mirror of
https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah.git
synced 2025-10-27 07:44:12 +01:00
200 lines
9.9 KiB
Markdown
200 lines
9.9 KiB
Markdown
# Eynollah
|
||
|
||
> Document Layout Analysis, Binarization and OCR with Deep Learning and Heuristics
|
||
|
||
[](https://pypi.org/project/eynollah/)
|
||
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/test-eynollah.yml)
|
||
[](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/actions/workflows/build-docker.yml)
|
||
[](https://opensource.org/license/apache-2-0/)
|
||
[](https://doi.org/10.1145/3604951.3605513)
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Features
|
||
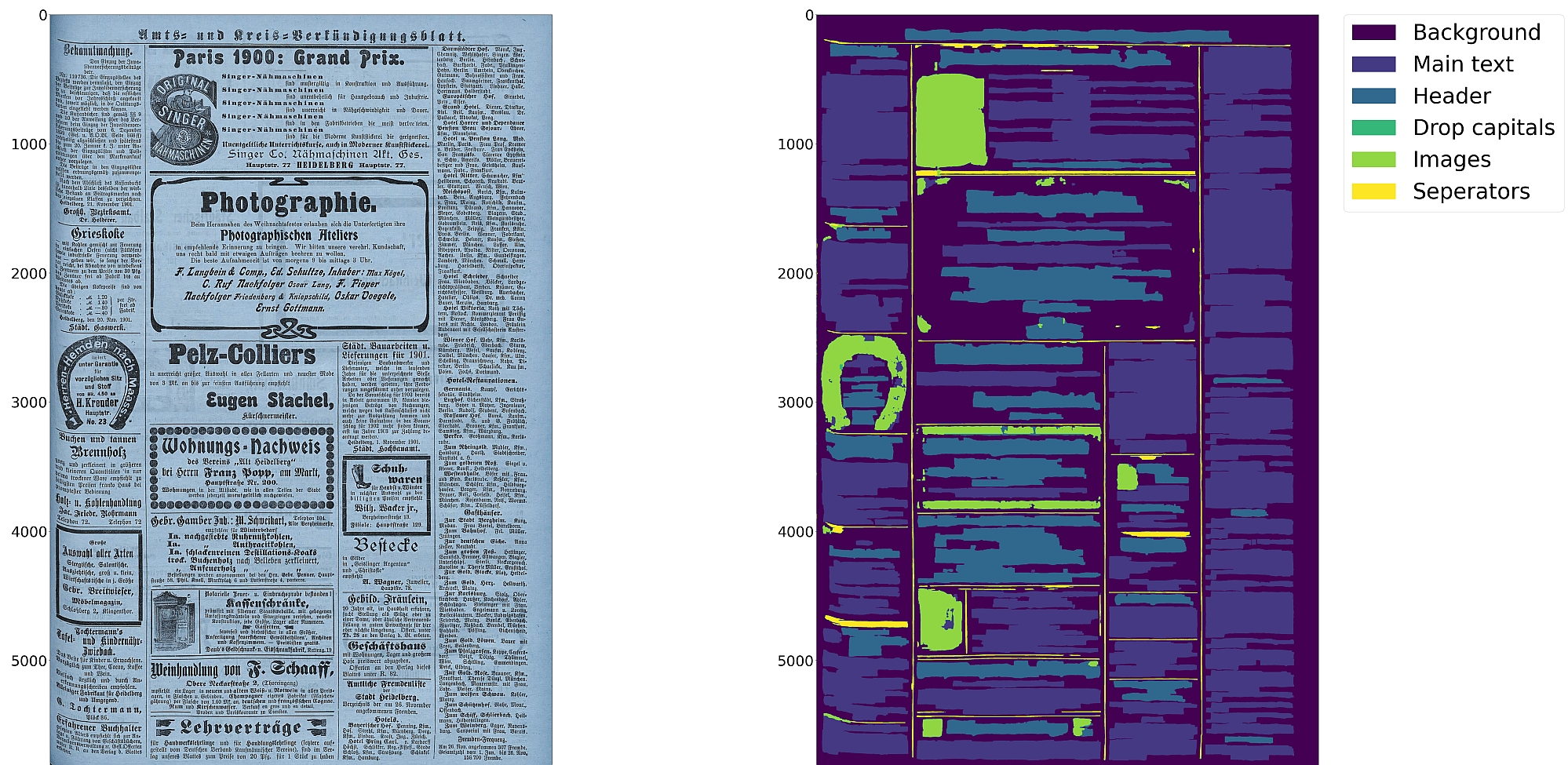
* Support for up to 10 segmentation classes:
|
||
* background, [page border](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyRand.html), [text region](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lytextregion.html#textregionen__textregion_), [text line](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/pagexml/pagecontent_xsd_Complex_Type_pc_TextLineType.html), [header](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyUeberschrift.html), [image](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyBildbereiche.html), [separator](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lySeparatoren.html), [marginalia](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyMarginalie.html), [initial](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyInitiale.html), [table](https://ocr-d.de/en/gt-guidelines/trans/lyTabellen.html)
|
||
* Support for various image optimization operations:
|
||
* cropping (border detection), binarization, deskewing, dewarping, scaling, enhancing, resizing
|
||
* Text line segmentation to bounding boxes or polygons (contours) including for curved lines and vertical text
|
||
* Detection of reading order (left-to-right or right-to-left)
|
||
* Output in [PAGE-XML](https://github.com/PRImA-Research-Lab/PAGE-XML)
|
||
* [OCR-D](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah#use-as-ocr-d-processor) interface
|
||
|
||
:warning: Development is currently focused on achieving the best possible quality of results for a wide variety of
|
||
historical documents and therefore processing can be very slow. We aim to improve this, but contributions are welcome.
|
||
|
||
## Installation
|
||
|
||
Python `3.8-3.11` with Tensorflow `<2.13` on Linux are currently supported.
|
||
|
||
For (limited) GPU support the CUDA toolkit needs to be installed.
|
||
|
||
You can either install from PyPI
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
pip install eynollah
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
or clone the repository, enter it and install (editable) with
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
git clone git@github.com:qurator-spk/eynollah.git
|
||
cd eynollah; pip install -e .
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Alternatively, you can run `make install` or `make install-dev` for editable installation.
|
||
|
||
To also install the dependencies for the OCR engines:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
pip install "eynollah[OCR]"
