K.eval(intersection / union))
|
||||
|
||||
# return mean metrics: remaining axes are (batch, classes)
|
||||
if flag_naive_mean:
|
||||
return K.mean(metric)
|
||||
|
||||
# take mean only over non-absent classes
|
||||
class_count = K.sum(mask, axis=0)
|
||||
non_zero = tf.greater(class_count, 0)
|
||||
non_zero_sum = tf.boolean_mask(K.sum(metric * mask, axis=0), non_zero)
|
||||
non_zero_count = tf.boolean_mask(class_count, non_zero)
|
||||
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print('Counts of inputs with class present, metrics for non-absent classes')
|
||||
print(K.eval(class_count), K.eval(non_zero_sum / non_zero_count))
|
||||
|
||||
return K.mean(non_zero_sum / non_zero_count)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def mean_iou(y_true, y_pred, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Compute mean Intersection over Union of two segmentation masks, via Keras.
|
||||
|
||||
Calls metrics_k(y_true, y_pred, metric_name='iou'), see there for allowed kwargs.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return seg_metrics(y_true, y_pred, metric_name='iou', **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def Mean_IOU(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
nb_classes = K.int_shape(y_pred)[-1]
|
||||
iou = []
|
||||
true_pixels = K.argmax(y_true, axis=-1)
|
||||
pred_pixels = K.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)
|
||||
void_labels = K.equal(K.sum(y_true, axis=-1), 0)
|
||||
for i in range(0, nb_classes): # exclude first label (background) and last label (void)
|
||||
true_labels = K.equal(true_pixels, i) # & ~void_labels
|
||||
pred_labels = K.equal(pred_pixels, i) # & ~void_labels
|
||||
inter = tf.to_int32(true_labels & pred_labels)
|
||||
union = tf.to_int32(true_labels | pred_labels)
|
||||
legal_batches = K.sum(tf.to_int32(true_labels), axis=1) > 0
|
||||
ious = K.sum(inter, axis=1) / K.sum(union, axis=1)
|
||||
iou.append(K.mean(tf.gather(ious, indices=tf.where(legal_batches)))) # returns average IoU of the same objects
|
||||
iou = tf.stack(iou)
|
||||
legal_labels = ~tf.debugging.is_nan(iou)
|
||||
iou = tf.gather(iou, indices=tf.where(legal_labels))
|
||||
return K.mean(iou)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def iou_vahid(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
nb_classes = tf.shape(y_true)[-1] + tf.to_int32(1)
|
||||
true_pixels = K.argmax(y_true, axis=-1)
|
||||
pred_pixels = K.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)
|
||||
iou = []
|
||||
|
||||
for i in tf.range(nb_classes):
|
||||
tp = K.sum(tf.to_int32(K.equal(true_pixels, i) & K.equal(pred_pixels, i)))
|
||||
fp = K.sum(tf.to_int32(K.not_equal(true_pixels, i) & K.equal(pred_pixels, i)))
|
||||
fn = K.sum(tf.to_int32(K.equal(true_pixels, i) & K.not_equal(pred_pixels, i)))
|
||||
iouh = tp / (tp + fp + fn)
|
||||
iou.append(iouh)
|
||||
return K.mean(iou)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def IoU_metric(Yi, y_predi):
|
||||
# mean Intersection over Union
|
||||
# Mean IoU = TP/(FN + TP + FP)
|
||||
y_predi = np.argmax(y_predi, axis=3)
|
||||
y_testi = np.argmax(Yi, axis=3)
|
||||
IoUs = []
|
||||
Nclass = int(np.max(Yi)) + 1
|
||||
for c in range(Nclass):
|
||||
TP = np.sum((Yi == c) & (y_predi == c))
|
||||
FP = np.sum((Yi != c) & (y_predi == c))
|
||||
FN = np.sum((Yi == c) & (y_predi != c))
|
||||
IoU = TP / float(TP + FP + FN)
|
||||
IoUs.append(IoU)
|
||||
return K.cast(np.mean(IoUs), dtype='float32')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def IoU_metric_keras(y_true, y_pred):
|
||||
# mean Intersection over Union
|
||||
# Mean IoU = TP/(FN + TP + FP)
|
||||
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
|
||||
sess = tf.Session()
|
||||
sess.run(init)
|
||||
|
||||
return IoU_metric(y_true.eval(session=sess), y_pred.eval(session=sess))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def jaccard_distance_loss(y_true, y_pred, smooth=100):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Jaccard = (|X & Y|)/ (|X|+ |Y| - |X & Y|)
|
||||
= sum(|A*B|)/(sum(|A|)+sum(|B|)-sum(|A*B|))
|
||||
|
||||
The jaccard distance loss is usefull for unbalanced datasets. This has been
|
||||
shifted so it converges on 0 and is smoothed to avoid exploding or disapearing
|
||||
gradient.
|
||||
|
||||
Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jaccard_index
|
||||
|
||||
@url: https://gist.github.com/wassname/f1452b748efcbeb4cb9b1d059dce6f96
|
||||
@author: wassname
|
||||
"""
|
||||
intersection = K.sum(K.abs(y_true * y_pred), axis=-1)
|
||||
sum_ = K.sum(K.abs(y_true) + K.abs(y_pred), axis=-1)
|
||||
jac = (intersection + smooth) / (sum_ - intersection + smooth)
|
||||
return (1 - jac) * smooth
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,760 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from tensorflow import keras
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.models import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.layers import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras import layers
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.regularizers import l2
|
||||
|
||||
##mlp_head_units = [512, 256]#[2048, 1024]
|
||||
###projection_dim = 64
|
||||
##transformer_layers = 2#8
|
||||
##num_heads = 1#4
|
||||
resnet50_Weights_path = './pretrained_model/resnet50_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5'
|
||||
IMAGE_ORDERING = 'channels_last'
|
||||
MERGE_AXIS = -1
|
||||
|
||||
def mlp(x, hidden_units, dropout_rate):
|
||||
for units in hidden_units:
|
||||
x = layers.Dense(units, activation=tf.nn.gelu)(x)
|
||||
x = layers.Dropout(dropout_rate)(x)
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
class Patches(layers.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, patch_size_x, patch_size_y):#__init__(self, **kwargs):#:__init__(self, patch_size):#__init__(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(Patches, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.patch_size_x = patch_size_x
|
||||
self.patch_size_y = patch_size_y
|
||||
|
||||
def call(self, images):
|
||||
#print(tf.shape(images)[1],'images')
|
||||
#print(self.patch_size,'self.patch_size')
|
||||
batch_size = tf.shape(images)[0]
|
||||
patches = tf.image.extract_patches(
|
||||
images=images,
|
||||
sizes=[1, self.patch_size_y, self.patch_size_x, 1],
|
||||
strides=[1, self.patch_size_y, self.patch_size_x, 1],
|
||||
rates=[1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
padding="VALID",
|
||||
)
|
||||
#patch_dims = patches.shape[-1]
|
||||
patch_dims = tf.shape(patches)[-1]
|
||||
patches = tf.reshape(patches, [batch_size, -1, patch_dims])
|
||||
return patches
|
||||
def get_config(self):
|
||||
|
||||
config = super().get_config().copy()
|
||||
config.update({
|
||||
'patch_size_x': self.patch_size_x,
|
||||
'patch_size_y': self.patch_size_y,
|
||||
})
|
||||
return config
|
||||
|
||||
class Patches_old(layers.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, patch_size):#__init__(self, **kwargs):#:__init__(self, patch_size):#__init__(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(Patches, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.patch_size = patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
def call(self, images):
|
||||
#print(tf.shape(images)[1],'images')
|
||||
#print(self.patch_size,'self.patch_size')
|
||||
batch_size = tf.shape(images)[0]
|
||||
patches = tf.image.extract_patches(
|
||||
images=images,
|
||||
sizes=[1, self.patch_size, self.patch_size, 1],
|
||||
strides=[1, self.patch_size, self.patch_size, 1],
|
||||
rates=[1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
padding="VALID",
|
||||
)
|
||||
patch_dims = patches.shape[-1]
|
||||
#print(patches.shape,patch_dims,'patch_dims')
|
||||
patches = tf.reshape(patches, [batch_size, -1, patch_dims])
|
||||
return patches
|
||||
def get_config(self):
|
||||
|
||||
config = super().get_config().copy()
|
||||
config.update({
|
||||
'patch_size': self.patch_size,
|
||||
})
|
||||
return config
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PatchEncoder(layers.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, num_patches, projection_dim):
|
||||
super(PatchEncoder, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.num_patches = num_patches
|
||||
self.projection = layers.Dense(units=projection_dim)
|
||||
self.position_embedding = layers.Embedding(
|
||||
input_dim=num_patches, output_dim=projection_dim
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def call(self, patch):
|
||||
positions = tf.range(start=0, limit=self.num_patches, delta=1)
|
||||
encoded = self.projection(patch) + self.position_embedding(positions)
|
||||
return encoded
|
||||
def get_config(self):
|
||||
|
||||
config = super().get_config().copy()
|
||||
config.update({
|
||||
'num_patches': self.num_patches,
|
||||
'projection': self.projection,
|
||||
'position_embedding': self.position_embedding,
|
||||
})
|
||||
return config
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def one_side_pad(x):
|
||||
x = ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING)(x)
|
||||
if IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_first':
|
||||
x = Lambda(lambda x: x[:, :, :-1, :-1])(x)
|
||||
elif IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_last':
|
||||
x = Lambda(lambda x: x[:, :-1, :-1, :])(x)
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def identity_block(input_tensor, kernel_size, filters, stage, block):
|
||||
"""The identity block is the block that has no conv layer at shortcut.
|
||||
# Arguments
|
||||
input_tensor: input tensor
|
||||
kernel_size: defualt 3, the kernel size of middle conv layer at main path
|
||||
filters: list of integers, the filterss of 3 conv layer at main path
|
||||
stage: integer, current stage label, used for generating layer names
|
||||
block: 'a','b'..., current block label, used for generating layer names
|
||||
# Returns
|
||||
Output tensor for the block.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
filters1, filters2, filters3 = filters
|
||||
|
||||
if IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_last':
|
||||
bn_axis = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bn_axis = 1
|
||||
|
||||
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
|
||||
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
|
||||
|
||||
x = Conv2D(filters1, (1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, name=conv_name_base + '2a')(input_tensor)
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name=bn_name_base + '2a')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = Conv2D(filters2, kernel_size, data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,
|
||||
padding='same', name=conv_name_base + '2b')(x)
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name=bn_name_base + '2b')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = Conv2D(filters3, (1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, name=conv_name_base + '2c')(x)
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name=bn_name_base + '2c')(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = layers.add([x, input_tensor])
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def conv_block(input_tensor, kernel_size, filters, stage, block, strides=(2, 2)):
|
||||
"""conv_block is the block that has a conv layer at shortcut
|
||||
# Arguments
|
||||
input_tensor: input tensor
|
||||
kernel_size: defualt 3, the kernel size of middle conv layer at main path
|
||||
filters: list of integers, the filterss of 3 conv layer at main path
|
||||
stage: integer, current stage label, used for generating layer names
|
||||
block: 'a','b'..., current block label, used for generating layer names
|
||||
# Returns
|
||||
Output tensor for the block.
|
||||
Note that from stage 3, the first conv layer at main path is with strides=(2,2)
|
||||
And the shortcut should have strides=(2,2) as well
|
||||
"""
|
||||
filters1, filters2, filters3 = filters
|
||||
|
||||
if IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_last':
|
||||
bn_axis = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bn_axis = 1
|
||||
|
||||
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
|
||||
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
|
||||
|
||||
x = Conv2D(filters1, (1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=strides,
|
||||
name=conv_name_base + '2a')(input_tensor)
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name=bn_name_base + '2a')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = Conv2D(filters2, kernel_size, data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, padding='same',
|
||||
name=conv_name_base + '2b')(x)
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name=bn_name_base + '2b')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = Conv2D(filters3, (1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, name=conv_name_base + '2c')(x)
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name=bn_name_base + '2c')(x)
|
||||
|
||||
shortcut = Conv2D(filters3, (1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=strides,
|
||||
name=conv_name_base + '1')(input_tensor)
|
||||
shortcut = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name=bn_name_base + '1')(shortcut)
|
||||
|
||||
x = layers.add([x, shortcut])
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def resnet50_unet_light(n_classes, input_height=224, input_width=224, taks="segmentation", weight_decay=1e-6, pretraining=False):
|
||||
assert input_height % 32 == 0
|
||||
assert input_width % 32 == 0
|
||||
|
||||
img_input = Input(shape=(input_height, input_width, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
if IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_last':
|
||||
bn_axis = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bn_axis = 1
|
||||
|
||||
x = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING)(img_input)
|
||||
x = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2), kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay),
|
||||
name='conv1')(x)
|
||||
f1 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name='bn_conv1')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2))(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1))
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
|
||||
f2 = one_side_pad(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
|
||||
f3 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
|
||||
f4 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
|
||||
f5 = x
|
||||
|
||||
if pretraining:
|
||||
model = Model(img_input, x).load_weights(resnet50_Weights_path)
|
||||
|
||||
v512_2048 = Conv2D(512, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(f5)
|
||||
v512_2048 = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(v512_2048)
|
||||
v512_2048 = Activation('relu')(v512_2048)
|
||||
|
||||
v512_1024 = Conv2D(512, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(f4)
|
||||
v512_1024 = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(v512_1024)
|
||||
v512_1024 = Activation('relu')(v512_1024)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(v512_2048)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, v512_1024], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f3], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f2], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f1], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, img_input], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = Conv2D(n_classes, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(o)
|
||||
if task == "segmentation":
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = (Activation('softmax'))(o)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
o = (Activation('sigmoid'))(o)
|
||||
|
||||
model = Model(img_input, o)
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def resnet50_unet(n_classes, input_height=224, input_width=224, task="segmentation", weight_decay=1e-6, pretraining=False):
|
||||
assert input_height % 32 == 0
|
||||
assert input_width % 32 == 0
|
||||
|
||||
img_input = Input(shape=(input_height, input_width, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
if IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_last':
|
||||
bn_axis = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bn_axis = 1
|
||||
|
||||
x = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING)(img_input)
|
||||
x = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2), kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay),
|
||||
name='conv1')(x)
|
||||
f1 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name='bn_conv1')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2))(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1))
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
|
||||
f2 = one_side_pad(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
|
||||
f3 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
|
||||
f4 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
|
||||
f5 = x
|
||||
|
||||
if pretraining:
|
||||
Model(img_input, x).load_weights(resnet50_Weights_path)
|
||||
|
||||
v1024_2048 = Conv2D(1024, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(
|
||||
f5)
|
||||
v1024_2048 = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(v1024_2048)
|
||||
v1024_2048 = Activation('relu')(v1024_2048)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(v1024_2048)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f4], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f3], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f2], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f1], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, img_input], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = Conv2D(n_classes, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(o)
|
||||
if task == "segmentation":
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = (Activation('softmax'))(o)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
o = (Activation('sigmoid'))(o)
|
||||
|
||||
model = Model(img_input, o)
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def vit_resnet50_unet(n_classes, patch_size_x, patch_size_y, num_patches, mlp_head_units=None, transformer_layers=8, num_heads =4, projection_dim = 64, input_height=224, input_width=224, task="segmentation", weight_decay=1e-6, pretraining=False):
|
||||
if mlp_head_units is None:
|
||||
mlp_head_units = [128, 64]
|
||||
inputs = layers.Input(shape=(input_height, input_width, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
#transformer_units = [
|
||||
#projection_dim * 2,
|
||||
#projection_dim,
|
||||
#] # Size of the transformer layers
|
||||
IMAGE_ORDERING = 'channels_last'
|
||||
bn_axis=3
|
||||
|
||||
x = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING)(inputs)
|
||||
x = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2),kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay), name='conv1')(x)
|
||||
f1 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name='bn_conv1')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2))(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1))
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
|
||||
f2 = one_side_pad(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
|
||||
f3 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
|
||||
f4 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
|
||||
f5 = x
|
||||
|
||||
if pretraining:
|
||||
model = Model(inputs, x).load_weights(resnet50_Weights_path)
|
||||
|
||||
#num_patches = x.shape[1]*x.shape[2]
|
||||
|
||||
#patch_size_y = input_height / x.shape[1]
|
||||
#patch_size_x = input_width / x.shape[2]
|
||||
#patch_size = patch_size_x * patch_size_y
|
||||
patches = Patches(patch_size_x, patch_size_y)(x)
