9.7 KiB
Models documentation
This suite of 15 models presents a document layout analysis (DLA) system for historical documents implemented by pixel-wise segmentation using a combination of a ResNet50 encoder with various U-Net decoders. In addition, heuristic methods are applied to detect marginals and to determine the reading order of text regions.
The detection and classification of multiple classes of layout elements such as headings, images, tables etc. as part of DLA is required in order to extract and process them in subsequent steps. Altogether, the combination of image detection, classification and segmentation on the wide variety that can be found in over 400 years of printed cultural heritage makes this a very challenging task. Deep learning models are complemented with heuristics for the detection of text lines, marginals, and reading order. Furthermore, an optional image enhancement step was added in case of documents that either have insufficient pixel density and/or require scaling. Also, a column classifier for the analysis of multi-column documents was added. With these additions, DLA performance was improved, and a high accuracy in the prediction of the reading order is accomplished.
Two Arabic/Persian terms form the name of the model suite: عين الله, which can be transcribed as "ain'allah" or "eynollah"; it translates into English as "God's Eye" -- it sees (nearly) everything on the document image.
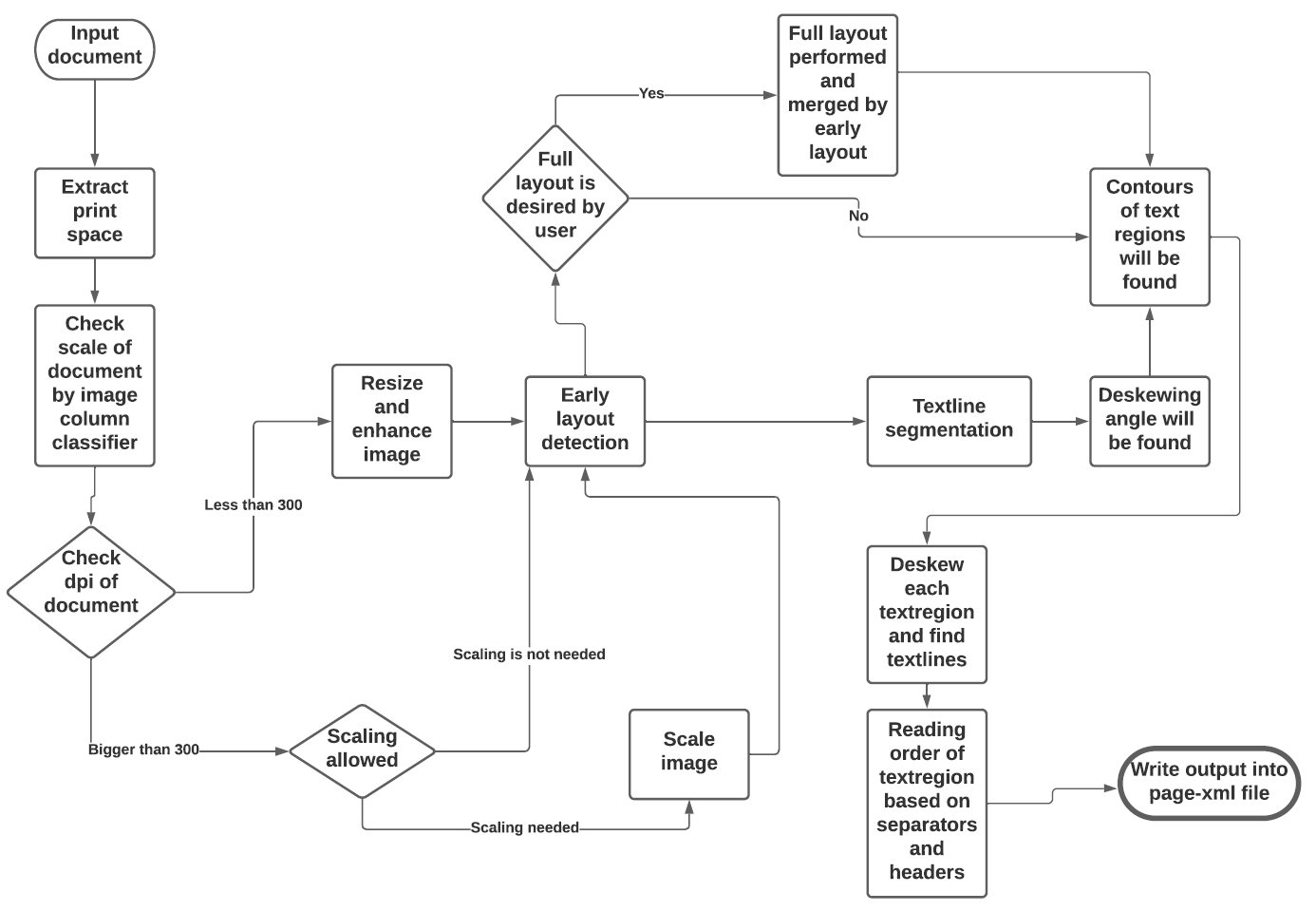
See the flowchart below for the different stages and how they interact:
Models
Image enhancement
Model card: Image Enhancement
This model addresses image resolution, specifically targeting documents with suboptimal resolution. In instances where the detection of document layout exhibits inadequate performance, the proposed enhancement aims to significantly improve the quality and clarity of the images, thus facilitating enhanced visual interpretation and analysis.