|
||
# or
|
||
make install EXTRAS=OCR
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## Models
|
||
Pretrained models can be downloaded from [zenodo](https://zenodo.org/records/17194824) or [huggingface](https://huggingface.co/SBB?search_models=eynollah).
|
||
|
||
For documentation on methods and models, have a look at [`models.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/models.md).
|
||
|
||
## Train
|
||
|
||
In case you want to train your own model with Eynollah, have a look at [`train.md`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/docs/train.md).
|
||
|
||
## Usage
|
||
|
||
Eynollah supports five use cases: layout analysis (segmentation), binarization,
|
||
image enhancement, text recognition (OCR), and (trainable) reading order detection.
|
||
|
||
### Layout Analysis
|
||
|
||
The layout analysis module is responsible for detecting layouts, identifying text lines, and determining reading order
|
||
using both heuristic methods or a machine-based reading order detection model.
|
||
|
||
Note that there are currently two supported ways for reading order detection: either as part of layout analysis based
|
||
on image input, or, currently under development, for given layout analysis results based on PAGE-XML data as input.
|
||
|
||
The command-line interface for layout analysis can be called like this:
|
||
|
||
```sh
|
||
eynollah layout \
|
||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||
-o <output directory> \
|
||
-m <directory containing model files> \
|
||
[OPTIONS]
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
The following options can be used to further configure the processing:
|
||
|
||
| option | description |
|
||
|-------------------|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||
| `-fl` | full layout analysis including all steps and segmentation classes |
|
||
| `-light` | lighter and faster but simpler method for main region detection and deskewing |
|
||
| `-tll` | this indicates the light textline and should be passed with light version |
|
||
| `-tab` | apply table detection |
|
||
| `-ae` | apply enhancement (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
|
||
| `-as` | apply scaling |
|
||
| `-cl` | apply contour detection for curved text lines instead of bounding boxes |
|
||
| `-ib` | apply binarization (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
|
||
| `-ep` | enable plotting (MUST always be used with `-sl`, `-sd`, `-sa`, `-si` or `-ae`) |
|
||
| `-eoi` | extract only images to output directory (other processing will not be done) |
|
||
| `-ho` | ignore headers for reading order dectection |
|
||
| `-si <directory>` | save image regions detected to this directory |
|
||
| `-sd <directory>` | save deskewed image to this directory |
|
||
| `-sl <directory>` | save layout prediction as plot to this directory |
|
||
| `-sp <directory>` | save cropped page image to this directory |
|
||
| `-sa <directory>` | save all (plot, enhanced/binary image, layout) to this directory |
|
||
|
||
If no option is set, the tool performs layout detection of main regions (background, text, images, separators
|
||
and marginals).