|
||||
# Encode patches.
|
||||
encoded_patches = PatchEncoder(num_patches, projection_dim)(patches)
|
||||
|
||||
for _ in range(transformer_layers):
|
||||
# Layer normalization 1.
|
||||
x1 = layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)(encoded_patches)
|
||||
# Create a multi-head attention layer.
|
||||
attention_output = layers.MultiHeadAttention(
|
||||
num_heads=num_heads, key_dim=projection_dim, dropout=0.1
|
||||
)(x1, x1)
|
||||
# Skip connection 1.
|
||||
x2 = layers.Add()([attention_output, encoded_patches])
|
||||
# Layer normalization 2.
|
||||
x3 = layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)(x2)
|
||||
# MLP.
|
||||
x3 = mlp(x3, hidden_units=mlp_head_units, dropout_rate=0.1)
|
||||
# Skip connection 2.
|
||||
encoded_patches = layers.Add()([x3, x2])
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_patches = tf.reshape(encoded_patches, [-1, x.shape[1], x.shape[2] , int( projection_dim / (patch_size_x * patch_size_y) )])
|
||||
|
||||
v1024_2048 = Conv2D( 1024 , (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(encoded_patches)
|
||||
v1024_2048 = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(v1024_2048)
|
||||
v1024_2048 = Activation('relu')(v1024_2048)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D( (2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(v1024_2048)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f4],axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o ,f3], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f2], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f1], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, inputs],axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = Conv2D(n_classes, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(o)
|
||||
if task == "segmentation":
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = (Activation('softmax'))(o)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
o = (Activation('sigmoid'))(o)
|
||||
|
||||
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=o)
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def vit_resnet50_unet_transformer_before_cnn(n_classes, patch_size_x, patch_size_y, num_patches, mlp_head_units=None, transformer_layers=8, num_heads =4, projection_dim = 64, input_height=224, input_width=224, task="segmentation", weight_decay=1e-6, pretraining=False):
|
||||
if mlp_head_units is None:
|
||||
mlp_head_units = [128, 64]
|
||||
inputs = layers.Input(shape=(input_height, input_width, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
##transformer_units = [
|
||||
##projection_dim * 2,
|
||||
##projection_dim,
|
||||
##] # Size of the transformer layers
|
||||
IMAGE_ORDERING = 'channels_last'
|
||||
bn_axis=3
|
||||
|
||||
patches = Patches(patch_size_x, patch_size_y)(inputs)
|
||||
# Encode patches.
|
||||
encoded_patches = PatchEncoder(num_patches, projection_dim)(patches)
|
||||
|
||||
for _ in range(transformer_layers):
|
||||
# Layer normalization 1.
|
||||
x1 = layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)(encoded_patches)
|
||||
# Create a multi-head attention layer.
|
||||
attention_output = layers.MultiHeadAttention(
|
||||
num_heads=num_heads, key_dim=projection_dim, dropout=0.1
|
||||
)(x1, x1)
|
||||
# Skip connection 1.
|
||||
x2 = layers.Add()([attention_output, encoded_patches])
|
||||
# Layer normalization 2.
|
||||
x3 = layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)(x2)
|
||||
# MLP.
|
||||
x3 = mlp(x3, hidden_units=mlp_head_units, dropout_rate=0.1)
|
||||
# Skip connection 2.
|
||||
encoded_patches = layers.Add()([x3, x2])
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_patches = tf.reshape(encoded_patches, [-1, input_height, input_width , int( projection_dim / (patch_size_x * patch_size_y) )])
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_patches = Conv2D(3, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay), name='convinput')(encoded_patches)
|
||||
|
||||
x = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING)(encoded_patches)
|
||||
x = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2),kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay), name='conv1')(x)
|
||||
f1 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name='bn_conv1')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2))(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1))
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
|
||||
f2 = one_side_pad(x)
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
|
||||
f3 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
|
||||
f4 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
|
||||
f5 = x
|
||||
|
||||
if pretraining:
|
||||
model = Model(encoded_patches, x).load_weights(resnet50_Weights_path)
|
||||
|
||||
v1024_2048 = Conv2D( 1024 , (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(x)
|
||||
v1024_2048 = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(v1024_2048)
|
||||
v1024_2048 = Activation('relu')(v1024_2048)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D( (2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(v1024_2048)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f4],axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o ,f3], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f2], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, f1], axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = (UpSampling2D((2, 2), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (concatenate([o, inputs],axis=MERGE_AXIS))
|
||||
o = (ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING))(o)
|
||||
o = (Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='valid', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay)))(o)
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = Activation('relu')(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = Conv2D(n_classes, (1, 1), padding='same', data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING,kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay))(o)
|
||||
if task == "segmentation":
|
||||
o = (BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis))(o)
|
||||
o = (Activation('softmax'))(o)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
o = (Activation('sigmoid'))(o)
|
||||
|
||||
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=o)
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def resnet50_classifier(n_classes,input_height=224,input_width=224,weight_decay=1e-6,pretraining=False):
|
||||
include_top=True
|
||||
assert input_height%32 == 0
|
||||
assert input_width%32 == 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_input = Input(shape=(input_height,input_width , 3 ))
|
||||
|
||||
if IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_last':
|
||||
bn_axis = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bn_axis = 1
|
||||
|
||||
x = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING)(img_input)
|
||||
x = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2),kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay), name='conv1')(x)
|
||||
f1 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name='bn_conv1')(x)
|
||||
x = Activation('relu')(x)
|
||||
x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3) , data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING , strides=(2, 2))(x)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1))
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
|
||||
f2 = one_side_pad(x )
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
|
||||
f3 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
|
||||
f4 = x
|
||||
|
||||
x = conv_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
|
||||
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
|
||||
f5 = x
|
||||
|
||||
if pretraining:
|
||||
Model(img_input, x).load_weights(resnet50_Weights_path)
|
||||
|
||||
x = AveragePooling2D((7, 7), name='avg_pool')(x)
|
||||
x = Flatten()(x)
|
||||
|
||||
##
|
||||
x = Dense(256, activation='relu', name='fc512')(x)
|
||||
x=Dropout(0.2)(x)
|
||||
##
|
||||
x = Dense(n_classes, activation='softmax', name='fc1000')(x)
|
||||
model = Model(img_input, x)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def machine_based_reading_order_model(n_classes,input_height=224,input_width=224,weight_decay=1e-6,pretraining=False):
|
||||
assert input_height%32 == 0
|
||||
assert input_width%32 == 0
|
||||
|
||||
img_input = Input(shape=(input_height,input_width , 3 ))
|
||||
|
||||
if IMAGE_ORDERING == 'channels_last':
|
||||
bn_axis = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bn_axis = 1
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING)(img_input)
|
||||
x1 = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING, strides=(2, 2),kernel_regularizer=l2(weight_decay), name='conv1')(x1)
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = BatchNormalization(axis=bn_axis, name='bn_conv1')(x1)
|
||||
x1 = Activation('relu')(x1)
|
||||
x1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3) , data_format=IMAGE_ORDERING , strides=(2, 2))(x1)
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = conv_block(x1, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1))
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = conv_block(x1, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = conv_block(x1, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = conv_block(x1, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
|
||||
x1 = identity_block(x1, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
|
||||
|
||||
if pretraining:
|
||||
Model(img_input , x1).load_weights(resnet50_Weights_path)
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = AveragePooling2D((7, 7), name='avg_pool1')(x1)
|
||||
flattened = Flatten()(x1)
|
||||
|
||||
o = Dense(256, activation='relu', name='fc512')(flattened)
|
||||
o=Dropout(0.2)(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = Dense(256, activation='relu', name='fc512a')(o)
|
||||
o=Dropout(0.2)(o)
|
||||
|
||||
o = Dense(n_classes, activation='sigmoid', name='fc1000')(o)
|
||||
model = Model(img_input , o)
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,474 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import json
|
||||
|
||||
import click
|
||||
|
||||
from eynollah.training.metrics import (
|
||||
soft_dice_loss,
|
||||
weighted_categorical_crossentropy
|
||||
)
|
||||
from eynollah.training.models import (
|
||||
PatchEncoder,
|
||||
Patches,
|
||||
machine_based_reading_order_model,
|
||||
resnet50_classifier,
|
||||
resnet50_unet,
|
||||
vit_resnet50_unet,
|
||||
vit_resnet50_unet_transformer_before_cnn
|
||||
)
|
||||
from eynollah.training.utils import (
|
||||
data_gen,
|
||||
generate_arrays_from_folder_reading_order,
|
||||
generate_data_from_folder_evaluation,
|
||||
generate_data_from_folder_training,
|
||||
get_one_hot,
|
||||
provide_patches,
|
||||
return_number_of_total_training_data
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from tensorflow.compat.v1.keras.backend import set_session
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD, Adam
|
||||
from sacred import Experiment
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import Callback
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
class SaveWeightsAfterSteps(Callback):
|
||||
def __init__(self, save_interval, save_path, _config):
|
||||
super(SaveWeightsAfterSteps, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.save_interval = save_interval
|
||||
self.save_path = save_path
|
||||
self.step_count = 0
|
||||
self._config = _config
|
||||
|
||||
def on_train_batch_end(self, batch, logs=None):
|
||||
self.step_count += 1
|
||||
|
||||
if self.step_count % self.save_interval ==0:
|
||||
save_file = f"{self.save_path}/model_step_{self.step_count}"
|
||||
#os.system('mkdir '+save_file)
|
||||
|
||||
self.model.save(save_file)
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(os.path.join(self.save_path, f"model_step_{self.step_count}"),"config.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(self._config, fp) # encode dict into JSON
|
||||
print(f"saved model as steps {self.step_count} to {save_file}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def configuration():
|
||||
config = tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()
|
||||
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
|
||||
session = tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config)
|
||||
set_session(session)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_dirs_or_files(input_data):
|
||||
image_input, labels_input = os.path.join(input_data, 'images/'), os.path.join(input_data, 'labels/')
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(input_data):
|
||||
# Check if training dir exists
|
||||
assert os.path.isdir(image_input), "{} is not a directory".format(image_input)
|
||||
assert os.path.isdir(labels_input), "{} is not a directory".format(labels_input)
|
||||
return image_input, labels_input
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ex = Experiment(save_git_info=False)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ex.config
|
||||
def config_params():
|
||||
n_classes = None # Number of classes. In the case of binary classification this should be 2.
|
||||
n_epochs = 1 # Number of epochs.
|
||||
input_height = 224 * 1 # Height of model's input in pixels.
|
||||
input_width = 224 * 1 # Width of model's input in pixels.
|
||||
weight_decay = 1e-6 # Weight decay of l2 regularization of model layers.
|
||||
n_batch = 1 # Number of batches at each iteration.
|
||||
learning_rate = 1e-4 # Set the learning rate.
|
||||
patches = False # Divides input image into smaller patches (input size of the model) when set to true. For the model to see the full image, like page extraction, set this to false.
|
||||
augmentation = False # To apply any kind of augmentation, this parameter must be set to true.
|
||||
flip_aug = False # If true, different types of flipping will be applied to the image. Types of flips are defined with "flip_index" in config_params.json.
|
||||
blur_aug = False # If true, different types of blurring will be applied to the image. Types of blur are defined with "blur_k" in config_params.json.
|
||||
padding_white = False # If true, white padding will be applied to the image.
|
||||
padding_black = False # If true, black padding will be applied to the image.
|
||||
scaling = False # If true, scaling will be applied to the image. The amount of scaling is defined with "scales" in config_params.json.
|
||||
shifting = False
|
||||
degrading = False # If true, degrading will be applied to the image. The amount of degrading is defined with "degrade_scales" in config_params.json.
|
||||
brightening = False # If true, brightening will be applied to the image. The amount of brightening is defined with "brightness" in config_params.json.
|
||||
binarization = False # If true, Otsu thresholding will be applied to augment the input with binarized images.
|
||||
adding_rgb_background = False
|
||||
adding_rgb_foreground = False
|
||||
add_red_textlines = False
|
||||
channels_shuffling = False
|
||||
dir_train = None # Directory of training dataset with subdirectories having the names "images" and "labels".
|
||||
dir_eval = None # Directory of validation dataset with subdirectories having the names "images" and "labels".
|
||||
dir_output = None # Directory where the output model will be saved.
|
||||
pretraining = False # Set to true to load pretrained weights of ResNet50 encoder.
|
||||
scaling_bluring = False # If true, a combination of scaling and blurring will be applied to the image.
|
||||
scaling_binarization = False # If true, a combination of scaling and binarization will be applied to the image.
|
||||
rotation = False # If true, a 90 degree rotation will be implemeneted.
|
||||
rotation_not_90 = False # If true rotation based on provided angles with thetha will be implemeneted.
|
||||
scaling_brightness = False # If true, a combination of scaling and brightening will be applied to the image.
|
||||
scaling_flip = False # If true, a combination of scaling and flipping will be applied to the image.
|
||||
thetha = None # Rotate image by these angles for augmentation.
|
||||
shuffle_indexes = None
|
||||
blur_k = None # Blur image for augmentation.
|
||||
scales = None # Scale patches for augmentation.
|
||||
degrade_scales = None # Degrade image for augmentation.
|
||||
brightness = None # Brighten image for augmentation.
|
||||
flip_index = None # Flip image for augmentation.
|
||||
continue_training = False # Set to true if you would like to continue training an already trained a model.
|
||||
transformer_patchsize_x = None # Patch size of vision transformer patches in x direction.
|
||||
transformer_patchsize_y = None # Patch size of vision transformer patches in y direction.
|
||||
transformer_num_patches_xy = None # Number of patches for vision transformer in x and y direction respectively.
|
||||
transformer_projection_dim = 64 # Transformer projection dimension. Default value is 64.
|
||||
transformer_mlp_head_units = [128, 64] # Transformer Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) head units. Default value is [128, 64]
|
||||
transformer_layers = 8 # transformer layers. Default value is 8.
|
||||
transformer_num_heads = 4 # Transformer number of heads. Default value is 4.
|
||||
transformer_cnn_first = True # We have two types of vision transformers. In one type, a CNN is applied first, followed by a transformer. In the other type, this order is reversed. If transformer_cnn_first is true, it means the CNN will be applied before the transformer. Default value is true.
|
||||
index_start = 0 # Index of model to continue training from. E.g. if you trained for 3 epochs and last index is 2, to continue from model_1.h5, set "index_start" to 3 to start naming model with index 3.
|
||||
dir_of_start_model = '' # Directory containing pretrained encoder to continue training the model.
|
||||
is_loss_soft_dice = False # Use soft dice as loss function. When set to true, "weighted_loss" must be false.
|
||||
weighted_loss = False # Use weighted categorical cross entropy as loss fucntion. When set to true, "is_loss_soft_dice" must be false.
