| .circleci | ||
| .github/workflows | ||
| qurator | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| CHANGELOG.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| ocrd-tool.json | ||
| README.md | ||
| requirements-test.txt | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| setup.py | ||
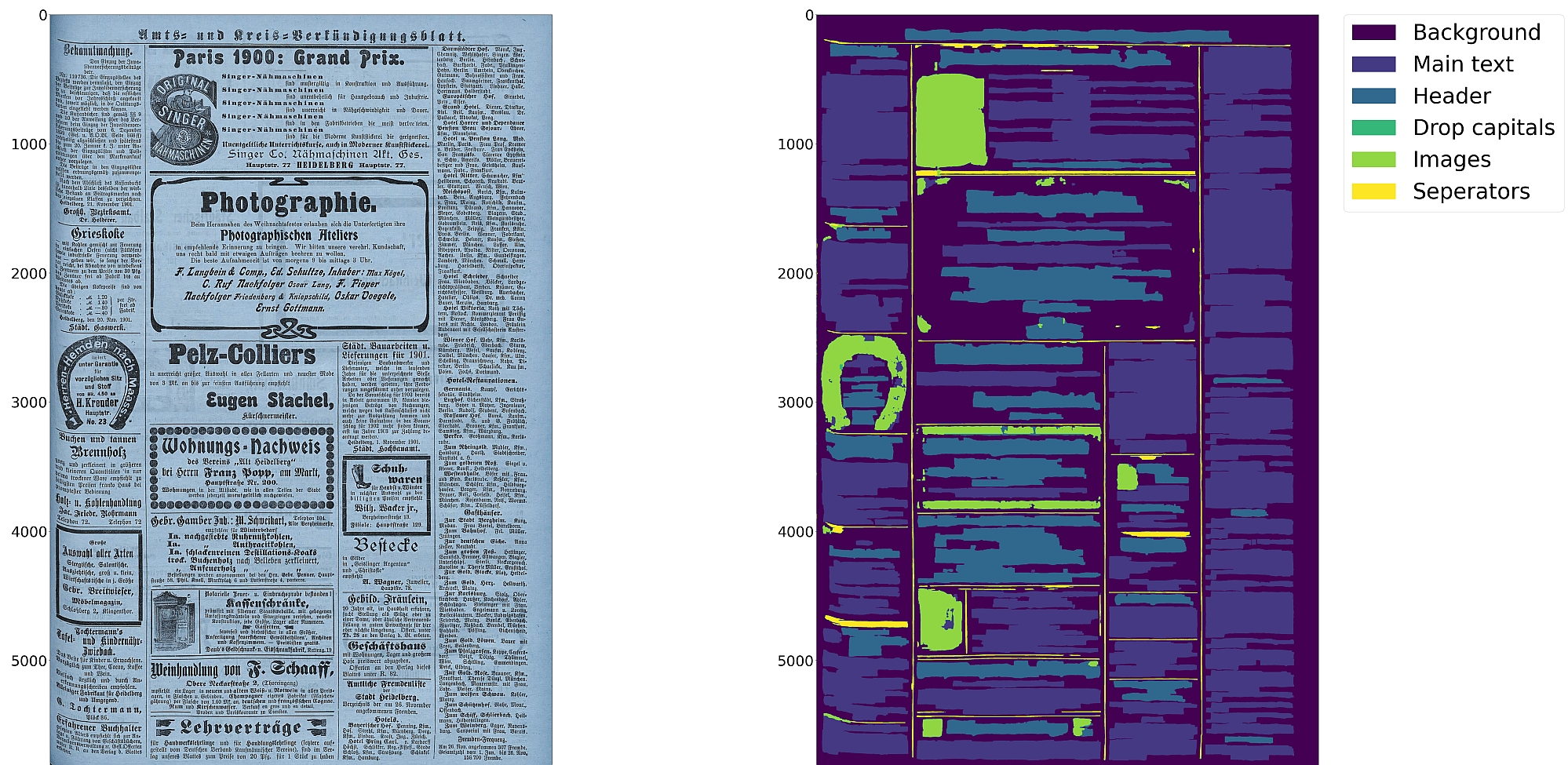
Eynollah
Perform document layout analysis (segmentation) from image data and return the results as PAGE-XML.
Installation
pip install . or
pip install . -e for editable installation
Alternatively, you can also use make with these targets:
make install or
make install-dev for editable installation
Models
In order to run this tool you need trained models. You can download our pretrained models from qurator-data.de.
Alternatively, running make models will download and extract models to $(PWD)/models_eynollah.
Training
In case you want to train your own model to use with Eynollah, have a look at sbb_pixelwise_segmentation.
Usage
The command-line interface can be called like this:
eynollah \
-i <image file name> \
-o <directory to write output xml or enhanced image> \
-m <directory of models> \
-fl <if true, the tool will perform full layout analysis> \
-ae <if true, the tool will resize and enhance the image and produce the resulting image as output. The rescaled and enhanced image will be saved in output directory> \
-as <if true, the tool will check whether the document needs rescaling or not> \
-cl <if true, the tool will extract the contours of curved textlines instead of rectangle bounding boxes> \
-si <if a directory is given here, the tool will output image regions inside documents there> \
-sd <if a directory is given, deskewed image will be saved there> \
-sa <if a directory is given, all plots needed for documentation will be saved there> \
-tab <if true, this tool will try to detect tables> \
-ib <in general, eynollah uses RGB as input but if the input document is strongly dark, bright or for any other reason you can turn binarized input on. This option does not mean that you have to provide a binary image, otherwise this means that the tool itself will binarized the RGB input document> \
-ho <if true, this tool would ignore headers role in reading order detection> \
-sl <if a directory is given, plot of layout will be saved there> \
-ep <if true, the tool will be enabled to save desired plot. This should be true alongside with -sl, -sd, -sa , -si or -ae options>
The tool performs better with RGB images than greyscale/binarized images.
Additional documentation can be found in the wiki.