Page extraction / border detection
Model card: Page Extraction/Border Detection
A problem that can negatively affect OCR are black margins around a page caused by document scanning. A deep learning model helps to crop to the page borders by using a pixel-wise segmentation method.
Column classification
Model card: Column Classification
This model is a trained classifier that recognizes the number of columns in a document by use of a training set with manual classification of all documents into six classes with either one, two, three, four, five, or six and more columns respectively.
Binarization
Model card: Binarization
This model is designed to tackle the intricate task of document image binarization, which involves segmentation of the image into white and black pixels. This process significantly contributes to the overall performance of the layout models, particularly in scenarios where the documents are degraded or exhibit subpar quality. The robust binarization capability of the model enables improved accuracy and reliability in subsequent layout analysis, thereby facilitating enhanced document understanding and interpretation.
Main region detection
Model card: Main Region Detection
This model has employed a different set of labels, including an artificial class specifically designed to encompass the text regions. The inclusion of this artificial class facilitates easier isolation of text regions by the model. This approach grants the advantage of training the model using downscaled images, which in turn leads to faster predictions during the inference phase. By incorporating this methodology, improved efficiency is achieved without compromising the model's ability to accurately identify and classify text regions within documents.
Main region detection (with scaling augmentation)
Model card: Main Region Detection (with scaling augmentation)
Utilizing scaling augmentation, this model leverages the capability to effectively segment elements of extremely high or low scales within documents. By harnessing this technique, the tool gains a significant advantage in accurately categorizing and isolating such elements, thereby enhancing its overall performance and enabling precise analysis of documents with varying scale characteristics.
Main region detection (with rotation augmentation)
Model card: Main Region Detection (with rotation augmentation)
This model takes advantage of rotation augmentation. This helps the tool to segment the vertical text regions in a robust way.
Main region detection (ensembled)
Model card: Main Region Detection (ensembled)
The robustness of this model is attained through an ensembling technique that combines the weights from various epochs. By employing this approach, the model achieves a high level of resilience and stability, effectively leveraging the strengths of multiple epochs to enhance its overall performance and deliver consistent and reliable results.
Full region detection (1,2-column documents)
Model card: Full Region Detection (1,2-column documents)
This model deals with documents comprising of one and two columns.
Full region detection (3,n-column documents)
Model card: Full Region Detection (3,n-column documents)
This model is responsible for detecting headers and drop capitals in documents with three or more columns.
Textline detection
Model card: Textline Detection
The method for textline detection combines deep learning and heuristics. In the deep learning part, an image-to-image model performs binary segmentation of the document into the classes textline vs. background. In the heuristics part, bounding boxes or contours are derived from binary segmentation.
Skewed documents can heavily affect textline detection accuracy, so robust deskewing is needed. But detecting textlines with rectangle bounding boxes cannot deal with partially curved textlines. To address this, a functionality specifically for documents with curved textlines was included. After finding the contour of a text region and its corresponding textline segmentation, the text region is cut into smaller vertical straps. For each strap, its textline segmentation is first deskewed and then the textlines are separated with the same heuristic method as for finding textline bounding boxes. Later, the strap is rotated back into its original orientation.
Textline detection (light)
Model card: Textline Detection Light (simpler but faster method)
The method for textline detection combines deep learning and heuristics. In the deep learning part, an image-to-image model performs binary segmentation of the document into the classes textline vs. background. In the heuristics part, bounding boxes or contours are derived from binary segmentation.
In the context of this textline model, a distinct labeling approach has been employed to ensure accurate predictions. Specifically, an artificial bounding class has been incorporated alongside the textline classes. This strategic inclusion effectively prevents any spurious connections between adjacent textlines during the prediction phase, thereby enhancing the model's ability to accurately identify and delineate individual textlines within documents. This model eliminates the need for additional heuristics in extracting textline contours.
Table detection
Model card: Table Detection
The objective of this model is to perform table segmentation in historical document images. Due to the pixel-wise segmentation approach employed and the presence of traditional tables predominantly composed of text, the detection of tables required the incorporation of heuristics to achieve reasonable performance. These heuristics were necessary to effectively identify and delineate tables within the historical document images, ensuring accurate segmentation and enabling subsequent analysis and interpretation.
Image detection
Model card: Image Detection
This model is used for the task of illustration detection only.
Reading order detection
Model card: Reading Order Detection
TODO
Heuristic methods
Additionally, some heuristic methods are employed to further improve the model predictions:
- After border detection, the largest contour is determined by a bounding box, and the image cropped to these coordinates.
- For text region detection, the image is scaled up to make it easier for the model to detect background space between text regions.
- A minimum area is defined for text regions in relation to the overall image dimensions, so that very small regions that are noise can be filtered out.
- Deskewing is applied on the text region level (due to regions having different degrees of skew) in order to improve the textline segmentation result.
- After deskewing, a calculation of the pixel distribution on the X-axis allows the separation of textlines (foreground) and background pixels.
- Finally, using the derived coordinates, bounding boxes are determined for each textline.