|
||||
data_is_provided = False # Only set this to true when you have already provided the input data and the train and eval data are in "dir_output".
|
||||
task = "segmentation" # This parameter defines task of model which can be segmentation, enhancement or classification.
|
||||
f1_threshold_classification = None # This threshold is used to consider models with an evaluation f1 scores bigger than it. The selected model weights undergo a weights ensembling. And avreage ensembled model will be written to output.
|
||||
classification_classes_name = None # Dictionary of classification classes names.
|
||||
backbone_type = None # As backbone we have 2 types of backbones. A vision transformer alongside a CNN and we call it "transformer" and only CNN called "nontransformer"
|
||||
save_interval = None
|
||||
dir_img_bin = None
|
||||
number_of_backgrounds_per_image = 1
|
||||
dir_rgb_backgrounds = None
|
||||
dir_rgb_foregrounds = None
|
||||
|
||||
@ex.automain
|
||||
def run(_config, n_classes, n_epochs, input_height,
|
||||
input_width, weight_decay, weighted_loss,
|
||||
index_start, dir_of_start_model, is_loss_soft_dice,
|
||||
n_batch, patches, augmentation, flip_aug,
|
||||
blur_aug, padding_white, padding_black, scaling, shifting, degrading,channels_shuffling,
|
||||
brightening, binarization, adding_rgb_background, adding_rgb_foreground, add_red_textlines, blur_k, scales, degrade_scales,shuffle_indexes,
|
||||
brightness, dir_train, data_is_provided, scaling_bluring,
|
||||
scaling_brightness, scaling_binarization, rotation, rotation_not_90,
|
||||
thetha, scaling_flip, continue_training, transformer_projection_dim,
|
||||
transformer_mlp_head_units, transformer_layers, transformer_num_heads, transformer_cnn_first,
|
||||
transformer_patchsize_x, transformer_patchsize_y,
|
||||
transformer_num_patches_xy, backbone_type, save_interval, flip_index, dir_eval, dir_output,
|
||||
pretraining, learning_rate, task, f1_threshold_classification, classification_classes_name, dir_img_bin, number_of_backgrounds_per_image,dir_rgb_backgrounds, dir_rgb_foregrounds):
|
||||
|
||||
if dir_rgb_backgrounds:
|
||||
list_all_possible_background_images = os.listdir(dir_rgb_backgrounds)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
list_all_possible_background_images = None
|
||||
|
||||
if dir_rgb_foregrounds:
|
||||
list_all_possible_foreground_rgbs = os.listdir(dir_rgb_foregrounds)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
list_all_possible_foreground_rgbs = None
|
||||
|
||||
if task == "segmentation" or task == "enhancement" or task == "binarization":
|
||||
if data_is_provided:
|
||||
dir_train_flowing = os.path.join(dir_output, 'train')
|
||||
dir_eval_flowing = os.path.join(dir_output, 'eval')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dir_flow_train_imgs = os.path.join(dir_train_flowing, 'images')
|
||||
dir_flow_train_labels = os.path.join(dir_train_flowing, 'labels')
|
||||
|
||||
dir_flow_eval_imgs = os.path.join(dir_eval_flowing, 'images')
|
||||
dir_flow_eval_labels = os.path.join(dir_eval_flowing, 'labels')
|
||||
|
||||
configuration()
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dir_img, dir_seg = get_dirs_or_files(dir_train)
|
||||
dir_img_val, dir_seg_val = get_dirs_or_files(dir_eval)
|
||||
|
||||
# make first a directory in output for both training and evaluations in order to flow data from these directories.
|
||||
dir_train_flowing = os.path.join(dir_output, 'train')
|
||||
dir_eval_flowing = os.path.join(dir_output, 'eval')
|
||||
|
||||
dir_flow_train_imgs = os.path.join(dir_train_flowing, 'images/')
|
||||
dir_flow_train_labels = os.path.join(dir_train_flowing, 'labels/')
|
||||
|
||||
dir_flow_eval_imgs = os.path.join(dir_eval_flowing, 'images/')
|
||||
dir_flow_eval_labels = os.path.join(dir_eval_flowing, 'labels/')
|
||||
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(dir_train_flowing):
|
||||
os.system('rm -rf ' + dir_train_flowing)
|
||||
os.makedirs(dir_train_flowing)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
os.makedirs(dir_train_flowing)
|
||||
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(dir_eval_flowing):
|
||||
os.system('rm -rf ' + dir_eval_flowing)
|
||||
os.makedirs(dir_eval_flowing)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
os.makedirs(dir_eval_flowing)
|
||||
|
||||
os.mkdir(dir_flow_train_imgs)
|
||||
os.mkdir(dir_flow_train_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
os.mkdir(dir_flow_eval_imgs)
|
||||
os.mkdir(dir_flow_eval_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
# set the gpu configuration
|
||||
configuration()
|
||||
|
||||
imgs_list=np.array(os.listdir(dir_img))
|
||||
segs_list=np.array(os.listdir(dir_seg))
|
||||
|
||||
imgs_list_test=np.array(os.listdir(dir_img_val))
|
||||
segs_list_test=np.array(os.listdir(dir_seg_val))
|
||||
|
||||
# writing patches into a sub-folder in order to be flowed from directory.
|
||||
provide_patches(imgs_list, segs_list, dir_img, dir_seg, dir_flow_train_imgs,
|
||||
dir_flow_train_labels, input_height, input_width, blur_k,
|
||||
blur_aug, padding_white, padding_black, flip_aug, binarization, adding_rgb_background,adding_rgb_foreground, add_red_textlines, channels_shuffling,
|
||||
scaling, shifting, degrading, brightening, scales, degrade_scales, brightness,
|
||||
flip_index,shuffle_indexes, scaling_bluring, scaling_brightness, scaling_binarization,
|
||||
rotation, rotation_not_90, thetha, scaling_flip, task, augmentation=augmentation,
|
||||
patches=patches, dir_img_bin=dir_img_bin,number_of_backgrounds_per_image=number_of_backgrounds_per_image,list_all_possible_background_images=list_all_possible_background_images, dir_rgb_backgrounds=dir_rgb_backgrounds, dir_rgb_foregrounds=dir_rgb_foregrounds,list_all_possible_foreground_rgbs=list_all_possible_foreground_rgbs)
|
||||
|
||||
provide_patches(imgs_list_test, segs_list_test, dir_img_val, dir_seg_val,
|
||||
dir_flow_eval_imgs, dir_flow_eval_labels, input_height, input_width,
|
||||
blur_k, blur_aug, padding_white, padding_black, flip_aug, binarization, adding_rgb_background, adding_rgb_foreground, add_red_textlines, channels_shuffling,
|
||||
scaling, shifting, degrading, brightening, scales, degrade_scales, brightness,
|
||||
flip_index, shuffle_indexes, scaling_bluring, scaling_brightness, scaling_binarization,
|
||||
rotation, rotation_not_90, thetha, scaling_flip, task, augmentation=False, patches=patches,dir_img_bin=dir_img_bin,number_of_backgrounds_per_image=number_of_backgrounds_per_image,list_all_possible_background_images=list_all_possible_background_images, dir_rgb_backgrounds=dir_rgb_backgrounds,dir_rgb_foregrounds=dir_rgb_foregrounds,list_all_possible_foreground_rgbs=list_all_possible_foreground_rgbs )
|
||||
|
||||
if weighted_loss:
|
||||
weights = np.zeros(n_classes)
|
||||
if data_is_provided:
|
||||
for obj in os.listdir(dir_flow_train_labels):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
label_obj = cv2.imread(dir_flow_train_labels + '/' + obj)
|
||||
label_obj_one_hot = get_one_hot(label_obj, label_obj.shape[0], label_obj.shape[1], n_classes)
|
||||
weights += (label_obj_one_hot.sum(axis=0)).sum(axis=0)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
for obj in os.listdir(dir_seg):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
label_obj = cv2.imread(dir_seg + '/' + obj)
|
||||
label_obj_one_hot = get_one_hot(label_obj, label_obj.shape[0], label_obj.shape[1], n_classes)
|
||||
weights += (label_obj_one_hot.sum(axis=0)).sum(axis=0)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
weights = 1.00 / weights
|
||||
|
||||
weights = weights / float(np.sum(weights))
|
||||
weights = weights / float(np.min(weights))
|
||||
weights = weights / float(np.sum(weights))
|
||||
|
||||
if continue_training:
|
||||
if backbone_type=='nontransformer':
|
||||
if is_loss_soft_dice and (task == "segmentation" or task == "binarization"):
|
||||
model = load_model(dir_of_start_model, compile=True, custom_objects={'soft_dice_loss': soft_dice_loss})
|
||||
if weighted_loss and (task == "segmentation" or task == "binarization"):
|
||||
model = load_model(dir_of_start_model, compile=True, custom_objects={'loss': weighted_categorical_crossentropy(weights)})
|
||||
if not is_loss_soft_dice and not weighted_loss:
|
||||
model = load_model(dir_of_start_model , compile=True)
|
||||
elif backbone_type=='transformer':
|
||||
if is_loss_soft_dice and (task == "segmentation" or task == "binarization"):
|
||||
model = load_model(dir_of_start_model, compile=True, custom_objects={"PatchEncoder": PatchEncoder, "Patches": Patches,'soft_dice_loss': soft_dice_loss})
|
||||
if weighted_loss and (task == "segmentation" or task == "binarization"):
|
||||
model = load_model(dir_of_start_model, compile=True, custom_objects={'loss': weighted_categorical_crossentropy(weights)})
|
||||
if not is_loss_soft_dice and not weighted_loss:
|
||||
model = load_model(dir_of_start_model , compile=True,custom_objects = {"PatchEncoder": PatchEncoder, "Patches": Patches})
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_start = 0
|
||||
if backbone_type=='nontransformer':
|
||||
model = resnet50_unet(n_classes, input_height, input_width, task, weight_decay, pretraining)
|
||||
elif backbone_type=='transformer':
|
||||
num_patches_x = transformer_num_patches_xy[0]
|
||||
num_patches_y = transformer_num_patches_xy[1]
|
||||
num_patches = num_patches_x * num_patches_y
|
||||
|
||||
if transformer_cnn_first:
|
||||
if input_height != (num_patches_y * transformer_patchsize_y * 32):
|
||||
print("Error: transformer_patchsize_y or transformer_num_patches_xy height value error . input_height should be equal to ( transformer_num_patches_xy height value * transformer_patchsize_y * 32)")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
if input_width != (num_patches_x * transformer_patchsize_x * 32):
|
||||
print("Error: transformer_patchsize_x or transformer_num_patches_xy width value error . input_width should be equal to ( transformer_num_patches_xy width value * transformer_patchsize_x * 32)")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
if (transformer_projection_dim % (transformer_patchsize_y * transformer_patchsize_x)) != 0:
|
||||
print("Error: transformer_projection_dim error. The remainder when parameter transformer_projection_dim is divided by (transformer_patchsize_y*transformer_patchsize_x) should be zero")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model = vit_resnet50_unet(n_classes, transformer_patchsize_x, transformer_patchsize_y, num_patches, transformer_mlp_head_units, transformer_layers, transformer_num_heads, transformer_projection_dim, input_height, input_width, task, weight_decay, pretraining)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if input_height != (num_patches_y * transformer_patchsize_y):
|
||||
print("Error: transformer_patchsize_y or transformer_num_patches_xy height value error . input_height should be equal to ( transformer_num_patches_xy height value * transformer_patchsize_y)")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
if input_width != (num_patches_x * transformer_patchsize_x):
|
||||
print("Error: transformer_patchsize_x or transformer_num_patches_xy width value error . input_width should be equal to ( transformer_num_patches_xy width value * transformer_patchsize_x)")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
if (transformer_projection_dim % (transformer_patchsize_y * transformer_patchsize_x)) != 0:
|
||||
print("Error: transformer_projection_dim error. The remainder when parameter transformer_projection_dim is divided by (transformer_patchsize_y*transformer_patchsize_x) should be zero")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
model = vit_resnet50_unet_transformer_before_cnn(n_classes, transformer_patchsize_x, transformer_patchsize_y, num_patches, transformer_mlp_head_units, transformer_layers, transformer_num_heads, transformer_projection_dim, input_height, input_width, task, weight_decay, pretraining)
|
||||
|
||||
#if you want to see the model structure just uncomment model summary.