|
||
The best output quality is produced when RGB images are used as input rather than greyscale or binarized images.
|
||
|
||
### Binarization
|
||
|
||
The binarization module performs document image binarization using pretrained pixelwise segmentation models.
|
||
|
||
The command-line interface for binarization of single image can be called like this:
|
||
|
||
```sh
|
||
eynollah binarization \
|
||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||
-o <output directory> \
|
||
-m <directory containing model files> \
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### OCR
|
||
|
||
The OCR module performs text recognition from images using two main families of pretrained models: CNN-RNN–based OCR and Transformer-based OCR.
|
||
|
||
The command-line interface for ocr can be called like this:
|
||
|
||
```sh
|
||
eynollah ocr \
|
||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||
-dx <directory of xmls> \
|
||
-o <output directory> \
|
||
-m <path to directory containing model files> | --model_name <path to specific model> \
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Machine-based-reading-order
|
||
|
||
The machine-based reading-order module employs a pretrained model to identify the reading order from layouts represented in PAGE-XML files.
|
||
|
||
The command-line interface for machine based reading order can be called like this:
|
||
|
||
```sh
|
||
eynollah machine-based-reading-order \
|
||
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
|
||
-xml <xml file name> | -dx <directory containing xml files> \
|
||
-m <path to directory containing model files> \
|
||
-o <output directory>
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
#### Use as OCR-D processor
|
||
|
||
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as [OCR-D](https://ocr-d.de) [processor](https://ocr-d.de/en/spec/cli),
|
||
formally described in [`ocrd-tool.json`](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/tree/main/src/eynollah/ocrd-tool.json).
|
||
|
||
In this case, the source image file group with (preferably) RGB images should be used as input like this:
|
||
|
||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||
|
||
If the input file group is PAGE-XML (from a previous OCR-D workflow step), Eynollah behaves as follows:
|
||
- existing regions are kept and ignored (i.e. in effect they might overlap segments from Eynollah results)
|
||
- existing annotation (and respective `AlternativeImage`s) are partially _ignored_:
|
||
- previous page frame detection (`cropped` images)
|
||
- previous derotation (`deskewed` images)
|
||
- previous thresholding (`binarized` images)
|
||
- if the page-level image nevertheless deviates from the original (`@imageFilename`)
|
||
(because some other preprocessing step was in effect like `denoised`), then
|
||
the output PAGE-XML will be based on that as new top-level (`@imageFilename`)
|
||
|
||
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-XYZ -O OCR-D-SEG -P models eynollah_layout_v0_5_0
|
||
|
||
Still, in general, it makes more sense to add other workflow steps **after** Eynollah.
|
||
|
||
There is also an OCR-D processor for the binarization:
|
||
|
||
ocrd-sbb-binarize -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P models default-2021-03-09
|
||
|
||
#### Additional documentation
|
||
|
||
Please check the [wiki](https://github.com/qurator-spk/eynollah/wiki).
|
||
|
||
## How to cite
|
||
|
||
If you find this tool useful in your work, please consider citing our paper:
|
||
|
||
```bibtex
|
||
@inproceedings{hip23rezanezhad,
|
||
title = {Document Layout Analysis with Deep Learning and Heuristics},
|
||
author = {Rezanezhad, Vahid and Baierer, Konstantin and Gerber, Mike and Labusch, Kai and Neudecker, Clemens},
|
||
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Historical Document Imaging and Processing {HIP} 2023,
|
||
San José, CA, USA, August 25-26, 2023},
|
||
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
|
||
address = {New York, NY, USA},
|
||
year = {2023},
|
||
pages = {73--78},
|
||
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3604951.3605513}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|