|
||||
model.summary()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if task == "segmentation" or task == "binarization":
|
||||
if not is_loss_soft_dice and not weighted_loss:
|
||||
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
|
||||
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate), metrics=['accuracy'])
|
||||
if is_loss_soft_dice:
|
||||
model.compile(loss=soft_dice_loss,
|
||||
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate), metrics=['accuracy'])
|
||||
if weighted_loss:
|
||||
model.compile(loss=weighted_categorical_crossentropy(weights),
|
||||
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate), metrics=['accuracy'])
|
||||
elif task == "enhancement":
|
||||
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error',
|
||||
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate), metrics=['accuracy'])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# generating train and evaluation data
|
||||
train_gen = data_gen(dir_flow_train_imgs, dir_flow_train_labels, batch_size=n_batch,
|
||||
input_height=input_height, input_width=input_width, n_classes=n_classes, task=task)
|
||||
val_gen = data_gen(dir_flow_eval_imgs, dir_flow_eval_labels, batch_size=n_batch,
|
||||
input_height=input_height, input_width=input_width, n_classes=n_classes, task=task)
|
||||
|
||||
##img_validation_patches = os.listdir(dir_flow_eval_imgs)
|
||||
##score_best=[]
|
||||
##score_best.append(0)
|
||||
|
||||
if save_interval:
|
||||
save_weights_callback = SaveWeightsAfterSteps(save_interval, dir_output, _config)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for i in tqdm(range(index_start, n_epochs + index_start)):
|
||||
if save_interval:
|
||||
model.fit(
|
||||
train_gen,
|
||||
steps_per_epoch=int(len(os.listdir(dir_flow_train_imgs)) / n_batch) - 1,
|
||||
validation_data=val_gen,
|
||||
validation_steps=1,
|
||||
epochs=1, callbacks=[save_weights_callback])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model.fit(
|
||||
train_gen,
|
||||
steps_per_epoch=int(len(os.listdir(dir_flow_train_imgs)) / n_batch) - 1,
|
||||
validation_data=val_gen,
|
||||
validation_steps=1,
|
||||
epochs=1)
|
||||
|
||||
model.save(os.path.join(dir_output,'model_'+str(i)))
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(os.path.join(dir_output,'model_'+str(i)),"config.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(_config, fp) # encode dict into JSON
|
||||
|
||||
#os.system('rm -rf '+dir_train_flowing)
|
||||
#os.system('rm -rf '+dir_eval_flowing)
|
||||
|
||||
#model.save(dir_output+'/'+'model'+'.h5')
|
||||
elif task=='classification':
|
||||
configuration()
|
||||
model = resnet50_classifier(n_classes, input_height, input_width, weight_decay, pretraining)
|
||||
|
||||
opt_adam = Adam(learning_rate=0.001)
|
||||
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
|
||||
optimizer = opt_adam,metrics=['accuracy'])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
list_classes = list(classification_classes_name.values())
|
||||
testX, testY = generate_data_from_folder_evaluation(dir_eval, input_height, input_width, n_classes, list_classes)
|
||||
|
||||
y_tot=np.zeros((testX.shape[0],n_classes))
|
||||
|
||||
score_best= [0]
|
||||
|
||||
num_rows = return_number_of_total_training_data(dir_train)
|
||||
weights=[]
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(n_epochs):
|
||||
history = model.fit( generate_data_from_folder_training(dir_train, n_batch , input_height, input_width, n_classes, list_classes), steps_per_epoch=num_rows / n_batch, verbose=1)#,class_weight=weights)
|
||||
|
||||
y_pr_class = []
|
||||
for jj in range(testY.shape[0]):
|
||||
y_pr=model.predict(testX[jj,:,:,:].reshape(1,input_height,input_width,3), verbose=0)
|
||||
y_pr_ind= np.argmax(y_pr,axis=1)
|
||||
y_pr_class.append(y_pr_ind)
|
||||
|
||||
y_pr_class = np.array(y_pr_class)
|
||||
f1score=f1_score(np.argmax(testY,axis=1), y_pr_class, average='macro')
|
||||
print(i,f1score)
|
||||
|
||||
if f1score>score_best[0]:
|
||||
score_best[0]=f1score
|
||||
model.save(os.path.join(dir_output,'model_best'))
|
||||
|
||||
if f1score > f1_threshold_classification:
|
||||
weights.append(model.get_weights() )
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if len(weights) >= 1:
|
||||
new_weights=list()
|
||||
for weights_list_tuple in zip(*weights):
|
||||
new_weights.append( [np.array(weights_).mean(axis=0) for weights_ in zip(*weights_list_tuple)] )
|
||||
|
||||
new_weights = [np.array(x) for x in new_weights]
|
||||
model_weight_averaged=tf.keras.models.clone_model(model)
|
||||
model_weight_averaged.set_weights(new_weights)
|
||||
|
||||
model_weight_averaged.save(os.path.join(dir_output,'model_ens_avg'))
|
||||
with open(os.path.join( os.path.join(dir_output,'model_ens_avg'), "config.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(_config, fp) # encode dict into JSON
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join( os.path.join(dir_output,'model_best'), "config.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(_config, fp) # encode dict into JSON
|
||||
|
||||
elif task=='reading_order':
|
||||
configuration()
|
||||
model = machine_based_reading_order_model(n_classes,input_height,input_width,weight_decay,pretraining)
|
||||
|
||||
dir_flow_train_imgs = os.path.join(dir_train, 'images')
|
||||
dir_flow_train_labels = os.path.join(dir_train, 'labels')
|
||||
|
||||
classes = os.listdir(dir_flow_train_labels)
|
||||
if augmentation:
|
||||
num_rows = len(classes)*(len(thetha) + 1)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
num_rows = len(classes)
|
||||
#ls_test = os.listdir(dir_flow_train_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
#f1score_tot = [0]
|
||||
indexer_start = 0
|
||||
# opt = SGD(learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.9)
|
||||
opt_adam = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0001)
|
||||
model.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy",
|
||||
optimizer = opt_adam,metrics=['accuracy'])
|
||||
|
||||
if save_interval:
|
||||
save_weights_callback = SaveWeightsAfterSteps(save_interval, dir_output, _config)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(n_epochs):
|
||||
if save_interval:
|
||||
history = model.fit(generate_arrays_from_folder_reading_order(dir_flow_train_labels, dir_flow_train_imgs, n_batch, input_height, input_width, n_classes, thetha, augmentation), steps_per_epoch=num_rows / n_batch, verbose=1, callbacks=[save_weights_callback])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
history = model.fit(generate_arrays_from_folder_reading_order(dir_flow_train_labels, dir_flow_train_imgs, n_batch, input_height, input_width, n_classes, thetha, augmentation), steps_per_epoch=num_rows / n_batch, verbose=1)
|
||||
model.save( os.path.join(dir_output,'model_'+str(i+indexer_start) ))
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(os.path.join(dir_output,'model_'+str(i)),"config.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(_config, fp) # encode dict into JSON
|
||||
'''
|
||||
if f1score>f1score_tot[0]:
|
||||
f1score_tot[0] = f1score
|
||||
model_dir = os.path.join(dir_out,'model_best')
|
||||
model.save(model_dir)
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
|
|
@ -1,365 +0,0 @@
|
|||
from typing import Sequence, Union
|
||||
from numbers import Number
|
||||
from functools import partial
|
||||
import itertools
|
||||
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import minimum_spanning_tree
|
||||
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, LineString
|
||||
from shapely.geometry.polygon import orient
|
||||
from shapely import set_precision
|
||||
from shapely.ops import unary_union, nearest_points
|
||||
|
||||
from .rotate import rotate_image, rotation_image_new
|
||||
|
||||
def contours_in_same_horizon(cy_main_hor):
|
||||
X1 = np.zeros((len(cy_main_hor), len(cy_main_hor)))
|
||||
X2 = np.zeros((len(cy_main_hor), len(cy_main_hor)))
|
||||
|
||||
X1[0::1, :] = cy_main_hor[:]
|
||||
X2 = X1.T
|
||||
|
||||
X_dif = np.abs(X2 - X1)
|
||||
args_help = np.array(range(len(cy_main_hor)))
|
||||
all_args = []
|
||||
for i in range(len(cy_main_hor)):
|
||||
list_h = list(args_help[X_dif[i, :] <= 20])
|
||||
list_h.append(i)
|
||||
if len(list_h) > 1:
|
||||
all_args.append(list(set(list_h)))
|
||||
return np.unique(np.array(all_args, dtype=object))
|
||||
|
||||
def find_contours_mean_y_diff(contours_main):
|
||||
M_main = [cv2.moments(contours_main[j]) for j in range(len(contours_main))]
|
||||
cy_main = [(M_main[j]["m01"] / (M_main[j]["m00"] + 1e-32)) for j in range(len(M_main))]
|
||||
return np.mean(np.diff(np.sort(np.array(cy_main))))
|
||||
|
||||
def get_text_region_boxes_by_given_contours(contours):
|
||||
return [cv2.boundingRect(contour)
|
||||
for contour in contours]
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_contours_area_of_image(image, contours, hierarchy, max_area=1.0, min_area=0.0, dilate=0):
|
||||
found_polygons_early = []
|
||||
for jv, contour in enumerate(contours):
|
||||
if len(contour) < 3: # A polygon cannot have less than 3 points
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
polygon = contour2polygon(contour, dilate=dilate)
|
||||
area = polygon.area
|
||||
if (area >= min_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]) and
|
||||
area <= max_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]) and
|
||||
hierarchy[0][jv][3] == -1):
|
||||
found_polygons_early.append(polygon2contour(polygon))
|
||||
return found_polygons_early
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(image, contours, hierarchy, max_area=1.0, min_area=0.0, dilate=0):
|
||||
found_polygons_early = []
|
||||
for jv, contour in enumerate(contours):
|
||||
if len(contour) < 3: # A polygon cannot have less than 3 points
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
polygon = contour2polygon(contour, dilate=dilate)
|
||||
# area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
|
||||
area = polygon.area
|
||||
##print(np.prod(thresh.shape[:2]))
|
||||
# Check that polygon has area greater than minimal area
|
||||
# print(hierarchy[0][jv][3],hierarchy )
|
||||
if (area >= min_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]) and
|
||||
area <= max_area * np.prod(image.shape[:2]) and
|
||||
# hierarchy[0][jv][3]==-1
|
||||
True):
|
||||
# print(contour[0][0][1])
|
||||
found_polygons_early.append(polygon2contour(polygon))
|
||||
return found_polygons_early
|
||||
|
||||
def find_center_of_contours(contours):
|
||||
moments = [cv2.moments(contour) for contour in contours]
|
||||
cx = [feat["m10"] / (feat["m00"] + 1e-32)
|
||||
for feat in moments]
|
||||
cy = [feat["m01"] / (feat["m00"] + 1e-32)
|
||||
for feat in moments]
|
||||
return cx, cy
|
||||
|
||||
def find_new_features_of_contours(contours):
|
||||
# areas = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contour) for contour in contours])
|
||||
cx, cy = find_center_of_contours(contours)
|
||||
slice_x = np.index_exp[:, 0, 0]
|
||||
slice_y = np.index_exp[:, 0, 1]
|
||||
if any(contour.ndim < 3 for contour in contours):
|
||||
slice_x = np.index_exp[:, 0]
|
||||
slice_y = np.index_exp[:, 1]
|
||||
x_min = np.array([np.min(contour[slice_x]) for contour in contours])
|
||||
x_max = np.array([np.max(contour[slice_x]) for contour in contours])
|
||||
y_min = np.array([np.min(contour[slice_y]) for contour in contours])
|
||||
y_max = np.array([np.max(contour[slice_y]) for contour in contours])
|
||||
# dis_x=np.abs(x_max-x_min)
|
||||
y_corr_x_min = np.array([contour[np.argmin(contour[slice_x])][slice_y[1:]]
|
||||
for contour in contours])
|
||||
|
||||
return cx, cy, x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max, y_corr_x_min
|
||||
|
||||
def find_features_of_contours(contours):
|
||||
y_min = np.array([np.min(contour[:,0,1]) for contour in contours])
|
||||
y_max = np.array([np.max(contour[:,0,1]) for contour in contours])
|
||||
|
||||
return y_min, y_max
|
||||
|
||||
def return_parent_contours(contours, hierarchy):
|
||||
contours_parent = [contours[i]
|
||||
for i in range(len(contours))
|
||||
if hierarchy[0][i][3] == -1]
|
||||
return contours_parent
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_interested_region(region_pre_p, label, min_area=0.0002):
|
||||
# pixels of images are identified by 5
|
||||
if region_pre_p.ndim == 3:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :, 0] == label) * 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :] == label) * 1
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(cnts_images.astype(np.uint8), 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
contours_imgs = return_parent_contours(contours_imgs, hierarchy)
|
||||
contours_imgs = filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(thresh, contours_imgs, hierarchy,
|
||||
max_area=1, min_area=min_area)
|
||||
return contours_imgs
|
||||
|
||||
def do_work_of_contours_in_image(contour, index_r_con, img, slope_first):
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[contour], color=1)
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first)
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img_copy, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
|
||||
return cont_int[0], index_r_con
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image_multi(cnts, img, slope_first, map=map):
|
||||
if not len(cnts):
|
||||
return [], []
|
||||
results = map(partial(do_work_of_contours_in_image,
|
||||
img=img,
|
||||
slope_first=slope_first,
|
||||
),
|
||||
cnts, range(len(cnts)))
|
||||
return tuple(zip(*results))
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image(cnts, img, slope_first):
|
||||
cnts_org = []
|
||||
# print(cnts,'cnts')
|
||||
for i in range(len(cnts)):
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[cnts[i]], color=1)
|
||||
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
# print(img.shape,'img')
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first)
|
||||
##print(img_copy.shape,'img_copy')
|
||||
# plt.imshow(img_copy)
|
||||
# plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img_copy, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
# print(np.shape(cont_int[0]))
|
||||
cnts_org.append(cont_int[0])
|
||||
|
||||
return cnts_org
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image_light_old(cnts, img, slope_first):
|
||||
zoom = 3
|
||||
img = cv2.resize(img, (img.shape[1] // zoom,
|
||||
img.shape[0] // zoom),
|
||||
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
cnts_org = []
|
||||
for cnt in cnts:
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[cnt // zoom], color=1)
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img_copy, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
cnts_org.append(cont_int[0] * zoom)
|
||||
|
||||
return cnts_org
|
||||
|
||||
def do_back_rotation_and_get_cnt_back(contour_par, index_r_con, img, slope_first, confidence_matrix):
|
||||
img_copy = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
img_copy = cv2.fillPoly(img_copy, pts=[contour_par], color=1)
|
||||
confidence_matrix_mapped_with_contour = confidence_matrix * img_copy
|
||||
confidence_contour = np.sum(confidence_matrix_mapped_with_contour) / float(np.sum(img_copy))
|
||||
|
||||
img_copy = rotation_image_new(img_copy, -slope_first).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img_copy, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
cont_int, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
if len(cont_int)==0:
|
||||
cont_int = [contour_par]
|
||||
confidence_contour = 0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 0] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[1] - img.shape[1])
|
||||
cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] = cont_int[0][:, 0, 1] + np.abs(img_copy.shape[0] - img.shape[0])
|
||||
return cont_int[0], index_r_con, confidence_contour
|
||||
|
||||
def get_textregion_contours_in_org_image_light(cnts, img, confidence_matrix):
|
||||
if not len(cnts):
|
||||
return []
|
||||
|
||||
confidence_matrix = cv2.resize(confidence_matrix,
|
||||
(img.shape[1] // 6, img.shape[0] // 6),
|
||||
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
|
||||
confs = []
|
||||
for cnt in cnts:
|
||||
cnt_mask = np.zeros(confidence_matrix.shape)
|
||||
cnt_mask = cv2.fillPoly(cnt_mask, pts=[cnt // 6], color=1.0)
|
||||
confs.append(np.sum(confidence_matrix * cnt_mask) / np.sum(cnt_mask))
|
||||
return confs
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_interested_textline(region_pre_p, label):
|
||||
# pixels of images are identified by 5
|
||||
if region_pre_p.ndim == 3:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :, 0] == label) * 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cnts_images = (region_pre_p[:, :] == label) * 1
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(cnts_images.astype(np.uint8), 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
contours_imgs, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
contours_imgs = return_parent_contours(contours_imgs, hierarchy)
|
||||
contours_imgs = filter_contours_area_of_image_tables(
|
||||
thresh, contours_imgs, hierarchy, max_area=1, min_area=0.000000003)
|
||||
return contours_imgs
|
||||
|
||||
def return_contours_of_image(image):
|
||||
if len(image.shape) == 2:
|
||||
image = image.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
imgray = image
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image = image.astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray, 0, 255, 0)
|
||||
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
return contours, hierarchy
|
||||
|
||||
def dilate_textline_contours(all_found_textline_polygons):
|
||||
return [[polygon2contour(contour2polygon(contour, dilate=6))
|
||||
for contour in region]
|
||||
for region in all_found_textline_polygons]
|
||||
|
||||
def dilate_textregion_contours(all_found_textline_polygons):
|
||||
return [polygon2contour(contour2polygon(contour, dilate=6))
|
||||
for contour in all_found_textline_polygons]
|
||||
|
||||
def contour2polygon(contour: Union[np.ndarray, Sequence[Sequence[Sequence[Number]]]], dilate=0):
|
||||
polygon = Polygon([point[0] for point in contour])
|
||||
if dilate:
|
||||
polygon = polygon.buffer(dilate)
|
||||
if polygon.geom_type == 'GeometryCollection':
|
||||
# heterogeneous result: filter zero-area shapes (LineString, Point)
|
||||
polygon = unary_union([geom for geom in polygon.geoms if geom.area > 0])
|
||||
if polygon.geom_type == 'MultiPolygon':
|
||||
# homogeneous result: construct convex hull to connect
|
||||
polygon = join_polygons(polygon.geoms)
|
||||
return make_valid(polygon)
|
||||
|
||||
def polygon2contour(polygon: Polygon) -> np.ndarray:
|
||||
polygon = np.array(polygon.exterior.coords[:-1], dtype=int)
|
||||
return np.maximum(0, polygon).astype(int)[:, np.newaxis]
|
||||
|
||||
def make_intersection(poly1, poly2):
|
||||
interp = poly1.intersection(poly2)
|
||||
# post-process
|
||||
if interp.is_empty or interp.area == 0.0:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
if interp.geom_type == 'GeometryCollection':
|
||||
# heterogeneous result: filter zero-area shapes (LineString, Point)
|
||||
interp = unary_union([geom for geom in interp.geoms if geom.area > 0])
|
||||
if interp.geom_type == 'MultiPolygon':
|
||||
# homogeneous result: construct convex hull to connect
|
||||
interp = join_polygons(interp.geoms)
|
||||
assert interp.geom_type == 'Polygon', interp.wkt
|
||||
interp = make_valid(interp)
|
||||
return interp
|
||||
|
||||
def make_valid(polygon: Polygon) -> Polygon:
|
||||
"""Ensures shapely.geometry.Polygon object is valid by repeated rearrangement/simplification/enlargement."""
|
||||
def isint(x):
|
||||
return isinstance(x, int) or int(x) == x
|
||||
# make sure rounding does not invalidate
|
||||
if not all(map(isint, np.array(polygon.exterior.coords).flat)) and polygon.minimum_clearance < 1.0:
|
||||
polygon = Polygon(np.round(polygon.exterior.coords))
|
||||
points = list(polygon.exterior.coords[:-1])
|
||||
# try by re-arranging points
|
||||
for split in range(1, len(points)):
|
||||
if polygon.is_valid or polygon.simplify(polygon.area).is_valid:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# simplification may not be possible (at all) due to ordering
|
||||
# in that case, try another starting point
|
||||
polygon = Polygon(points[-split:]+points[:-split])
|
||||
# try by simplification
|
||||
for tolerance in range(int(polygon.area + 1.5)):
|
||||
if polygon.is_valid:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# simplification may require a larger tolerance
|
||||
polygon = polygon.simplify(tolerance + 1)
|
||||
# try by enlarging
|
||||
for tolerance in range(1, int(polygon.area + 2.5)):
|
||||
if polygon.is_valid:
|
||||
break
|
||||
# enlargement may require a larger tolerance
|
||||
polygon = polygon.buffer(tolerance)
|
||||
assert polygon.is_valid, polygon.wkt
|
||||
return polygon
|
||||
|
||||
def join_polygons(polygons: Sequence[Polygon], scale=20) -> Polygon:
|
||||
"""construct concave hull (alpha shape) from input polygons by connecting their pairwise nearest points"""
|
||||
# ensure input polygons are simply typed and all oriented equally
|
||||
polygons = [orient(poly)
|
||||
for poly in itertools.chain.from_iterable(
|
||||
[poly.geoms
|
||||
if poly.geom_type in ['MultiPolygon', 'GeometryCollection']
|
||||
else [poly]
|
||||
for poly in polygons])]
|
||||
npoly = len(polygons)
|
||||
if npoly == 1:
|
||||
return polygons[0]
|
||||
# find min-dist path through all polygons (travelling salesman)
|
||||
pairs = itertools.combinations(range(npoly), 2)
|
||||
dists = np.zeros((npoly, npoly), dtype=float)
|
||||
for i, j in pairs:
|
||||
dist = polygons[i].distance(polygons[j])
|
||||
if dist < 1e-5:
|
||||
dist = 1e-5 # if pair merely touches, we still need to get an edge
|
||||
dists[i, j] = dist
|
||||
dists[j, i] = dist
|
||||
dists = minimum_spanning_tree(dists, overwrite=True)
|
||||
# add bridge polygons (where necessary)
|
||||
for prevp, nextp in zip(*dists.nonzero()):
|
||||
prevp = polygons[prevp]
|
||||
nextp = polygons[nextp]
|
||||
nearest = nearest_points(prevp, nextp)
|
||||
bridgep = orient(LineString(nearest).buffer(max(1, scale/5), resolution=1), -1)
|
||||
polygons.append(bridgep)
|
||||
jointp = unary_union(polygons)
|
||||
if jointp.geom_type == 'MultiPolygon':
|
||||
jointp = unary_union(jointp.geoms)
|
||||
assert jointp.geom_type == 'Polygon', jointp.wkt
|
||||
# follow-up calculations will necessarily be integer;
|
||||
# so anticipate rounding here and then ensure validity
|
||||
jointp2 = set_precision(jointp, 1.0)
|
||||
if jointp2.geom_type != 'Polygon' or not jointp2.is_valid:
|
||||
jointp2 = Polygon(np.round(jointp.exterior.coords))
|
||||
jointp2 = make_valid(jointp2)
|
||||
assert jointp2.geom_type == 'Polygon', jointp2.wkt
|
||||
return jointp2
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
|||
from multiprocessing import shared_memory
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from functools import wraps
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
@contextmanager
|
||||
def share_ndarray(array: np.ndarray):
|
||||
size = np.dtype(array.dtype).itemsize * np.prod(array.shape)
|
||||
shm = shared_memory.SharedMemory(create=True, size=size)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
shared_array = np.ndarray(array.shape, dtype=array.dtype, buffer=shm.buf)
|
||||
shared_array[:] = array[:]
|
||||
shared_array.flags["WRITEABLE"] = False
|
||||
yield dict(shape=array.shape, dtype=array.dtype, name=shm.name)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
shm.close()
|
||||
shm.unlink()
|
||||
|
||||
@contextmanager
|
||||
def ndarray_shared(array: dict):
|
||||
shm = shared_memory.SharedMemory(name=array['name'])
|
||||
try:
|
||||
array = np.ndarray(array['shape'], dtype=array['dtype'], buffer=shm.buf)
|
||||
yield array
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
shm.close()
|
||||
|
||||
def wrap_ndarray_shared(kw=None):
|
||||
def wrapper(f):
|
||||
if kw is None:
|
||||
@wraps(f)
|
||||
def shared_func(array, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
with ndarray_shared(array) as ndarray:
|
||||
return f(ndarray, *args, **kwargs)
|
||||
return shared_func
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@wraps(f)
|
||||
def shared_func(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
array = kwargs.pop(kw)
|
||||
with ndarray_shared(array) as ndarray:
|
||||
kwargs[kw] = ndarray
|
||||
return f(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
return shared_func
|
||||
return wrapper
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,510 +0,0 @@
|
|||
import math
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
|
||||
from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter1d
|
||||
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
|
||||
from Bio import pairwise2
|
||||
|
||||
from .resize import resize_image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def decode_batch_predictions(pred, num_to_char, max_len = 128):
|
||||
# input_len is the product of the batch size and the
|
||||
# number of time steps.
|
||||
input_len = np.ones(pred.shape[0]) * pred.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# Decode CTC predictions using greedy search.
|
||||
# decoded is a tuple with 2 elements.
|
||||
decoded = tf.keras.backend.ctc_decode(pred,
|
||||
input_length = input_len,
|
||||
beam_width = 100)
|
||||
# The outputs are in the first element of the tuple.
|
||||
# Additionally, the first element is actually a list,
|
||||
# therefore we take the first element of that list as well.
|
||||
#print(decoded,'decoded')
|
||||
decoded = decoded[0][0][:, :max_len]
|
||||
|
||||
#print(decoded, decoded.shape,'decoded')
|
||||
|
||||
output = []
|
||||
for d in decoded:
|
||||
# Convert the predicted indices to the corresponding chars.
|
||||
d = tf.strings.reduce_join(num_to_char(d))
|
||||
d = d.numpy().decode("utf-8")
|
||||
output.append(d)
|
||||
return output
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def distortion_free_resize(image, img_size):
|
||||
w, h = img_size
|
||||
image = tf.image.resize(image, size=(h, w), preserve_aspect_ratio=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check tha amount of padding needed to be done.
|
||||
pad_height = h - tf.shape(image)[0]
|
||||
pad_width = w - tf.shape(image)[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# Only necessary if you want to do same amount of padding on both sides.
|
||||
if pad_height % 2 != 0:
|
||||
height = pad_height // 2
|
||||
pad_height_top = height + 1
|
||||
pad_height_bottom = height
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pad_height_top = pad_height_bottom = pad_height // 2
|
||||
|
||||
if pad_width % 2 != 0:
|
||||
width = pad_width // 2
|
||||
pad_width_left = width + 1
|
||||
pad_width_right = width
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pad_width_left = pad_width_right = pad_width // 2
|
||||
|
||||
image = tf.pad(
|
||||
image,
|
||||
paddings=[
|
||||
[pad_height_top, pad_height_bottom],
|
||||
[pad_width_left, pad_width_right],
|
||||
[0, 0],
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
image = tf.transpose(image, (1, 0, 2))
|
||||
image = tf.image.flip_left_right(image)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
def return_start_and_end_of_common_text_of_textline_ocr_without_common_section(textline_image):
|
||||
width = np.shape(textline_image)[1]
|
||||
height = np.shape(textline_image)[0]
|
||||
common_window = int(0.06*width)
|
||||
|
||||
width1 = int ( width/2. - common_window )
|
||||
width2 = int ( width/2. + common_window )
|
||||
|
||||
img_sum = np.sum(textline_image[:,:,0], axis=0)
|
||||
sum_smoothed = gaussian_filter1d(img_sum, 3)
|
||||
|
||||
peaks_real, _ = find_peaks(sum_smoothed, height=0)
|
||||
if len(peaks_real)>70:
|
||||
|
||||
peaks_real = peaks_real[(peaks_real<width2) & (peaks_real>width1)]
|
||||
|
||||
arg_max = np.argmax(sum_smoothed[peaks_real])
|
||||
peaks_final = peaks_real[arg_max]
|
||||
return peaks_final
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# Function to fit text inside the given area
|
||||
def fit_text_single_line(draw, text, font_path, max_width, max_height):
|
||||
initial_font_size = 50
|
||||
font_size = initial_font_size
|
||||
while font_size > 10: # Minimum font size
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
|
||||
text_bbox = draw.textbbox((0, 0), text, font=font) # Get text bounding box
|
||||
text_width = text_bbox[2] - text_bbox[0]
|
||||
text_height = text_bbox[3] - text_bbox[1]
|
||||
|
||||
if text_width <= max_width and text_height <= max_height:
|
||||
return font # Return the best-fitting font
|
||||
|
||||
font_size -= 2 # Reduce font size and retry
|
||||
|
||||
return ImageFont.truetype(font_path, 10) # Smallest font fallback
|
||||
|
||||
def return_textlines_split_if_needed(textline_image, textline_image_bin=None):
|
||||
|
||||
split_point = return_start_and_end_of_common_text_of_textline_ocr_without_common_section(textline_image)
|
||||
if split_point:
|
||||
image1 = textline_image[:, :split_point,:]# image.crop((0, 0, width2, height))
|
||||
image2 = textline_image[:, split_point:,:]#image.crop((width1, 0, width, height))
|
||||
if textline_image_bin is not None:
|
||||
image1_bin = textline_image_bin[:, :split_point,:]# image.crop((0, 0, width2, height))
|
||||
image2_bin = textline_image_bin[:, split_point:,:]#image.crop((width1, 0, width, height))
|
||||
return [image1, image2], [image1_bin, image2_bin]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return [image1, image2], None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return None, None
|
||||
def preprocess_and_resize_image_for_ocrcnn_model(img, image_height, image_width):
|
||||
if img.shape[0]==0 or img.shape[1]==0:
|
||||
img_fin = np.ones((image_height, image_width, 3))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ratio = image_height /float(img.shape[0])
|
||||
w_ratio = int(ratio * img.shape[1])
|
||||
|
||||
if w_ratio <= image_width:
|
||||
width_new = w_ratio
|
||||
else:
|
||||
width_new = image_width
|
||||
|
||||
if width_new == 0:
|
||||
width_new = img.shape[1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img = resize_image(img, image_height, width_new)
|
||||
img_fin = np.ones((image_height, image_width, 3))*255
|
||||
|
||||
img_fin[:,:width_new,:] = img[:,:,:]
|
||||
img_fin = img_fin / 255.
|
||||
return img_fin
|
||||
|
||||
def get_deskewed_contour_and_bb_and_image(contour, image, deskew_angle):
|
||||
(h_in, w_in) = image.shape[:2]
|
||||
center = (w_in // 2, h_in // 2)
|
||||
|
||||
rotation_matrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, deskew_angle, 1.0)
|
||||
|
||||
cos_angle = abs(rotation_matrix[0, 0])
|
||||
sin_angle = abs(rotation_matrix[0, 1])
|
||||
new_w = int((h_in * sin_angle) + (w_in * cos_angle))
|
||||
new_h = int((h_in * cos_angle) + (w_in * sin_angle))
|
||||
|
||||
rotation_matrix[0, 2] += (new_w / 2) - center[0]
|
||||
rotation_matrix[1, 2] += (new_h / 2) - center[1]
|
||||
|
||||
deskewed_image = cv2.warpAffine(image, rotation_matrix, (new_w, new_h))
|
||||
|
||||
contour_points = np.array(contour, dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
transformed_points = cv2.transform(np.array([contour_points]), rotation_matrix)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(np.array(transformed_points, dtype=np.int32))
|
||||
cropped_textline = deskewed_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]
|
||||
|
||||
return cropped_textline
|
||||
|
||||
def rotate_image_with_padding(image, angle, border_value=(0,0,0)):
|
||||
# Get image dimensions
|
||||
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
|
||||
|
||||
# Calculate the center of the image
|
||||
center = (w // 2, h // 2)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the rotation matrix
|
||||
rotation_matrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Compute the new bounding dimensions
|
||||
cos = abs(rotation_matrix[0, 0])
|
||||
sin = abs(rotation_matrix[0, 1])
|
||||
new_w = int((h * sin) + (w * cos))
|
||||
new_h = int((h * cos) + (w * sin))
|
||||
|
||||
# Adjust the rotation matrix to account for translation
|
||||
rotation_matrix[0, 2] += (new_w / 2) - center[0]
|
||||
rotation_matrix[1, 2] += (new_h / 2) - center[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# Perform the rotation
|
||||
try:
|
||||
rotated_image = cv2.warpAffine(image, rotation_matrix, (new_w, new_h), borderValue=border_value)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
rotated_image = np.copy(image)
|
||||
|
||||
return rotated_image
|
||||
|
||||
def get_orientation_moments(contour):
|
||||
moments = cv2.moments(contour)
|
||||
if moments["mu20"] - moments["mu02"] == 0: # Avoid division by zero
|
||||
return 90 if moments["mu11"] > 0 else -90
|
||||
else:
|
||||
angle = 0.5 * np.arctan2(2 * moments["mu11"], moments["mu20"] - moments["mu02"])
|
||||
return np.degrees(angle) # Convert radians to degrees
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_orientation_moments_of_mask(mask):
|
||||
mask=mask.astype('uint8')
|
||||
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask[:,:,0], cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
largest_contour = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea) if contours else None
|
||||
|
||||
moments = cv2.moments(largest_contour)
|
||||
if moments["mu20"] - moments["mu02"] == 0: # Avoid division by zero
|
||||
return 90 if moments["mu11"] > 0 else -90
|
||||
else:
|
||||
angle = 0.5 * np.arctan2(2 * moments["mu11"], moments["mu20"] - moments["mu02"])
|
||||
return np.degrees(angle) # Convert radians to degrees
|
||||
|
||||
def get_contours_and_bounding_boxes(mask):
|
||||
# Find contours in the binary mask
|
||||
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
|
||||
largest_contour = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea) if contours else None
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the bounding rectangle for the contour
|
||||
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(largest_contour)
|
||||
#bounding_boxes.append((x, y, w, h))
|
||||
|
||||
return x, y, w, h
|
||||
|
||||
def return_splitting_point_of_image(image_to_spliited):
|
||||
width = np.shape(image_to_spliited)[1]
|
||||
height = np.shape(image_to_spliited)[0]
|
||||
common_window = int(0.03*width)
|
||||
|
||||
width1 = int ( common_window)
|
||||
width2 = int ( width - common_window )
|
||||
|
||||
img_sum = np.sum(image_to_spliited[:,:,0], axis=0)
|
||||
sum_smoothed = gaussian_filter1d(img_sum, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
peaks_real, _ = find_peaks(sum_smoothed, height=0)
|
||||
peaks_real = peaks_real[(peaks_real<width2) & (peaks_real>width1)]
|
||||
|
||||
arg_sort = np.argsort(sum_smoothed[peaks_real])
|
||||
peaks_sort_4 = peaks_real[arg_sort][::-1][:3]
|
||||
|
||||
return np.sort(peaks_sort_4)
|
||||
|
||||
def break_curved_line_into_small_pieces_and_then_merge(img_curved, mask_curved, img_bin_curved=None):
|
||||
peaks_4 = return_splitting_point_of_image(img_curved)
|
||||
if len(peaks_4)>0:
|
||||
imgs_tot = []
|
||||
|
||||
for ind in range(len(peaks_4)+1):
|
||||
if ind==0:
|
||||
img = img_curved[:, :peaks_4[ind], :]
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin = img_bin_curved[:, :peaks_4[ind], :]
|
||||
mask = mask_curved[:, :peaks_4[ind], :]
|
||||
elif ind==len(peaks_4):
|
||||
img = img_curved[:, peaks_4[ind-1]:, :]
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin = img_bin_curved[:, peaks_4[ind-1]:, :]
|
||||
mask = mask_curved[:, peaks_4[ind-1]:, :]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img = img_curved[:, peaks_4[ind-1]:peaks_4[ind], :]
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin = img_bin_curved[:, peaks_4[ind-1]:peaks_4[ind], :]
|
||||
mask = mask_curved[:, peaks_4[ind-1]:peaks_4[ind], :]
|
||||
|
||||
or_ma = get_orientation_moments_of_mask(mask)
|
||||
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
imgs_tot.append([img, mask, or_ma, img_bin] )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
imgs_tot.append([img, mask, or_ma] )
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
w_tot_des_list = []
|
||||
w_tot_des = 0
|
||||
imgs_deskewed_list = []
|
||||
imgs_bin_deskewed_list = []
|
||||
|
||||
for ind in range(len(imgs_tot)):
|
||||
img_in = imgs_tot[ind][0]
|
||||
mask_in = imgs_tot[ind][1]
|
||||
ori_in = imgs_tot[ind][2]
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in = imgs_tot[ind][3]
|
||||
|
||||
if abs(ori_in)<45:
|
||||
img_in_des = rotate_image_with_padding(img_in, ori_in, border_value=(255,255,255) )
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in_des = rotate_image_with_padding(img_bin_in, ori_in, border_value=(255,255,255) )
|
||||
mask_in_des = rotate_image_with_padding(mask_in, ori_in)
|
||||
mask_in_des = mask_in_des.astype('uint8')
|
||||
|
||||
#new bounding box
|
||||
x_n, y_n, w_n, h_n = get_contours_and_bounding_boxes(mask_in_des[:,:,0])
|
||||
|
||||
if w_n==0 or h_n==0:
|
||||
img_in_des = np.copy(img_in)
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in_des = np.copy(img_bin_in)
|
||||
w_relative = int(32 * img_in_des.shape[1]/float(img_in_des.shape[0]) )
|
||||
if w_relative==0:
|
||||
w_relative = img_in_des.shape[1]
|
||||
img_in_des = resize_image(img_in_des, 32, w_relative)
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in_des = resize_image(img_bin_in_des, 32, w_relative)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
mask_in_des = mask_in_des[y_n:y_n+h_n, x_n:x_n+w_n, :]
|
||||
img_in_des = img_in_des[y_n:y_n+h_n, x_n:x_n+w_n, :]
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in_des = img_bin_in_des[y_n:y_n+h_n, x_n:x_n+w_n, :]
|
||||
|
||||
w_relative = int(32 * img_in_des.shape[1]/float(img_in_des.shape[0]) )
|
||||
if w_relative==0:
|
||||
w_relative = img_in_des.shape[1]
|
||||
img_in_des = resize_image(img_in_des, 32, w_relative)
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in_des = resize_image(img_bin_in_des, 32, w_relative)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_in_des = np.copy(img_in)
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in_des = np.copy(img_bin_in)
|
||||
w_relative = int(32 * img_in_des.shape[1]/float(img_in_des.shape[0]) )
|
||||
if w_relative==0:
|
||||
w_relative = img_in_des.shape[1]
|
||||
img_in_des = resize_image(img_in_des, 32, w_relative)
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_in_des = resize_image(img_bin_in_des, 32, w_relative)
|
||||
|
||||
w_tot_des+=img_in_des.shape[1]
|
||||
w_tot_des_list.append(img_in_des.shape[1])
|
||||
imgs_deskewed_list.append(img_in_des)
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
imgs_bin_deskewed_list.append(img_bin_in_des)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_final_deskewed = np.zeros((32, w_tot_des, 3))+255
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_final_deskewed = np.zeros((32, w_tot_des, 3))+255
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_bin_final_deskewed = None
|
||||
|
||||
w_indexer = 0
|
||||
for ind in range(len(w_tot_des_list)):
|
||||
img_final_deskewed[:,w_indexer:w_indexer+w_tot_des_list[ind],:] = imgs_deskewed_list[ind][:,:,:]
|
||||
if img_bin_curved is not None:
|
||||
img_bin_final_deskewed[:,w_indexer:w_indexer+w_tot_des_list[ind],:] = imgs_bin_deskewed_list[ind][:,:,:]
|
||||
w_indexer = w_indexer+w_tot_des_list[ind]
|
||||
return img_final_deskewed, img_bin_final_deskewed
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return img_curved, img_bin_curved
|
||||
|
||||
def return_textline_contour_with_added_box_coordinate(textline_contour, box_ind):
|
||||
textline_contour[:,0] = textline_contour[:,0] + box_ind[2]
|
||||
textline_contour[:,1] = textline_contour[:,1] + box_ind[0]
|
||||
return textline_contour
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def return_rnn_cnn_ocr_of_given_textlines(image,
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons,
|
||||
all_box_coord,
|
||||
prediction_model,
|
||||
b_s_ocr, num_to_char,
|
||||
textline_light=False,
|
||||
curved_line=False):
|
||||
max_len = 512
|
||||
padding_token = 299
|
||||
image_width = 512#max_len * 4
|
||||
image_height = 32
|
||||
ind_tot = 0
|
||||
#cv2.imwrite('./img_out.png', image_page)
|
||||
ocr_all_textlines = []
|
||||
cropped_lines_region_indexer = []
|
||||
cropped_lines_meging_indexing = []
|
||||
cropped_lines = []
|
||||
indexer_text_region = 0
|
||||
|
||||
for indexing, ind_poly_first in enumerate(all_found_textline_polygons):
|
||||
#ocr_textline_in_textregion = []
|
||||
if len(ind_poly_first)==0:
|
||||
cropped_lines_region_indexer.append(indexer_text_region)
|
||||
cropped_lines_meging_indexing.append(0)
|
||||
img_fin = np.ones((image_height, image_width, 3))*1
|
||||
cropped_lines.append(img_fin)
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for indexing2, ind_poly in enumerate(ind_poly_first):
|
||||
cropped_lines_region_indexer.append(indexer_text_region)
|
||||
if not (textline_light or curved_line):
|
||||
ind_poly = copy.deepcopy(ind_poly)
|
||||
box_ind = all_box_coord[indexing]
|
||||
|
||||
ind_poly = return_textline_contour_with_added_box_coordinate(ind_poly, box_ind)
|
||||
#print(ind_poly_copy)
|
||||
ind_poly[ind_poly<0] = 0
|
||||
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(ind_poly)
|
||||
|
||||
w_scaled = w * image_height/float(h)
|
||||
|
||||
mask_poly = np.zeros(image.shape)
|
||||
|
||||
img_poly_on_img = np.copy(image)
|
||||
|
||||
mask_poly = cv2.fillPoly(mask_poly, pts=[ind_poly], color=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
mask_poly = mask_poly[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]
|
||||
img_crop = img_poly_on_img[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]
|
||||
|
||||
img_crop[mask_poly==0] = 255
|
||||
|
||||
if w_scaled < 640:#1.5*image_width:
|
||||
img_fin = preprocess_and_resize_image_for_ocrcnn_model(img_crop, image_height, image_width)
|
||||
cropped_lines.append(img_fin)
|
||||
cropped_lines_meging_indexing.append(0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
splited_images, splited_images_bin = return_textlines_split_if_needed(img_crop, None)
|
||||
|
||||
if splited_images:
|
||||
img_fin = preprocess_and_resize_image_for_ocrcnn_model(splited_images[0],
|
||||
image_height,
|
||||
image_width)
|
||||
cropped_lines.append(img_fin)
|
||||
cropped_lines_meging_indexing.append(1)
|
||||
|
||||
img_fin = preprocess_and_resize_image_for_ocrcnn_model(splited_images[1],
|
||||
image_height,
|
||||
image_width)
|
||||
|
||||
cropped_lines.append(img_fin)
|
||||
cropped_lines_meging_indexing.append(-1)
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_fin = preprocess_and_resize_image_for_ocrcnn_model(img_crop,
|
||||
image_height,
|
||||
image_width)
|
||||
cropped_lines.append(img_fin)
|
||||
cropped_lines_meging_indexing.append(0)
|
||||
|
||||
indexer_text_region+=1
|
||||
|
||||
extracted_texts = []
|
||||
|
||||
n_iterations = math.ceil(len(cropped_lines) / b_s_ocr)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(n_iterations):
|
||||
if i==(n_iterations-1):
|
||||
n_start = i*b_s_ocr
|
||||
imgs = cropped_lines[n_start:]
|
||||
imgs = np.array(imgs)
|
||||
imgs = imgs.reshape(imgs.shape[0], image_height, image_width, 3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
n_start = i*b_s_ocr
|
||||
n_end = (i+1)*b_s_ocr
|
||||
imgs = cropped_lines[n_start:n_end]
|
||||
imgs = np.array(imgs).reshape(b_s_ocr, image_height, image_width, 3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
preds = prediction_model.predict(imgs, verbose=0)
|
||||
|
||||
pred_texts = decode_batch_predictions(preds, num_to_char)
|
||||
|
||||
for ib in range(imgs.shape[0]):
|
||||
pred_texts_ib = pred_texts[ib].replace("[UNK]", "")
|
||||
extracted_texts.append(pred_texts_ib)
|
||||
|
||||
extracted_texts_merged = [extracted_texts[ind]
|
||||
if cropped_lines_meging_indexing[ind]==0
|
||||
else extracted_texts[ind]+" "+extracted_texts[ind+1]
|
||||
if cropped_lines_meging_indexing[ind]==1
|
||||
else None
|
||||
for ind in range(len(cropped_lines_meging_indexing))]
|
||||
|
||||
extracted_texts_merged = [ind for ind in extracted_texts_merged if ind is not None]
|
||||
unique_cropped_lines_region_indexer = np.unique(cropped_lines_region_indexer)
|
||||
|
||||
ocr_all_textlines = []
|
||||
for ind in unique_cropped_lines_region_indexer:
|
||||
ocr_textline_in_textregion = []
|
||||
extracted_texts_merged_un = np.array(extracted_texts_merged)[np.array(cropped_lines_region_indexer)==ind]
|
||||
for it_ind, text_textline in enumerate(extracted_texts_merged_un):
|
||||
ocr_textline_in_textregion.append(text_textline)
|
||||
ocr_all_textlines.append(ocr_textline_in_textregion)
|
||||
return ocr_all_textlines
|
||||
|
||||
def biopython_align(str1, str2):
|
||||
alignments = pairwise2.align.globalms(str1, str2, 2, -1, -2, -2)
|
||||
best_alignment = alignments[0] # Get the best alignment
|
||||
return best_alignment.seqA, best_alignment.seqB
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,253 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# pylint: disable=too-many-locals,wrong-import-position,too-many-lines,too-many-statements,chained-comparison,fixme,broad-except,c-extension-no-member
|
||||
# pylint: disable=import-error
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
import os.path
|
||||
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
|
||||
from .utils.xml import create_page_xml, xml_reading_order
|
||||
from .utils.counter import EynollahIdCounter
|
||||
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import getLogger
|
||||
from ocrd_models.ocrd_page import (
|
||||
BorderType,
|
||||
CoordsType,
|
||||
PcGtsType,
|
||||
TextLineType,
|
||||
TextEquivType,
|
||||
TextRegionType,
|
||||
ImageRegionType,
|
||||
TableRegionType,
|
||||
SeparatorRegionType,
|
||||
to_xml
|
||||
)
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
class EynollahXmlWriter:
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *, dir_out, image_filename, curved_line,textline_light, pcgts=None):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger('eynollah.writer')
|
||||
self.counter = EynollahIdCounter()
|
||||
self.dir_out = dir_out
|
||||
self.image_filename = image_filename
|
||||
self.output_filename = os.path.join(self.dir_out or "", self.image_filename_stem) + ".xml"
|
||||
self.curved_line = curved_line
|
||||
self.textline_light = textline_light
|
||||
self.pcgts = pcgts
|
||||
self.scale_x = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
self.scale_y = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
self.height_org = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
self.width_org = None # XXX set outside __init__
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def image_filename_stem(self):
|
||||
return Path(Path(self.image_filename).name).stem
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_page_coords(self, cont_page):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter calculate_page_coords')
|
||||
points_page_print = ""
|
||||
for _, contour in enumerate(cont_page[0]):
|
||||
if len(contour) == 2:
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[0]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_page_print += ','
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[1]) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[0][0]) / self.scale_x))
|
||||
points_page_print += ','
|
||||
points_page_print += str(int((contour[0][1] ) / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_page_print = points_page_print + ' '
|
||||
return points_page_print[:-1]
|
||||
|
||||
def serialize_lines_in_region(self, text_region, all_found_textline_polygons, region_idx, page_coord, all_box_coord, slopes, counter, ocr_all_textlines_textregion):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter serialize_lines_in_region')
|
||||
for j, polygon_textline in enumerate(all_found_textline_polygons[region_idx]):
|
||||
coords = CoordsType()
|
||||
textline = TextLineType(id=counter.next_line_id, Coords=coords)
|
||||
if ocr_all_textlines_textregion:
|
||||
# FIXME: add OCR confidence
|
||||
textline.set_TextEquiv([TextEquivType(Unicode=ocr_all_textlines_textregion[j])])
|
||||
text_region.add_TextLine(textline)
|
||||
text_region.set_orientation(-slopes[region_idx])
|
||||
region_bboxes = all_box_coord[region_idx]
|
||||
points_co = ''
|
||||
for point in polygon_textline:
|
||||
if len(point) != 2:
|
||||
point = point[0]
|
||||
point_x = point[0] + page_coord[2]
|
||||
point_y = point[1] + page_coord[0]
|
||||
# FIXME: or actually... not self.textline_light and not self.curved_line or np.abs(slopes[region_idx]) > 45?
|
||||
if not self.textline_light and not (self.curved_line and np.abs(slopes[region_idx]) <= 45):
|
||||
point_x += region_bboxes[2]
|
||||
point_y += region_bboxes[0]
|
||||
point_x = max(0, int(point_x / self.scale_x))
|
||||
point_y = max(0, int(point_y / self.scale_y))
|
||||
points_co += str(point_x) + ',' + str(point_y) + ' '
|
||||
coords.set_points(points_co[:-1])
|
||||
|
||||
def write_pagexml(self, pcgts):
|
||||
self.logger.info("output filename: '%s'", self.output_filename)
|
||||
with open(self.output_filename, 'w') as f:
|
||||
f.write(to_xml(pcgts))
|
||||
|
||||
def build_pagexml_no_full_layout(
|
||||
self, found_polygons_text_region,
|
||||
page_coord, order_of_texts, id_of_texts,
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons,
|
||||
all_box_coord,
|
||||
found_polygons_text_region_img,
|
||||
found_polygons_marginals_left, found_polygons_marginals_right,
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_left, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_right,
|
||||
all_box_coord_marginals_left, all_box_coord_marginals_right,
|
||||
slopes, slopes_marginals_left, slopes_marginals_right,
|
||||
cont_page, polygons_seplines,
|
||||
found_polygons_tables,
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
return self.build_pagexml_full_layout(
|
||||
found_polygons_text_region, [],
|
||||
page_coord, order_of_texts, id_of_texts,
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons, [],
|
||||
all_box_coord, [],
|
||||
found_polygons_text_region_img, found_polygons_tables, [],
|
||||
found_polygons_marginals_left, found_polygons_marginals_right,
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_left, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_right,
|
||||
all_box_coord_marginals_left, all_box_coord_marginals_right,
|
||||
slopes, [], slopes_marginals_left, slopes_marginals_right,
|
||||
cont_page, polygons_seplines,
|
||||
**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def build_pagexml_full_layout(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
found_polygons_text_region, found_polygons_text_region_h,
|
||||
page_coord, order_of_texts, id_of_texts,
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons, all_found_textline_polygons_h,
|
||||
all_box_coord, all_box_coord_h,
|
||||
found_polygons_text_region_img, found_polygons_tables, found_polygons_drop_capitals,
|
||||
found_polygons_marginals_left,found_polygons_marginals_right,
|
||||
all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_left, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_right,
|
||||
all_box_coord_marginals_left, all_box_coord_marginals_right,
|
||||
slopes, slopes_h, slopes_marginals_left, slopes_marginals_right,
|
||||
cont_page, polygons_seplines,
|
||||
ocr_all_textlines=None, ocr_all_textlines_h=None,
|
||||
ocr_all_textlines_marginals_left=None, ocr_all_textlines_marginals_right=None,
|
||||
ocr_all_textlines_drop=None,
|
||||
conf_contours_textregions=None, conf_contours_textregions_h=None,
|
||||
skip_layout_reading_order=False):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter build_pagexml')
|
||||
|
||||
# create the file structure
|
||||
pcgts = self.pcgts if self.pcgts else create_page_xml(self.image_filename, self.height_org, self.width_org)
|
||||
page = pcgts.get_Page()
|
||||
page.set_Border(BorderType(Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_page_coords(cont_page))))
|
||||
|
||||
counter = EynollahIdCounter()
|
||||
if len(order_of_texts):
|
||||
_counter_marginals = EynollahIdCounter(region_idx=len(order_of_texts))
|
||||
id_of_marginalia_left = [_counter_marginals.next_region_id
|
||||
for _ in found_polygons_marginals_left]
|
||||
id_of_marginalia_right = [_counter_marginals.next_region_id
|
||||
for _ in found_polygons_marginals_right]
|
||||
xml_reading_order(page, order_of_texts, id_of_marginalia_left, id_of_marginalia_right)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm, region_contour in enumerate(found_polygons_text_region):
|
||||
textregion = TextRegionType(
|
||||
id=counter.next_region_id, type_='paragraph',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, page_coord,
|
||||
skip_layout_reading_order))
|
||||
)
|
||||
if conf_contours_textregions:
|
||||
textregion.Coords.set_conf(conf_contours_textregions[mm])
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(textregion)
|
||||
if ocr_all_textlines:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = ocr_all_textlines[mm]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = None
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(textregion, all_found_textline_polygons, mm, page_coord,
|
||||
all_box_coord, slopes, counter, ocr_textlines)
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.debug('len(found_polygons_text_region_h) %s', len(found_polygons_text_region_h))
|
||||
for mm, region_contour in enumerate(found_polygons_text_region_h):
|
||||
textregion = TextRegionType(
|
||||
id=counter.next_region_id, type_='heading',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, page_coord))
|
||||
)
|
||||
if conf_contours_textregions_h:
|
||||
textregion.Coords.set_conf(conf_contours_textregions_h[mm])
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(textregion)
|
||||
if ocr_all_textlines_h:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = ocr_all_textlines_h[mm]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = None
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(textregion, all_found_textline_polygons_h, mm, page_coord,
|
||||
all_box_coord_h, slopes_h, counter, ocr_textlines)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm, region_contour in enumerate(found_polygons_marginals_left):
|
||||
marginal = TextRegionType(
|
||||
id=counter.next_region_id, type_='marginalia',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, page_coord))
|
||||
)
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(marginal)
|
||||
if ocr_all_textlines_marginals_left:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = ocr_all_textlines_marginals_left[mm]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = None
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(marginal, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_left, mm, page_coord, all_box_coord_marginals_left, slopes_marginals_left, counter, ocr_textlines)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm, region_contour in enumerate(found_polygons_marginals_right):
|
||||
marginal = TextRegionType(
|
||||
id=counter.next_region_id, type_='marginalia',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, page_coord))
|
||||
)
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(marginal)
|
||||
if ocr_all_textlines_marginals_right:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = ocr_all_textlines_marginals_right[mm]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = None
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(marginal, all_found_textline_polygons_marginals_right, mm, page_coord,
|
||||
all_box_coord_marginals_right, slopes_marginals_right, counter, ocr_textlines)
|
||||
|
||||
for mm, region_contour in enumerate(found_polygons_drop_capitals):
|
||||
dropcapital = TextRegionType(
|
||||
id=counter.next_region_id, type_='drop-capital',
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, page_coord))
|
||||
)
|
||||
page.add_TextRegion(dropcapital)
|
||||
all_box_coord_drop = [[0, 0, 0, 0]]
|
||||
slopes_drop = [0]
|
||||
if ocr_all_textlines_drop:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = ocr_all_textlines_drop[mm]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ocr_textlines = None
|
||||
self.serialize_lines_in_region(dropcapital, [[found_polygons_drop_capitals[mm]]], 0, page_coord,
|
||||
all_box_coord_drop, slopes_drop, counter, ocr_textlines)
|
||||
|
||||
for region_contour in found_polygons_text_region_img:
|
||||
page.add_ImageRegion(
|
||||
ImageRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id,
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, page_coord))))
|
||||
|
||||
for region_contour in polygons_seplines:
|
||||
page.add_SeparatorRegion(
|
||||
SeparatorRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id,
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, [0, 0, 0, 0]))))
|
||||
|
||||
for region_contour in found_polygons_tables:
|
||||
page.add_TableRegion(
|
||||
TableRegionType(id=counter.next_region_id,
|
||||
Coords=CoordsType(points=self.calculate_polygon_coords(region_contour, page_coord))))
|
||||
|
||||
return pcgts
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_polygon_coords(self, contour, page_coord, skip_layout_reading_order=False):
|
||||
self.logger.debug('enter calculate_polygon_coords')
|
||||
coords = ''
|
||||
for point in contour:
|
||||
if len(point) != 2:
|
||||
point = point[0]
|
||||
point_x = point[0]
|
||||
point_y = point[1]
|
||||
if not skip_layout_reading_order:
|
||||
point_x += page_coord[2]
|
||||
point_y += page_coord[0]
|
||||
point_x = int(point_x / self.scale_x)
|
||||
point_y = int(point_y / self.scale_y)
|
||||
coords += str(point_x) + ',' + str(point_y) + ' '
|
||||
return coords[:-1]
|
||||
|
||||
54
tests/base.py
Normal file
54
tests/base.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
|||
# pylint: disable=unused-import
|
||||
|
||||
from os.path import dirname, realpath
|
||||
from os import chdir
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import io
|
||||
import collections
|
||||
from unittest import TestCase as VanillaTestCase, skip, main as unittests_main
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import disableLogging, initLogging
|
||||
|
||||
def main(fn=None):
|
||||
if fn:
|
||||
sys.exit(pytest.main([fn]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
unittests_main()
|
||||
|
||||
class TestCase(VanillaTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def setUpClass(cls):
|
||||
chdir(dirname(realpath(__file__)) + '/..')
|
||||
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
disableLogging()
|
||||
initLogging()
|
||||
|
||||
class CapturingTestCase(TestCase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A TestCase that needs to capture stderr/stdout and invoke click CLI.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
|
||||
def _setup_pytest_capfd(self, capfd):
|
||||
self.capfd = capfd
|
||||
|
||||
def invoke_cli(self, cli, args):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Substitution for click.CliRunner.invooke that works together nicely
|
||||
with unittests/pytest capturing stdout/stderr.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.capture_out_err() # XXX snapshot just before executing the CLI
|
||||
code = 0
|
||||
sys.argv[1:] = args # XXX necessary because sys.argv reflects pytest args not cli args
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cli.main(args=args)
|
||||
except SystemExit as e:
|
||||
code = e.code
|
||||
out, err = self.capture_out_err()
|
||||
return code, out, err
|
||||
|
||||
def capture_out_err(self):
|
||||
return self.capfd.readouterr()
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
|||
from eynollah.utils.counter import EynollahIdCounter
|
||||
from tests.base import main
|
||||
from qurator.eynollah.utils.counter import EynollahIdCounter
|
||||
|
||||
def test_counter_string():
|
||||
c = EynollahIdCounter()
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,3 +29,5 @@ def test_counter_methods():
|
|||
c.inc('region', -9)
|
||||
assert c.get('region') == 1
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main(__file__)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,8 +1,11 @@
|
|||
import cv2
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from eynollah.utils.pil_cv2 import check_dpi
|
||||
from qurator.eynollah.utils.pil_cv2 import check_dpi
|
||||
from tests.base import main
|
||||
|
||||
def test_dpi():
|
||||
fpath = str(Path(__file__).parent.joinpath('resources', 'kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif'))
|
||||
assert 230 == check_dpi(cv2.imread(fpath))
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main(__file__)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,351 +1,24 @@
|
|||
from os import environ
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from eynollah.cli import (
|
||||
layout as layout_cli,
|
||||
binarization as binarization_cli,
|
||||
enhancement as enhancement_cli,
|
||||
machine_based_reading_order as mbreorder_cli,
|
||||
ocr as ocr_cli,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from click.testing import CliRunner
|
||||
from ocrd_modelfactory import page_from_file
|
||||
from ocrd_models.constants import NAMESPACES as NS
|
||||
from ocrd_utils import pushd_popd
|
||||
from tests.base import CapturingTestCase as TestCase, main
|
||||
from qurator.eynollah.cli import main as eynollah_cli
|
||||
|
||||
testdir = Path(__file__).parent.resolve()
|
||||
|
||||
MODELS_LAYOUT = environ.get('MODELS_LAYOUT', str(testdir.joinpath('..', 'models_layout_v0_5_0').resolve()))
|
||||
MODELS_OCR = environ.get('MODELS_OCR', str(testdir.joinpath('..', 'models_ocr_v0_5_1').resolve()))
|
||||
MODELS_BIN = environ.get('MODELS_BIN', str(testdir.joinpath('..', 'default-2021-03-09').resolve()))
|
||||
EYNOLLAH_MODELS = environ.get('EYNOLLAH_MODELS', str(testdir.joinpath('..', 'models_eynollah').resolve()))
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"options",
|
||||
[
|
||||
[], # defaults
|
||||
#["--allow_scaling", "--curved-line"],
|
||||
["--allow_scaling", "--curved-line", "--full-layout"],
|
||||
["--allow_scaling", "--curved-line", "--full-layout", "--reading_order_machine_based"],
|
||||
["--allow_scaling", "--curved-line", "--full-layout", "--reading_order_machine_based",
|
||||
"--textline_light", "--light_version"],
|
||||
# -ep ...
|
||||
# -eoi ...
|
||||
# FIXME: find out whether OCR extra was installed, otherwise skip these
|
||||
["--do_ocr"],
|
||||
["--do_ocr", "--light_version", "--textline_light"],
|
||||
["--do_ocr", "--transformer_ocr"],
|
||||
#["--do_ocr", "--transformer_ocr", "--light_version", "--textline_light"],
|
||||
["--do_ocr", "--transformer_ocr", "--light_version", "--textline_light", "--full-layout"],
|
||||
# --skip_layout_and_reading_order
|
||||
], ids=str)
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_layout_filename(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog, options):
|
||||
infile = testdir.joinpath('resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif')
|
||||
outfile = tmp_path / 'kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.xml'
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_LAYOUT,
|
||||
'-i', str(infile),
|
||||
'-o', str(outfile.parent),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'eynollah'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(layout_cli, args + options, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
assert str(infile) in logmsgs
|
||||
assert outfile.exists()
|
||||
tree = page_from_file(str(outfile)).etree
|
||||
regions = tree.xpath("//page:TextRegion", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
assert len(regions) >= 2, "result is inaccurate"
|
||||
regions = tree.xpath("//page:SeparatorRegion", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
assert len(regions) >= 2, "result is inaccurate"
|
||||
lines = tree.xpath("//page:TextLine", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
assert len(lines) == 31, "result is inaccurate" # 29 paragraph lines, 1 page and 1 catch-word line
|
||||
class TestEynollahRun(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"options",
|
||||
[
|
||||
["--tables"],
|
||||
["--tables", "--full-layout"],
|
||||
["--tables", "--full-layout", "--textline_light", "--light_version"],
|
||||
], ids=str)
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_layout_filename2(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog, options):
|
||||
infile = testdir.joinpath('resources/euler_rechenkunst01_1738_0025.tif')
|
||||
outfile = tmp_path / 'euler_rechenkunst01_1738_0025.xml'
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_LAYOUT,
|
||||
'-i', str(infile),
|
||||
'-o', str(outfile.parent),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'eynollah'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(layout_cli, args + options, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
assert str(infile) in logmsgs
|
||||
assert outfile.exists()
|
||||
tree = page_from_file(str(outfile)).etree
|
||||
regions = tree.xpath("//page:TextRegion", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
assert len(regions) >= 2, "result is inaccurate"
|
||||
regions = tree.xpath("//page:TableRegion", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
# model/decoding is not very precise, so (depending on mode) we can get fractures/splits/FP
|
||||
assert len(regions) >= 1, "result is inaccurate"
|
||||
regions = tree.xpath("//page:SeparatorRegion", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
assert len(regions) >= 2, "result is inaccurate"
|
||||
lines = tree.xpath("//page:TextLine", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
assert len(lines) >= 2, "result is inaccurate" # mostly table (if detected correctly), but 1 page and 1 catch-word line
|
||||
def test_full_run(self):
|
||||
with pushd_popd(tempdir=True) as tempdir:
|
||||
code, out, err = self.invoke_cli(eynollah_cli, [
|
||||
'-m', EYNOLLAH_MODELS,
|
||||
'-i', str(testdir.joinpath('resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif')),
|
||||
'-o', tempdir
|
||||
])
|
||||
print(code, out, err)
|
||||
assert not code
|
||||
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_layout_directory(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog):
|
||||
indir = testdir.joinpath('resources')
|
||||
outdir = tmp_path
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_LAYOUT,
|
||||
'-di', str(indir),
|
||||
'-o', str(outdir),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'eynollah'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(layout_cli, args, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
assert len([logmsg for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('Job done in')]) == 2
|
||||
assert any(logmsg for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('All jobs done in'))
|
||||
assert len(list(outdir.iterdir())) == 2
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"options",
|
||||
[
|
||||
[], # defaults
|
||||
["--no-patches"],
|
||||
], ids=str)
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_binarization_filename(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog, options):
|
||||
infile = testdir.joinpath('resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif')
|
||||
outfile = tmp_path.joinpath('kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.png')
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_BIN,
|
||||
'-i', str(infile),
|
||||
'-o', str(outfile),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'SbbBinarizer'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(binarization_cli, args + options, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
assert any(True for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('Predicting'))
|
||||
assert outfile.exists()
|
||||
with Image.open(infile) as original_img:
|
||||
original_size = original_img.size
|
||||
with Image.open(outfile) as binarized_img:
|
||||
binarized_size = binarized_img.size
|
||||
assert original_size == binarized_size
|
||||
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_binarization_directory(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog):
|
||||
indir = testdir.joinpath('resources')
|
||||
outdir = tmp_path
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_BIN,
|
||||
'-di', str(indir),
|
||||
'-o', str(outdir),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'SbbBinarizer'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(binarization_cli, args, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
assert len([logmsg for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('Predicting')]) == 2
|
||||
assert len(list(outdir.iterdir())) == 2
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"options",
|
||||
[
|
||||
[], # defaults
|
||||
["-sos"],
|
||||
], ids=str)
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_enhancement_filename(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog, options):
|
||||
infile = testdir.joinpath('resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif')
|
||||
outfile = tmp_path.joinpath('kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.png')
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_LAYOUT,
|
||||
'-i', str(infile),
|
||||
'-o', str(outfile.parent),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'enhancement'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(enhancement_cli, args + options, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
assert any(True for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('Image was enhanced')), logmsgs
|
||||
assert outfile.exists()
|
||||
with Image.open(infile) as original_img:
|
||||
original_size = original_img.size
|
||||
with Image.open(outfile) as enhanced_img:
|
||||
enhanced_size = enhanced_img.size
|
||||
assert (original_size == enhanced_size) == ("-sos" in options)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_enhancement_directory(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog):
|
||||
indir = testdir.joinpath('resources')
|
||||
outdir = tmp_path
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_LAYOUT,
|
||||
'-di', str(indir),
|
||||
'-o', str(outdir),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'enhancement'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(enhancement_cli, args, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
assert len([logmsg for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('Image was enhanced')]) == 2
|
||||
assert len(list(outdir.iterdir())) == 2
|
||||
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_mbreorder_filename(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog):
|
||||
infile = testdir.joinpath('resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.xml')
|
||||
outfile = tmp_path.joinpath('kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.xml')
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_LAYOUT,
|
||||
'-i', str(infile),
|
||||
'-o', str(outfile.parent),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'mbreorder'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(mbreorder_cli, args, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
# FIXME: mbreorder has no logging!
|
||||
#assert any(True for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('???')), logmsgs
|
||||
assert outfile.exists()
|
||||
#in_tree = page_from_file(str(infile)).etree
|
||||
#in_order = in_tree.xpath("//page:OrderedGroup//@regionRef", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
out_tree = page_from_file(str(outfile)).etree
|
||||
out_order = out_tree.xpath("//page:OrderedGroup//@regionRef", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
#assert len(out_order) >= 2, "result is inaccurate"
|
||||
#assert in_order != out_order
|
||||
assert out_order == ['r_1_1', 'r_2_1', 'r_2_2', 'r_2_3']
|
||||
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_mbreorder_directory(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog):
|
||||
indir = testdir.joinpath('resources')
|
||||
outdir = tmp_path
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_LAYOUT,
|
||||
'-di', str(indir),
|
||||
'-o', str(outdir),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'mbreorder'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(mbreorder_cli, args, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
# FIXME: mbreorder has no logging!
|
||||
#assert len([logmsg for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('???')]) == 2
|
||||
assert len(list(outdir.iterdir())) == 2
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"options",
|
||||
[
|
||||
[], # defaults
|
||||
["-doit", #str(outrenderfile.parent)],
|
||||
],
|
||||
["-trocr"],
|
||||
], ids=str)
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_ocr_filename(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog, options):
|
||||
infile = testdir.joinpath('resources/kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.tif')
|
||||
outfile = tmp_path.joinpath('kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.xml')
|
||||
outrenderfile = tmp_path.joinpath('render').joinpath('kant_aufklaerung_1784_0020.png')
|
||||
outrenderfile.parent.mkdir()
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_OCR,
|
||||
'-i', str(infile),
|
||||
'-dx', str(infile.parent),
|
||||
'-o', str(outfile.parent),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.DEBUG)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'eynollah'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
if "-doit" in options:
|
||||
options.insert(options.index("-doit") + 1, str(outrenderfile.parent))
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(ocr_cli, args + options, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
# FIXME: ocr has no logging!
|
||||
#assert any(True for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('???')), logmsgs
|
||||
assert outfile.exists()
|
||||
if "-doit" in options:
|
||||
assert outrenderfile.exists()
|
||||
#in_tree = page_from_file(str(infile)).etree
|
||||
#in_order = in_tree.xpath("//page:OrderedGroup//@regionRef", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
out_tree = page_from_file(str(outfile)).etree
|
||||
out_texts = out_tree.xpath("//page:TextLine/page:TextEquiv[last()]/page:Unicode/text()", namespaces=NS)
|
||||
assert len(out_texts) >= 2, ("result is inaccurate", out_texts)
|
||||
assert sum(map(len, out_texts)) > 100, ("result is inaccurate", out_texts)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_run_eynollah_ocr_directory(tmp_path, pytestconfig, caplog):
|
||||
indir = testdir.joinpath('resources')
|
||||
outdir = tmp_path
|
||||
args = [
|
||||
'-m', MODELS_OCR,
|
||||
'-di', str(indir),
|
||||
'-dx', str(indir),
|
||||
'-o', str(outdir),
|
||||
]
|
||||
if pytestconfig.getoption('verbose') > 0:
|
||||
args.extend(['-l', 'DEBUG'])
|
||||
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
|
||||
def only_eynollah(logrec):
|
||||
return logrec.name == 'eynollah'
|
||||
runner = CliRunner()
|
||||
with caplog.filtering(only_eynollah):
|
||||
result = runner.invoke(ocr_cli, args, catch_exceptions=False)
|
||||
assert result.exit_code == 0, result.stdout
|
||||
logmsgs = [logrec.message for logrec in caplog.records]
|
||||
# FIXME: ocr has no logging!
|
||||
#assert any(True for logmsg in logmsgs if logmsg.startswith('???')), logmsgs
|
||||
assert len(list(outdir.iterdir())) == 2
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main(__file__)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
|||
def test_utils_import():
|
||||
import eynollah.utils
|
||||
import eynollah.utils.contour
|
||||
import eynollah.utils.drop_capitals
|
||||
import eynollah.utils.is_nan
|
||||
import eynollah.utils.rotate
|
||||
import qurator.eynollah.utils
|
||||
import qurator.eynollah.utils.contour
|
||||
import qurator.eynollah.utils.drop_capitals
|
||||
import qurator.eynollah.utils.drop_capitals
|
||||
import qurator.eynollah.utils.is_nan
|
||||
import qurator.eynollah.utils.rotate
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
|||
from eynollah.utils.xml import create_page_xml
|
||||
from pytest import main
|
||||
from qurator.eynollah.utils.xml import create_page_xml
|
||||
from ocrd_models.ocrd_page import to_xml
|
||||
|
||||
PAGE_2019 = 'http://schema.primaresearch.org/PAGE/gts/pagecontent/2019-07-15'
|
||||
|
|
@ -8,3 +9,6 @@ def test_create_xml():
|
|||
xmlstr = to_xml(pcgts)
|
||||
assert 'xmlns:pc="%s"' % PAGE_2019 in xmlstr
|
||||
assert 'Metadata' in xmlstr
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main([__file__])
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# Use NVIDIA base image
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.8.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the working directory
|
||||
WORKDIR /app
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Set environment variable for GitPython
|
||||
ENV GIT_PYTHON_REFRESH=quiet
|
||||
|
||||
# Install Python and pip
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --fix-broken && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y \
|
||||
python3 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3-distutils \
|
||||
python3-setuptools \
|
||||
python3-wheel && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy and install Python dependencies
|
||||
COPY requirements.txt .
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the rest of the application
|
||||
COPY . .
|
||||
|
||||
# Specify the entry point
|
||||
CMD ["python3", "train.py", "with", "config_params_docker.json"]
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# Training eynollah
|
||||
|
||||
This README explains the technical details of how to set up and run training, for detailed information on parameterization, see [`docs/train.md`](../docs/train.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
This folder contains the source code for training an encoder model for document image segmentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Clone the repository and install eynollah along with the dependencies necessary for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah
|
||||
cd eynollah
|
||||
pip install '.[training]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Pretrained encoder
|
||||
|
||||
Download our pretrained weights and add them to a `train/pretrained_model` folder:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
cd train
|
||||
wget -O pretrained_model.tar.gz https://zenodo.org/records/17243320/files/pretrained_model_v0_5_1.tar.gz?download=1
|
||||
tar xf pretrained_model.tar.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Binarization training data
|
||||
|
||||
A small sample of training data for binarization experiment can be found [on
|
||||
zenodo](https://zenodo.org/records/17243320/files/training_data_sample_binarization_v0_5_1.tar.gz?download=1),
|
||||
which contains `images` and `labels` folders.
|
||||
|
||||
### Helpful tools
|
||||
|
||||
* [`pagexml2img`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/page2img)
|
||||
> Tool to extract 2-D or 3-D RGB images from PAGE-XML data. In the former case, the output will be 1 2-D image array which each class has filled with a pixel value. In the case of a 3-D RGB image,
|
||||
each class will be defined with a RGB value and beside images, a text file of classes will also be produced.
|
||||
* [`cocoSegmentationToPng`](https://github.com/nightrome/cocostuffapi/blob/17acf33aef3c6cc2d6aca46dcf084266c2778cf0/PythonAPI/pycocotools/cocostuffhelper.py#L130)
|
||||
> Convert COCO GT or results for a single image to a segmentation map and write it to disk.
|
||||
* [`ocrd-segment-extract-pages`](https://github.com/OCR-D/ocrd_segment/blob/master/ocrd_segment/extract_pages.py)
|
||||
> Extract region classes and their colours in mask (pseg) images. Allows the color map as free dict parameter, and comes with a default that mimics PageViewer's coloring for quick debugging; it also warns when regions do overlap.
|
||||
|
||||
### Train using Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Build the Docker image:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd train
|
||||
docker build -t model-training .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd train
|
||||
docker run --gpus all -v $PWD:/entry_point_dir model-training
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "transformer",
|
||||
"task": "segmentation",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 2,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 0,
|
||||
"input_height" : 448,
|
||||
"input_width" : 448,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 1,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"patches" : false,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"augmentation" : true,
|
||||
"flip_aug" : false,
|
||||
"blur_aug" : false,
|
||||
"scaling" : false,
|
||||
"adding_rgb_background": true,
|
||||
"adding_rgb_foreground": true,
|
||||
"add_red_textlines": false,
|
||||
"channels_shuffling": false,
|
||||
"degrading": false,
|
||||
"brightening": false,
|
||||
"binarization" : true,
|
||||
"scaling_bluring" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_flip" : false,
|
||||
"rotation": false,
|
||||
"rotation_not_90": false,
|
||||
"transformer_num_patches_xy": [56, 56],
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_x": 4,
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_y": 4,
|
||||
"transformer_projection_dim": 64,
|
||||
"transformer_mlp_head_units": [128, 64],
|
||||
"transformer_layers": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_num_heads": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_cnn_first": false,
|
||||
"blur_k" : ["blur","guass","median"],
|
||||
"scales" : [0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9],
|
||||
"brightness" : [1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 2],
|
||||
"degrade_scales" : [0.2, 0.4],
|
||||
"flip_index" : [0, 1, -1],
|
||||
"shuffle_indexes" : [ [0,2,1], [1,2,0], [1,0,2] , [2,1,0]],
|
||||
"thetha" : [5, -5],
|
||||
"number_of_backgrounds_per_image": 2,
|
||||
"continue_training": false,
|
||||
"index_start" : 0,
|
||||
"dir_of_start_model" : " ",
|
||||
"weighted_loss": false,
|
||||
"is_loss_soft_dice": false,
|
||||
"data_is_provided": false,
|
||||
"dir_train": "/home/vahid/Documents/test/sbb_pixelwise_segmentation/test_label/pageextractor_test/train_new",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "/home/vahid/Documents/test/sbb_pixelwise_segmentation/test_label/pageextractor_test/eval_new",
|
||||
"dir_output": "/home/vahid/Documents/test/sbb_pixelwise_segmentation/test_label/pageextractor_test/output_new",
|
||||
"dir_rgb_backgrounds": "/home/vahid/Documents/1_2_test_eynollah/set_rgb_background",
|
||||
"dir_rgb_foregrounds": "/home/vahid/Documents/1_2_test_eynollah/out_set_rgb_foreground",
|
||||
"dir_img_bin": "/home/vahid/Documents/test/sbb_pixelwise_segmentation/test_label/pageextractor_test/train_new/images_bin"
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"backbone_type" : "nontransformer",
|
||||
"task": "segmentation",
|
||||
"n_classes" : 3,
|
||||
"n_epochs" : 1,
|
||||
"input_height" : 672,
|
||||
"input_width" : 448,
|
||||
"weight_decay" : 1e-6,
|
||||
"n_batch" : 4,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-4,
|
||||
"patches" : false,
|
||||
"pretraining" : true,
|
||||
"augmentation" : false,
|
||||
"flip_aug" : false,
|
||||
"blur_aug" : true,
|
||||
"scaling" : true,
|
||||
"adding_rgb_background": false,
|
||||
"adding_rgb_foreground": false,
|
||||
"add_red_textlines": false,
|
||||
"channels_shuffling": true,
|
||||
"degrading": true,
|
||||
"brightening": true,
|
||||
"binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_bluring" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_binarization" : false,
|
||||
"scaling_flip" : false,
|
||||
"rotation": false,
|
||||
"rotation_not_90": true,
|
||||
"transformer_num_patches_xy": [14, 21],
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_x": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_patchsize_y": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_projection_dim": 64,
|
||||
"transformer_mlp_head_units": [128, 64],
|
||||
"transformer_layers": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_num_heads": 1,
|
||||
"transformer_cnn_first": true,
|
||||
"blur_k" : ["blur","gauss","median"],
|
||||
"scales" : [0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9],
|
||||
"brightness" : [1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 2],
|
||||
"degrade_scales" : [0.2, 0.4],
|
||||
"flip_index" : [0, 1, -1],
|
||||
"shuffle_indexes" : [ [0,2,1], [1,2,0], [1,0,2] , [2,1,0]],
|
||||
"thetha" : [5, -5],
|
||||
"number_of_backgrounds_per_image": 2,
|
||||
"continue_training": false,
|
||||
"index_start" : 0,
|
||||
"dir_of_start_model" : " ",
|
||||
"weighted_loss": false,
|
||||
"is_loss_soft_dice": true,
|
||||
"data_is_provided": false,
|
||||
"dir_train": "/entry_point_dir/train",
|
||||
"dir_eval": "/entry_point_dir/eval",
|
||||
"dir_output": "/entry_point_dir/output"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"use_case": "textline",
|
||||
"textregions":{ "rest_as_paragraph": 1, "header":2 , "heading":2 , "marginalia":3 },
|
||||
"imageregion":4,
|
||||
"separatorregion":5,
|
||||
"graphicregions" :{"rest_as_decoration":6},
|
||||
"columns_width":{"1":1000, "2":1300, "3":1600, "4":2000, "5":2300, "6":2500}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
|
|||
sacred
|
||||
seaborn
|
||||
numpy <1.24.0
|
||||
tqdm
|
||||
imutils
|
||||
scipy
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"scales" : [ 0.5, 0.55, 0.6, 0.65, 0.7, 0.75, 0.8, 0.85, 0.9]
|
||||
}
|
||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue